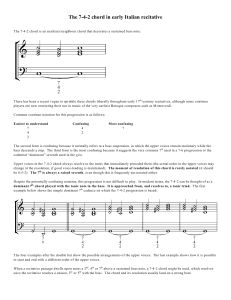
The 7-4-2 chord in early Italian recitative
... The second form is confusing because it normally refers to a bass suspension, in which the upper voices remain stationary while the bass descends a step. The third form is the most confusing because it suggests the very common 7 th used in a 7-6 progression or the cadential “dominant” seventh used i ...
... The second form is confusing because it normally refers to a bass suspension, in which the upper voices remain stationary while the bass descends a step. The third form is the most confusing because it suggests the very common 7 th used in a 7-6 progression or the cadential “dominant” seventh used i ...
Music Theory answers
... What might indicate that the tonal center or key of a piece is changing? Accidentals start to appear consistently or the composer writes in a key change Minor scales have up to 3 lowered pitches as compared to major scales. What is the scale degree that must be lowered for a piece to sound minor? 3 ...
... What might indicate that the tonal center or key of a piece is changing? Accidentals start to appear consistently or the composer writes in a key change Minor scales have up to 3 lowered pitches as compared to major scales. What is the scale degree that must be lowered for a piece to sound minor? 3 ...
Figured Bass and Tonality Recognition
... In this Gavotte, whose figured bass is given below (see Figure 11), the harmony is a seventh chord on the dominant of D (A - C# - E - G). But in some other contexts, it can be a sixth chord on the root of F# (this analysis being the one produced by our algorithm). More generally, we must limit the s ...
... In this Gavotte, whose figured bass is given below (see Figure 11), the harmony is a seventh chord on the dominant of D (A - C# - E - G). But in some other contexts, it can be a sixth chord on the root of F# (this analysis being the one produced by our algorithm). More generally, we must limit the s ...
File - Ms Jones` GCSE Class
... structures from before the breakdown of tonality or pushing forwards into atonal music. Music developed quickly through the 20th Century, and was largely based on exploration and experimentation, leading to new trends, techniques and sounds The Expressionist movement was strongest in Germany at the ...
... structures from before the breakdown of tonality or pushing forwards into atonal music. Music developed quickly through the 20th Century, and was largely based on exploration and experimentation, leading to new trends, techniques and sounds The Expressionist movement was strongest in Germany at the ...
storage/MUS001-Quiz Three
... A. The years following 1900 saw more fundamental changes in the language of music than any time since the beginning of the baroque era. B. Twentieth-century music follows the same general principles of musical structure as earlier periods. C. Twentieth-century music relies less on pre-established re ...
... A. The years following 1900 saw more fundamental changes in the language of music than any time since the beginning of the baroque era. B. Twentieth-century music follows the same general principles of musical structure as earlier periods. C. Twentieth-century music relies less on pre-established re ...
Relations between Keys and Modes
... Both Schubert and Brahms created high drama by relating keys a semitone apart with affective intent (as described in the Appendix). The tonic was often serene, and the Neapolitan key turbulent, but sometimes the reverse could be true. The ‘Neapolitan complex’ shown here, for example, is an ideal for ...
... Both Schubert and Brahms created high drama by relating keys a semitone apart with affective intent (as described in the Appendix). The tonic was often serene, and the Neapolitan key turbulent, but sometimes the reverse could be true. The ‘Neapolitan complex’ shown here, for example, is an ideal for ...
Music Theory answers
... What might indicate that the tonal center or key of a piece is changing? Accidentals start to appear consistently or the composer writes in a key change Minor scales have up to 3 lowered pitches as compared to major scales. What is the scale degree that must be lowered for a piece to sound minor? 3 ...
... What might indicate that the tonal center or key of a piece is changing? Accidentals start to appear consistently or the composer writes in a key change Minor scales have up to 3 lowered pitches as compared to major scales. What is the scale degree that must be lowered for a piece to sound minor? 3 ...
6-Many Streams Flowing
... One of the hallmarks of art music from the Twentieth century to the present, and a frustration if you’re one of those music historians who like to assign labels to entire periods of music, is the many creative and aesthetic streams that flow during the era. In this Learning Activity, we’ll highl ...
... One of the hallmarks of art music from the Twentieth century to the present, and a frustration if you’re one of those music historians who like to assign labels to entire periods of music, is the many creative and aesthetic streams that flow during the era. In this Learning Activity, we’ll highl ...
Untitled document.docx
... Explain how three composers of the romantic era used programme music to great effect, referring to tonality and expressive use of resources. In Berlioz’s Symphonie Fantastique, the composer uses tonality for expressive purposes, to describe the many disturbing visions of an infatuated artist. The fi ...
... Explain how three composers of the romantic era used programme music to great effect, referring to tonality and expressive use of resources. In Berlioz’s Symphonie Fantastique, the composer uses tonality for expressive purposes, to describe the many disturbing visions of an infatuated artist. The fi ...
Twentieth Century New scales New chords (almost any combination
... Uses “Standard” minor scale, but combines Brazilian folk‐music sound with the sense of J.S. Bach’s counterpoint ...
... Uses “Standard” minor scale, but combines Brazilian folk‐music sound with the sense of J.S. Bach’s counterpoint ...
mathematics and music
... century and which is still being extended today. As you proceed through this unit following the details of the interaction between music and mathematics, be aware of the subtleties ...
... century and which is still being extended today. As you proceed through this unit following the details of the interaction between music and mathematics, be aware of the subtleties ...
A GUIDE TO THE TERMINOLOGY OF GERMAN HARMONY
... pitches (e.g., A minor and C major). To complete the reduction of the major-mode diatonic triads to the three harmonic functions, all that remains is to interpret the triad on the leading tone as an incomplete dominant seventh chord (often symbolized as “D 7” with a diagonal slash through the “D”). ...
... pitches (e.g., A minor and C major). To complete the reduction of the major-mode diatonic triads to the three harmonic functions, all that remains is to interpret the triad on the leading tone as an incomplete dominant seventh chord (often symbolized as “D 7” with a diagonal slash through the “D”). ...
Elements of Music - Harmony
... **If a melody centers around the note C, it is said to be in the Key of C. Keys can also be major or minor. Each key has a family of chords associated with it. Modulation is the process of changing from one key center (tonic) to another. Sometimes a piece of music will have several different key cen ...
... **If a melody centers around the note C, it is said to be in the Key of C. Keys can also be major or minor. Each key has a family of chords associated with it. Modulation is the process of changing from one key center (tonic) to another. Sometimes a piece of music will have several different key cen ...
Se quema la chumbamba (Familia Valera Miranda)
... o Homophonic passages, when all voices move together (bs.5, 21-3, 28-32, etc.) o Note that bass line sometimes moves more slowly, underpinning the upper voices ...
... o Homophonic passages, when all voices move together (bs.5, 21-3, 28-32, etc.) o Note that bass line sometimes moves more slowly, underpinning the upper voices ...
Lewin, David “A Formal Theory of Generalized Tonal Functions”
... moves as well. A “Relative”-operation then takes you a minor third down from a major chord and a minor third up from a minor chord. The leap of a major third is called a “Leittone-exchange”. From a major chord a “L”-operation takes you a major third up, from a minor chord the “L”-operation takes you ...
... moves as well. A “Relative”-operation then takes you a minor third down from a major chord and a minor third up from a minor chord. The leap of a major third is called a “Leittone-exchange”. From a major chord a “L”-operation takes you a major third up, from a minor chord the “L”-operation takes you ...
Tippett * Concerto for double string orchestra: movement I
... At b.91 the tonal centre reaches F minor, relatively far removed from the home key and marking the star t of the collapse of the frenetic movement of the Development. A series of descending fif ths leads to E flat minor (b.97). A fur ther step to A flat occur s at b. 107, the point that marks ...
... At b.91 the tonal centre reaches F minor, relatively far removed from the home key and marking the star t of the collapse of the frenetic movement of the Development. A series of descending fif ths leads to E flat minor (b.97). A fur ther step to A flat occur s at b. 107, the point that marks ...
The Neapolitan Chord (Phrygian II) Definition The Neapolitan chord
... It is often found in minor mode but may also be found in major. It most often appears in first inversion (with an unaltered note in the bass), so is most often referred to ...
... It is often found in minor mode but may also be found in major. It most often appears in first inversion (with an unaltered note in the bass), so is most often referred to ...
Chromaticism II: Tonicization/Modulation
... that lie entirely within a new key. Modulation generally employs two features: the cadential establishment of the new key; and a subsequent re-start in that new key. In music where cadential confirmation is less likely (e.g., many development sections, and much 19th-century music), modulation can be ...
... that lie entirely within a new key. Modulation generally employs two features: the cadential establishment of the new key; and a subsequent re-start in that new key. In music where cadential confirmation is less likely (e.g., many development sections, and much 19th-century music), modulation can be ...
class9#
... is indicated by an uplifting alteration -- #, and a downward movement is indicated by a downgrading alteration -- b. Consider the two chord progressions in the note example to these class notes). The first chord in both progressions consists of exactly the music-level pitch-classes (and music pitche ...
... is indicated by an uplifting alteration -- #, and a downward movement is indicated by a downgrading alteration -- b. Consider the two chord progressions in the note example to these class notes). The first chord in both progressions consists of exactly the music-level pitch-classes (and music pitche ...
Required Graduate Music Theory Examinations
... Note: The levels should be completed in the order given with the program in practice mode, not mastery mode. Individuals may work on more or fewer levels depending on their own review needs. ...
... Note: The levels should be completed in the order given with the program in practice mode, not mastery mode. Individuals may work on more or fewer levels depending on their own review needs. ...
Aural Revision Grade 6
... Question A: To sing or play from memory the upper part of a two-part phrase played twice by the examiner. Question B: To sing a melody from score, with an accompaniment played by the examiner. Question C: To identify a cadence as perfect or imperfect. V - I :Perfect Cadence (full stop) Ends on the t ...
... Question A: To sing or play from memory the upper part of a two-part phrase played twice by the examiner. Question B: To sing a melody from score, with an accompaniment played by the examiner. Question C: To identify a cadence as perfect or imperfect. V - I :Perfect Cadence (full stop) Ends on the t ...
pacaci
... melodical gestures, join to form subphrases, which join to form phrases etc. When musicians play, they mark the endnings of these tone groups. This rule marks the phrase and subphrase endings by creating minute accelerandos and decelerandos within phrases and subphrases according to a parabolic func ...
... melodical gestures, join to form subphrases, which join to form phrases etc. When musicians play, they mark the endnings of these tone groups. This rule marks the phrase and subphrase endings by creating minute accelerandos and decelerandos within phrases and subphrases according to a parabolic func ...
Tonality

Tonality is a musical system in which pitches or chords are arranged so as to induce a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, and attractions. The pitch or chord with the greatest stability is called the tonic. The most common use of the term ""is to designate the arrangement of musical phenomena around a referential tonic in European music from about 1600 to about 1910"" (Hyer 2001). While today classical musics may practice or avoid any sort of tonality, harmony in popular musics remains tonal in some sense, and harmony in folk and jazz musics include many, if not all, modal or tonal characteristics, while having different properties from common-practice classical music.""All harmonic idioms in popular music are tonal, and none is without function"" (Tagg 2003, 534).""Tonality is an organized system of tones (e.g., the tones of a major or minor scale) in which one tone (the tonic) becomes the central point to which the remaining tones are related. In tonality, the tonic (tonal center) is the tone of complete relaxation, the target toward which other tones lead"" (Benward & Saker 2003, 36).""Tonal music is music that is unified and dimensional. Music is unified if it is exhaustively referable to a precompositional system generated by a single constructive principle derived from a basic scale-type; it is dimensional if it can nonetheless be distinguished from that precompositional ordering"" (Pitt 1995, 299).The term tonalité originated with Alexandre-Étienne Choron (1810) and was borrowed by François-Joseph Fétis in 1840 (Reti 1958,; Simms 1975, 119; Judd 1998a, 5; Heyer 2001; Brown 2005, xiii). According to Carl Dahlhaus, however, the term tonalité was only coined by Castil-Blaze in 1821 (Dahlhaus 1967, 960; Dahlhaus 1980, 51).Although Fétis used it as a general term for a system of musical organization and spoke of types de tonalités rather than a single system, today the term is most often used to refer to major–minor tonality, the system of musical organization of the common practice period. Major-minor tonality is also called harmonic tonality, diatonic tonality, common practice tonality, functional tonality, or just tonality.