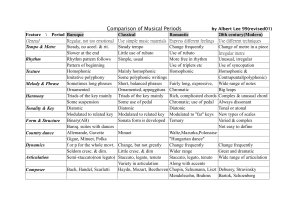
Document
... MELODY IN A COMPOSITION INCLUDES 1. THE PROMINENT MELODIC LINES AND THE REPETION AND VARIATION OF THES MELODIC LINES THROUGHOUT THE COMPOSITION. 2. THE RANGE AND CONTOUR OF MELODIC MATERIAL. 3. THE PHRASE STRUCTURE OF THE MELODIC LINES. 4. THE SCALE BASIS FOR MELODIC MATERIALS. 5. THE RELATIONSHIP A ...
... MELODY IN A COMPOSITION INCLUDES 1. THE PROMINENT MELODIC LINES AND THE REPETION AND VARIATION OF THES MELODIC LINES THROUGHOUT THE COMPOSITION. 2. THE RANGE AND CONTOUR OF MELODIC MATERIAL. 3. THE PHRASE STRUCTURE OF THE MELODIC LINES. 4. THE SCALE BASIS FOR MELODIC MATERIALS. 5. THE RELATIONSHIP A ...
Musical Terms: Musicians use certain words and phrases (that may
... common usage) to describe musical elements. Music is made of pitches (notes or tones) that can be altered to be higher or lower. Pitches can also be altered by duration; the length of time a pitch lasts. Pitch can also be altered in terms of dynamics and tone quality (timbre). Scales and Intervals a ...
... common usage) to describe musical elements. Music is made of pitches (notes or tones) that can be altered to be higher or lower. Pitches can also be altered by duration; the length of time a pitch lasts. Pitch can also be altered in terms of dynamics and tone quality (timbre). Scales and Intervals a ...
On Tonal Dynamics and Musical Meaning - Signata
... So far, we have only tried to uncontroversially (re)organize some trivial but important aspects of tonal architecture and modulation. his body of Pythagorean tonal doxa, however, leaves out some elementary and semiotically interesting questions. First of all, what are the grounds for the anchoring o ...
... So far, we have only tried to uncontroversially (re)organize some trivial but important aspects of tonal architecture and modulation. his body of Pythagorean tonal doxa, however, leaves out some elementary and semiotically interesting questions. First of all, what are the grounds for the anchoring o ...
study guide - Junior High Band
... c. Sevenths resolve to thirds. d. Connect guide tones to other chord members using passing tones. e. When a continuous guide tone line runs out, start over on the third of seventh of the next chord. ...
... c. Sevenths resolve to thirds. d. Connect guide tones to other chord members using passing tones. e. When a continuous guide tone line runs out, start over on the third of seventh of the next chord. ...
History of Music 1700s to the 20th century
... with romantic techniques Mahler is best known for his huge symphonies & beautiful orchestration; 1st composer with an American connection conductor of the NY Philharmonic ...
... with romantic techniques Mahler is best known for his huge symphonies & beautiful orchestration; 1st composer with an American connection conductor of the NY Philharmonic ...
File
... Is there a definitive key signature and do the cadences support the key signature or tonality? How do you know? Is the piece major or minor? How do you know? Does the key or tonality remain the same throughout the piece? ...
... Is there a definitive key signature and do the cadences support the key signature or tonality? How do you know? Is the piece major or minor? How do you know? Does the key or tonality remain the same throughout the piece? ...
MUSICAL ELEMENTS
... • Tonality has a psychological aspect associated with it. – Music that is atonal can be disturbing to the listener. (Atonal has NO specific key.) -- The listener expects to hear certain sounds that complete the musical pattern. ...
... • Tonality has a psychological aspect associated with it. – Music that is atonal can be disturbing to the listener. (Atonal has NO specific key.) -- The listener expects to hear certain sounds that complete the musical pattern. ...
AP-Music-Theory-Study-Guide
... o Enharmonically equivalent keys- two keys that sound the same (C# major and Db major) o Parallel keys- major and minor keys with same tonic (ex. C major and c minor) o Change of mode (mode mixture)- switch between parallel keys o Relative keys- major and minor keys with same key signature (ex. C ma ...
... o Enharmonically equivalent keys- two keys that sound the same (C# major and Db major) o Parallel keys- major and minor keys with same tonic (ex. C major and c minor) o Change of mode (mode mixture)- switch between parallel keys o Relative keys- major and minor keys with same key signature (ex. C ma ...
Harmony, Key, and Texture from 11/13/14 and
... • The interweaving of melody and harmony • Monophonic - one unaccompanied melody • Homophonic - one melody with some type of accompaniment (most common texture) • Polyphonic - two or more melodies at the same time.May be with or without accompaniment. This is "the crowning achievement of Western Mus ...
... • The interweaving of melody and harmony • Monophonic - one unaccompanied melody • Homophonic - one melody with some type of accompaniment (most common texture) • Polyphonic - two or more melodies at the same time.May be with or without accompaniment. This is "the crowning achievement of Western Mus ...
Harmonic Analysis 1: Homophonic Texture
... The third harmony in the example above is ambiguous, because there are only two pitches: C and E. The missing note of the triad could be either G (for CEG, a I chord) or A (for ACE=vi). To resolve ambiguities like this one: 1. Consider the harmonic progressions from section 5.3. Sometimes this will ...
... The third harmony in the example above is ambiguous, because there are only two pitches: C and E. The missing note of the triad could be either G (for CEG, a I chord) or A (for ACE=vi). To resolve ambiguities like this one: 1. Consider the harmonic progressions from section 5.3. Sometimes this will ...
Voice leading from IV-V
... is repeated in the V chord. These progressions are known as parallel fifths and parallel octaves, and should be avoided when writing homophonic and homorhythmic music. One correct way of voice leading from IV to V is to use the non-common tone technique, as shown in bar 2. Raise the bass (we're stil ...
... is repeated in the V chord. These progressions are known as parallel fifths and parallel octaves, and should be avoided when writing homophonic and homorhythmic music. One correct way of voice leading from IV to V is to use the non-common tone technique, as shown in bar 2. Raise the bass (we're stil ...
TEST 6 STUDY GUIDE
... 11. The combination of two traditional chords sounding together is known as 12. A fourth chord is 13. A chord made of tones only a half step or a whole step apart is known as 14. Striking a group of adjacent keys on a piano with the fist or forearm will result in 15. To create fresh sounds, twentiet ...
... 11. The combination of two traditional chords sounding together is known as 12. A fourth chord is 13. A chord made of tones only a half step or a whole step apart is known as 14. Striking a group of adjacent keys on a piano with the fist or forearm will result in 15. To create fresh sounds, twentiet ...
The History of Music, Second Edition
... intense, powerful style. Bloch demonstrated that a composer need not be limited to one particular approach. His music ranges from extreme consonance to extreme dissonance, from strong tonality to almost no tonality, depending upon the character of a particular work.] 8. Describe the music of America ...
... intense, powerful style. Bloch demonstrated that a composer need not be limited to one particular approach. His music ranges from extreme consonance to extreme dissonance, from strong tonality to almost no tonality, depending upon the character of a particular work.] 8. Describe the music of America ...
Musicianship notes - University High School 2014
... # sharp- raises pitch one half step x double sharp- raises pitch two half steps, or one full step b flat- lowers pitch one half step bb double flat- lowers pitch two half steps, or one full step natural- cancels out all sharps and flats, including key signature Enharmonic Equivalence Two pitches tha ...
... # sharp- raises pitch one half step x double sharp- raises pitch two half steps, or one full step b flat- lowers pitch one half step bb double flat- lowers pitch two half steps, or one full step natural- cancels out all sharps and flats, including key signature Enharmonic Equivalence Two pitches tha ...
Tonality

Tonality is a musical system in which pitches or chords are arranged so as to induce a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, and attractions. The pitch or chord with the greatest stability is called the tonic. The most common use of the term ""is to designate the arrangement of musical phenomena around a referential tonic in European music from about 1600 to about 1910"" (Hyer 2001). While today classical musics may practice or avoid any sort of tonality, harmony in popular musics remains tonal in some sense, and harmony in folk and jazz musics include many, if not all, modal or tonal characteristics, while having different properties from common-practice classical music.""All harmonic idioms in popular music are tonal, and none is without function"" (Tagg 2003, 534).""Tonality is an organized system of tones (e.g., the tones of a major or minor scale) in which one tone (the tonic) becomes the central point to which the remaining tones are related. In tonality, the tonic (tonal center) is the tone of complete relaxation, the target toward which other tones lead"" (Benward & Saker 2003, 36).""Tonal music is music that is unified and dimensional. Music is unified if it is exhaustively referable to a precompositional system generated by a single constructive principle derived from a basic scale-type; it is dimensional if it can nonetheless be distinguished from that precompositional ordering"" (Pitt 1995, 299).The term tonalité originated with Alexandre-Étienne Choron (1810) and was borrowed by François-Joseph Fétis in 1840 (Reti 1958,; Simms 1975, 119; Judd 1998a, 5; Heyer 2001; Brown 2005, xiii). According to Carl Dahlhaus, however, the term tonalité was only coined by Castil-Blaze in 1821 (Dahlhaus 1967, 960; Dahlhaus 1980, 51).Although Fétis used it as a general term for a system of musical organization and spoke of types de tonalités rather than a single system, today the term is most often used to refer to major–minor tonality, the system of musical organization of the common practice period. Major-minor tonality is also called harmonic tonality, diatonic tonality, common practice tonality, functional tonality, or just tonality.