The Octave - Bill Troxler
... The human mind interprets both notes in the octave as being essentially the same. That’s because the overtones of both notes are nearly identical. (More about overtones and harmonics later). Because tones that are an octave apart seem more or less identical, they bear the same name. The octave tone ...
... The human mind interprets both notes in the octave as being essentially the same. That’s because the overtones of both notes are nearly identical. (More about overtones and harmonics later). Because tones that are an octave apart seem more or less identical, they bear the same name. The octave tone ...
(pdf)
... GIS of Z7 does not represent the chromatic intervals, but the number of scale steps between two notes. 4. The Generalized Tonnetz In this section we will introduce the generalized Tonnetz. Definition 4.1. Let G0 = (S, G, int∗ ) be a commutative GIS and assume that the group G is generated by a finit ...
... GIS of Z7 does not represent the chromatic intervals, but the number of scale steps between two notes. 4. The Generalized Tonnetz In this section we will introduce the generalized Tonnetz. Definition 4.1. Let G0 = (S, G, int∗ ) be a commutative GIS and assume that the group G is generated by a finit ...
View printable PDF of 6.4 AdditionalContemporaryScales
... Octatonic scales = A scale of alternating whole steps and half steps. Octatonic scales may be h-W or W-h. A whole-half octatonic is also called a diminished scale. There are three distinct octatonic scales. ...
... Octatonic scales = A scale of alternating whole steps and half steps. Octatonic scales may be h-W or W-h. A whole-half octatonic is also called a diminished scale. There are three distinct octatonic scales. ...
MTO 15.2: Brown, Axis Tonality
... between the two main key areas of the movement, cinching its connection to the movement’s axis tonality. (5) [8] Further details support this axis reading. For instance, shortly after the primary theme, the solo cello plays the main motive of the movement (G-F -C -B ) in counterpoint with the rising ...
... between the two main key areas of the movement, cinching its connection to the movement’s axis tonality. (5) [8] Further details support this axis reading. For instance, shortly after the primary theme, the solo cello plays the main motive of the movement (G-F -C -B ) in counterpoint with the rising ...
MU2201 : Analysing Western Art Music
... structure”) combines an upper-voice Urlinie (“fundamental line”) and a bass Bassbrechung (“bass arpeggiation”, I-V-I, regarded both harmonically, as chords on tonic and dominant, and melodically, as an arpeggiation of the tonic triad). It can take three main forms, all with stepwise descents in the ...
... structure”) combines an upper-voice Urlinie (“fundamental line”) and a bass Bassbrechung (“bass arpeggiation”, I-V-I, regarded both harmonically, as chords on tonic and dominant, and melodically, as an arpeggiation of the tonic triad). It can take three main forms, all with stepwise descents in the ...
Yet Another 72-Noter - Masters Program in Digital Musics
... present an accumulation of progressively more complex harmonic ratios. These would have been but a succession of two simple appoggiatura resolutions without the addition of the second pedal on SYMBOL Eb. They resolve it all to the lower energy state of the 8:5 sixth on A, effecting thereby a progres ...
... present an accumulation of progressively more complex harmonic ratios. These would have been but a succession of two simple appoggiatura resolutions without the addition of the second pedal on SYMBOL Eb. They resolve it all to the lower energy state of the 8:5 sixth on A, effecting thereby a progres ...
44. Jerry Goldsmith Planet of the Apes: The Hunt (opening)
... 45-51: The riff now returns to the C tonal centre from the beginning of the piece. The long held notes are on the horns for the first time. Isolated, fragmentary notes on xylophone, create an almost pointillist texture. 52-58: The music then builds rapidly to the second climax. Two-note, rising semi ...
... 45-51: The riff now returns to the C tonal centre from the beginning of the piece. The long held notes are on the horns for the first time. Isolated, fragmentary notes on xylophone, create an almost pointillist texture. 52-58: The music then builds rapidly to the second climax. Two-note, rising semi ...
Psychological Bulletin - Jacobs University Mathematics
... Very short intervals tend to be overestimated. Large intervals tend to be underestimated. In the range of 40 to 600 ms, the subjective duration of time interval is proportional to the physical duration plus a constant of approximately 80 ms ...
... Very short intervals tend to be overestimated. Large intervals tend to be underestimated. In the range of 40 to 600 ms, the subjective duration of time interval is proportional to the physical duration plus a constant of approximately 80 ms ...
Symmetry in the First Movement of Martin Bresnick`s Piano Trio
... beat in measure 12, the 4th measure of phrase 2) the cello and violin momentarily share the central D, as they have three times previously, but now switch roles. The cello sustains D while the violin takes the cello’s process and inverts its pitches. This makes D the lowest tone in upside-down arche ...
... beat in measure 12, the 4th measure of phrase 2) the cello and violin momentarily share the central D, as they have three times previously, but now switch roles. The cello sustains D while the violin takes the cello’s process and inverts its pitches. This makes D the lowest tone in upside-down arche ...
Band 8 - I Know How To
... o Figure out transitions in multi-meter music. o Count rhythms using both ta’s and titi’s and numbers. o Count out a multi-measure rest accurately. o Recognize and perform a repeat. o Recognize and perform a first and second ending. o Find the end of a piece of music. o Follow the musical symbols to ...
... o Figure out transitions in multi-meter music. o Count rhythms using both ta’s and titi’s and numbers. o Count out a multi-measure rest accurately. o Recognize and perform a repeat. o Recognize and perform a first and second ending. o Find the end of a piece of music. o Follow the musical symbols to ...
Comparative (Ethno)Musicology. - Institut 13: Ethnomusikologie
... more interpretative parameters such as tempo, phrasing, accentuation, timbre, etc. the extent to which such decisions may be made by some members of a gamelan ensemble, and thus the issue of their would-be “improvisatory” nature, can best be understood by comparing it to another musical system where ...
... more interpretative parameters such as tempo, phrasing, accentuation, timbre, etc. the extent to which such decisions may be made by some members of a gamelan ensemble, and thus the issue of their would-be “improvisatory” nature, can best be understood by comparing it to another musical system where ...
Violin sound quality: can it be controlled within the parameters of
... equally spaced harmonic intervals that are all whole number multiples of the fundamental frequency. Harmonics therefore lie along an equal interval measurement scale. The frequencies of notes in the twelve semitone equal temperament musical scale are divided up according to the frequency spacing wit ...
... equally spaced harmonic intervals that are all whole number multiples of the fundamental frequency. Harmonics therefore lie along an equal interval measurement scale. The frequencies of notes in the twelve semitone equal temperament musical scale are divided up according to the frequency spacing wit ...
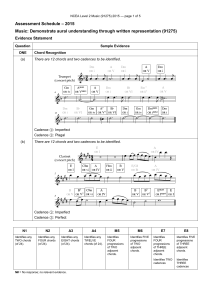
NCEA Level 2 Music (91275) 2015 Assessment Schedule
... Harp [or the instrument identified in (a) (i)] Element: harmony accompanies the melody by playing chords / playing broken chords (arpeggios) at the beginning, then by playing (strummed) chords / playing chords that continue after the melody stops. ...
... Harp [or the instrument identified in (a) (i)] Element: harmony accompanies the melody by playing chords / playing broken chords (arpeggios) at the beginning, then by playing (strummed) chords / playing chords that continue after the melody stops. ...
Glossary - Theory Essentials Home Page
... augmented sixth chord (noun) a chord that is built with a lowered sixth scale degree and a raised fourth scale degree; these two chord tones typically resolve in contrary motion to the dominant scale degree of a key augmented triad (noun) one of the four types of triads; it is constructed by raising ...
... augmented sixth chord (noun) a chord that is built with a lowered sixth scale degree and a raised fourth scale degree; these two chord tones typically resolve in contrary motion to the dominant scale degree of a key augmented triad (noun) one of the four types of triads; it is constructed by raising ...
pdf - Santa Fe Institute
... Most tuning systems attempt to resolve some or all of the five constraints listed above. The best fit may also reflect and incorporate other theoretical, cultural, historical, and even aesthetic factors. These five constraints, which appear to operate at a different, less culturally specific level, ...
... Most tuning systems attempt to resolve some or all of the five constraints listed above. The best fit may also reflect and incorporate other theoretical, cultural, historical, and even aesthetic factors. These five constraints, which appear to operate at a different, less culturally specific level, ...
2 steady beats of sound - Elm Grove Middle School Band
... beginning of the music after the clef sign. • The Time Signature has two numbers, one above the other. • The top number tells you how many steady beats are in each measure. • The bottom number tells you what value note illustrates the steady beat. ...
... beginning of the music after the clef sign. • The Time Signature has two numbers, one above the other. • The top number tells you how many steady beats are in each measure. • The bottom number tells you what value note illustrates the steady beat. ...
D:\EIGENE~1\CHOROI~1\PROSPE~1\BORDUN~1\Bordunleier GB
... - a third may play intermittently with a bass tuned a whole tone (= a second) lower. - a fourth player may be added with a bass tuned a whole tone higher than the second. Through this, a rich variety of sound effects, including ‘beat tones’ will be made possibble, with the second player playing a co ...
... - a third may play intermittently with a bass tuned a whole tone (= a second) lower. - a fourth player may be added with a bass tuned a whole tone higher than the second. Through this, a rich variety of sound effects, including ‘beat tones’ will be made possibble, with the second player playing a co ...
The Rehearsal Techniques of Robert Shaw
... wrote it. Thankfully, however, the same mind that produced those words also very consciously and deliberately developed techniques to overcome that insecurity. Throughout his career, Robert Shaw believed that choral ensembles should exist on the same level of artistic competence as professional orch ...
... wrote it. Thankfully, however, the same mind that produced those words also very consciously and deliberately developed techniques to overcome that insecurity. Throughout his career, Robert Shaw believed that choral ensembles should exist on the same level of artistic competence as professional orch ...
BL Answer Key
... 39. The ____________ is mainly used by the men and is also called the F clef. a. Treble Clef b. Alto Clef c. Bass Clef 40. Sharps, flats or naturals occurring in a piece of music that are not in a key signature are referred to as_____. a. rhythms b. staves c. accidentals 41. Moderately soft is _____ ...
... 39. The ____________ is mainly used by the men and is also called the F clef. a. Treble Clef b. Alto Clef c. Bass Clef 40. Sharps, flats or naturals occurring in a piece of music that are not in a key signature are referred to as_____. a. rhythms b. staves c. accidentals 41. Moderately soft is _____ ...
Intervals and Pitch - The Sound of Numbers
... 4. The frequency that is down one octave from 900 Hz then up two ifths from that is found by setting n = −1 and m = 2, so the answer is 2−1 (3/2)2 900 = (1/2)(3/2)2 900 = 1012 12 Hz. ¹Negative exponents indicate division: a−n = ...
... 4. The frequency that is down one octave from 900 Hz then up two ifths from that is found by setting n = −1 and m = 2, so the answer is 2−1 (3/2)2 900 = (1/2)(3/2)2 900 = 1012 12 Hz. ¹Negative exponents indicate division: a−n = ...
Scales and temperaments: the fivefold way
... 9Carl A. Eitz, Das mathematisch-reine Tonsystem, Leipzig, 1891. A similar notation ...
... 9Carl A. Eitz, Das mathematisch-reine Tonsystem, Leipzig, 1891. A similar notation ...
Using Whole Tone Scales in Improvisation
... In the notes of this series the focus will be on bridging the gap between musical theory and practice. The target audience is the jazz performer who reads music and has a good understanding of chord progressions and traditional harmony. ...
... In the notes of this series the focus will be on bridging the gap between musical theory and practice. The target audience is the jazz performer who reads music and has a good understanding of chord progressions and traditional harmony. ...
Tuning Systems
... Almost all music traditions recognize the octave18 . When note Y has a frequency19 that is twice the frequency of note Z, then note Y is one octave higher than note Z. A simple mathematical way to say this is that the ratio20 of the frequencies is 2:1. Two notes that are exactly one octave apart sou ...
... Almost all music traditions recognize the octave18 . When note Y has a frequency19 that is twice the frequency of note Z, then note Y is one octave higher than note Z. A simple mathematical way to say this is that the ratio20 of the frequencies is 2:1. Two notes that are exactly one octave apart sou ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.