Lecture 15
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
REM-off
... Both NE and ACh are found to alter the response to excitatory inputs to layer Ib moreso than layer Ia. Since those excitatory inputs are known to arise from different sources (olfactory bulb / extrinsic vs. other cortical areas / intrinsic), this means that the same layer II neuron, with dendrites i ...
... Both NE and ACh are found to alter the response to excitatory inputs to layer Ib moreso than layer Ia. Since those excitatory inputs are known to arise from different sources (olfactory bulb / extrinsic vs. other cortical areas / intrinsic), this means that the same layer II neuron, with dendrites i ...
The relative advantages of sparse versus distributed encoding for
... recording, one often uses the concept of fine tuning, which refers to a given neuron being activated by only a small proportion of the stimuli belonging to a certain set. If the set of stimuli considered, on the whole, activates neurons distributed evenly over the network, the two concepts can be ta ...
... recording, one often uses the concept of fine tuning, which refers to a given neuron being activated by only a small proportion of the stimuli belonging to a certain set. If the set of stimuli considered, on the whole, activates neurons distributed evenly over the network, the two concepts can be ta ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 12-03
... o “Rest and Digest” Stimulates visceral activity Conserves energy and promotes sedentary activities o Preganglionic neurons located in brainstem and sacral spinal cord o Preganglionic axons are long since parasympathetic ganglia are located close to target organ and branch very little to give fi ...
... o “Rest and Digest” Stimulates visceral activity Conserves energy and promotes sedentary activities o Preganglionic neurons located in brainstem and sacral spinal cord o Preganglionic axons are long since parasympathetic ganglia are located close to target organ and branch very little to give fi ...
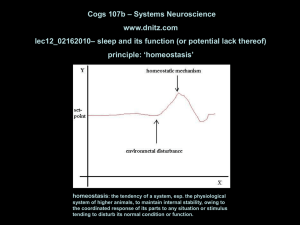
Metabolic acidosis inhibits hypothalamic warm
... controlled by the POAH, resulting in heat stroke (5). Future studies, therefore, will want to address several questions that have been raised by the work of Wright and Boulant (11). Do metabolic disturbances in acid-base balance alter various behavioral and physiological mechanisms of thermoregulati ...
... controlled by the POAH, resulting in heat stroke (5). Future studies, therefore, will want to address several questions that have been raised by the work of Wright and Boulant (11). Do metabolic disturbances in acid-base balance alter various behavioral and physiological mechanisms of thermoregulati ...
Neurons & the Nervous System
... • Resting potential: electric potential when neuron not firing (-70 millivolts) • Depolarization: neuron reduces resting potential by becoming positively charged ...
... • Resting potential: electric potential when neuron not firing (-70 millivolts) • Depolarization: neuron reduces resting potential by becoming positively charged ...
Millisecond-Timescale Optical Control of Neural Dynamics in the
... was safely expressed, and could mediate optical neuromodulation, in primate neocortex over many months. These findings highlight a methodology for investigating the causal role of specific cell types in nonhuman primate neural computation, cognition, and behavior, and open up the possibility of a ne ...
... was safely expressed, and could mediate optical neuromodulation, in primate neocortex over many months. These findings highlight a methodology for investigating the causal role of specific cell types in nonhuman primate neural computation, cognition, and behavior, and open up the possibility of a ne ...
Appendix S1 Relation of local short
... contribute to local EEG considerably and others insignificantly. What is the contribution of volume conduction effect in this context? Firstly, volume conduction effect is distance dependent: the larger the distance of the recording electrode from the current source, the less informative the measure ...
... contribute to local EEG considerably and others insignificantly. What is the contribution of volume conduction effect in this context? Firstly, volume conduction effect is distance dependent: the larger the distance of the recording electrode from the current source, the less informative the measure ...
Artificial Neural Networks
... Human brain is most powerful pattern recognition engine ever invented, however, it is not very good at serially processing huge quantities of discrete data. ...
... Human brain is most powerful pattern recognition engine ever invented, however, it is not very good at serially processing huge quantities of discrete data. ...
Neural Nets
... Inputs are transmitted electrochemically across the input synapses Input potentials are summed. If the potential reaches a threshold, a pulse or action potential moves down the axon. (The neuron has “fired”.) The pulse is distributed at the axonal arborization to the input synapses of other neurons. ...
... Inputs are transmitted electrochemically across the input synapses Input potentials are summed. If the potential reaches a threshold, a pulse or action potential moves down the axon. (The neuron has “fired”.) The pulse is distributed at the axonal arborization to the input synapses of other neurons. ...
Page | 1 CHAPTER 2: THE BIOLOGY OF BEHAVIOR The Nervous
... How do we distinguish a gentle touch from a big hug? A strong stimulus—a slap rather than a tap—can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often. But it does not affect the action potential’s strength or speed. Squeezing a trigger harder won’t make a bullet go faster. ...
... How do we distinguish a gentle touch from a big hug? A strong stimulus—a slap rather than a tap—can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often. But it does not affect the action potential’s strength or speed. Squeezing a trigger harder won’t make a bullet go faster. ...
Optogenetic Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ofMRI
... the same location. After allowing animal recovery time and opsin expression time, the animal was scanned using a 7T small animal. Animals were intubated with the tracheal tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and ...
... the same location. After allowing animal recovery time and opsin expression time, the animal was scanned using a 7T small animal. Animals were intubated with the tracheal tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and ...
CNS: Brain and Spinal Cord
... Vestibular nuclei in the medulla and directly from sensory pathways) it integrates all this info, then sends a "blueprint" to the cortex (via the thalamus) about how to produce a smooth movement. input from the cerebellum reduces the number of motor units activated for a particular movement, so that ...
... Vestibular nuclei in the medulla and directly from sensory pathways) it integrates all this info, then sends a "blueprint" to the cortex (via the thalamus) about how to produce a smooth movement. input from the cerebellum reduces the number of motor units activated for a particular movement, so that ...
chapter 11-nerve tissue
... sheaths. This can lead to abnormal sensations, muscle weakness and decreased motor function. 2) MS is characterized by frequent attacks, each causing ...
... sheaths. This can lead to abnormal sensations, muscle weakness and decreased motor function. 2) MS is characterized by frequent attacks, each causing ...
Az alvás és ébrenlét, gondolkodás, morális és emocionális
... Inhibitory pathways are shown in red, and the excitatory pathways in green. The blue circle indicates cholinerg neurons of the LDT and PPT; green boxes indicate aminergic nuclei; and the red box indicates the VLPO. - Aminergic regions such as the TMN, LC and DR promote wakefulness by direct excitato ...
... Inhibitory pathways are shown in red, and the excitatory pathways in green. The blue circle indicates cholinerg neurons of the LDT and PPT; green boxes indicate aminergic nuclei; and the red box indicates the VLPO. - Aminergic regions such as the TMN, LC and DR promote wakefulness by direct excitato ...
chapter 11 the somatosensory system and topographic organization
... Various kinds of sensory receptors are distributed over the entire body surface as well as in the muscles, joints, and internal organs. Because each receptor has a specific location in space, it transmits information about what is happening at its particular location. The region of space within whic ...
... Various kinds of sensory receptors are distributed over the entire body surface as well as in the muscles, joints, and internal organs. Because each receptor has a specific location in space, it transmits information about what is happening at its particular location. The region of space within whic ...
File
... Presynaptic neuron- sends signal Postsynaptic neuron- receives signal How does this happen? The arrival of an action potential at an axon’s terminal triggers the release of NEUROTRANSMITTERS- chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks ...
... Presynaptic neuron- sends signal Postsynaptic neuron- receives signal How does this happen? The arrival of an action potential at an axon’s terminal triggers the release of NEUROTRANSMITTERS- chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks ...
Ch. 3 S. 1
... Neurotransmitters are involved in _____________________ people do. Whenever a person waves a hand, yawns, or thinks about a friend, neurotransmitters are involved. Some diseases and psychological disorders may also be caused by the presence of too much or too little of various neurotransmitters. Res ...
... Neurotransmitters are involved in _____________________ people do. Whenever a person waves a hand, yawns, or thinks about a friend, neurotransmitters are involved. Some diseases and psychological disorders may also be caused by the presence of too much or too little of various neurotransmitters. Res ...
Marginal chimera state at cross-frequency locking of pulse
... Studies of the dynamics of globally coupled populations of oscillators, pioneered more than 40 years ago by Winfree and Kuramoto [1], are the focus of current research due to numerous applications in diverse fields from physics to neuroscience, but also due to striking effects such as synchronizatio ...
... Studies of the dynamics of globally coupled populations of oscillators, pioneered more than 40 years ago by Winfree and Kuramoto [1], are the focus of current research due to numerous applications in diverse fields from physics to neuroscience, but also due to striking effects such as synchronizatio ...
Synaptic reverberation underlying mnemonic persistent activity
... require neuromodulatory signals such as acetylcholine15. Even if single cells are not bistable, the behavior of a cortical network is always the result of the interplay between intrinsic cellular properties and synaptic mechanisms16. Experiments and biophysical modeling on the neural basis of persis ...
... require neuromodulatory signals such as acetylcholine15. Even if single cells are not bistable, the behavior of a cortical network is always the result of the interplay between intrinsic cellular properties and synaptic mechanisms16. Experiments and biophysical modeling on the neural basis of persis ...
Prenatal and postnatal development of laterally
... shape of the map. The orientation preference distribution is also biased towards horizontal and vertical, as seen in ferret visual cortex [10]. These results are the main novel component of this work. To our knowledge, only one other computational model has been tested in this way; the postnatal tra ...
... shape of the map. The orientation preference distribution is also biased towards horizontal and vertical, as seen in ferret visual cortex [10]. These results are the main novel component of this work. To our knowledge, only one other computational model has been tested in this way; the postnatal tra ...
Modeling and Detecting Deep Brain Activity with MEG
... MEG and EEG source modeling, the cortical grey matter is supposed to support the primary neural currents generating the external signals. The current flow resulting from postsynaptic potentials (PSP) is classically modeled by an equivalent current dipole (ECD). The ECD is oriented along the directio ...
... MEG and EEG source modeling, the cortical grey matter is supposed to support the primary neural currents generating the external signals. The current flow resulting from postsynaptic potentials (PSP) is classically modeled by an equivalent current dipole (ECD). The ECD is oriented along the directio ...
Why light
... If a neurons dumps a lot of excitatory neurotransmitter substance, its activity will cause following neurons to increase their rate of activity. If a neurons dumps a lot of inhibitory neurotransmitter substance, its activity will cause following neurons to decrease their rate of activity. The Retina ...
... If a neurons dumps a lot of excitatory neurotransmitter substance, its activity will cause following neurons to increase their rate of activity. If a neurons dumps a lot of inhibitory neurotransmitter substance, its activity will cause following neurons to decrease their rate of activity. The Retina ...
Competitive Dynamics in Cortical Responses to Visual Stimuli
... suppress the other one. Although both pools of excitatory neurons were active, neither was as active as it would have been in the sole presence of its preferred stimulus, and thus the network operated in what we termed normalization mode. If the strength of the inhibition was increased, the network ...
... suppress the other one. Although both pools of excitatory neurons were active, neither was as active as it would have been in the sole presence of its preferred stimulus, and thus the network operated in what we termed normalization mode. If the strength of the inhibition was increased, the network ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.