Ch 31: Urinary System
... - Involuntary movement of body part in response to stimulus - Occur without involving the conscious portions of the brain - Signal sent to spinal cord & immediately back to source - Usually help keep you from being hurt ...
... - Involuntary movement of body part in response to stimulus - Occur without involving the conscious portions of the brain - Signal sent to spinal cord & immediately back to source - Usually help keep you from being hurt ...
PPT - UCLA Health
... • Some mechanisms present during development may not play important role in the mature brain. • Initial connections involved chemotropic guidance and myelination processes, are not present in the mature brain. • Drastic pruning of interneuronal connections do not occur in the adult. • Thus the mech ...
... • Some mechanisms present during development may not play important role in the mature brain. • Initial connections involved chemotropic guidance and myelination processes, are not present in the mature brain. • Drastic pruning of interneuronal connections do not occur in the adult. • Thus the mech ...
5. Ruiz G., en Homeopathy Jorurnal, 91, 80-84 (2002)
... each step is interpreted in terms of stochastic resonance, a non-linear response of certain systems when perturbed by noise and a weak periodic signal, which increasingly enhanced at the output as the magnitude of the noise grows towards an optimal value for maximum signal amplification. The possibl ...
... each step is interpreted in terms of stochastic resonance, a non-linear response of certain systems when perturbed by noise and a weak periodic signal, which increasingly enhanced at the output as the magnitude of the noise grows towards an optimal value for maximum signal amplification. The possibl ...
criteria of artificial neural network in reconition of pattern and image
... called FR. Similarly FA occurs when imposter is recognized as a true speaker. Neural networks learn complex mappings between inputs and outputs and are particularly useful when the underlying statistics of the considered tasks are not well understood. Neural Networks being relatively new approach is ...
... called FR. Similarly FA occurs when imposter is recognized as a true speaker. Neural networks learn complex mappings between inputs and outputs and are particularly useful when the underlying statistics of the considered tasks are not well understood. Neural Networks being relatively new approach is ...
Nervous System
... important to survival? *topic key question# 3: Why is the nervous system important to survival? Its important to survival cause it helps you feel what you touch, see what your eyes mainly point at, smell what ever sent comes to your nose, taste what ever you put in your mouth, and hear what ever noi ...
... important to survival? *topic key question# 3: Why is the nervous system important to survival? Its important to survival cause it helps you feel what you touch, see what your eyes mainly point at, smell what ever sent comes to your nose, taste what ever you put in your mouth, and hear what ever noi ...
States of consciousness
... Some sy it is a period for restoration and having a survival function Generally believed sleep is NB for normal functioning Sleep deprivation is a form of stress and have negative effects on concentration and ...
... Some sy it is a period for restoration and having a survival function Generally believed sleep is NB for normal functioning Sleep deprivation is a form of stress and have negative effects on concentration and ...
2320lecture22
... • Since attention has a profound effect on perception, one would expect it to have some measurable effect on the brain • This has been confirmed with a variety of techniques: EEG, fMRI/PET, Unit Recordings ...
... • Since attention has a profound effect on perception, one would expect it to have some measurable effect on the brain • This has been confirmed with a variety of techniques: EEG, fMRI/PET, Unit Recordings ...
module 6 - sandrablake
... stimulated. When the neuron is recharged, at rest, and capable of generating another action potential, a _____________________ ________________________ exists. An interesting fact about how a neuron fires is called the all-or-none principle. This means that a neuron always fires with the same intens ...
... stimulated. When the neuron is recharged, at rest, and capable of generating another action potential, a _____________________ ________________________ exists. An interesting fact about how a neuron fires is called the all-or-none principle. This means that a neuron always fires with the same intens ...
State-dependent computations - Frankfurt Institute for Advanced
... some temporal features, particularly simple features such as the interval between two events. Thus, the question is not whether time can be centrally represented in a spatial code, but how this is achieved. A second approach in artificial neural-network models was to implicitly represent time using ...
... some temporal features, particularly simple features such as the interval between two events. Thus, the question is not whether time can be centrally represented in a spatial code, but how this is achieved. A second approach in artificial neural-network models was to implicitly represent time using ...
Repetition and the brain: neural models of stimulus
... of neural models that have been proposed to account for repetition suppression (RS). We focus primarily on studies using visually presented objects and their effects on the ventral object processing stream, to maximize overlap between monkey and human studies. We evaluate the neural models in terms ...
... of neural models that have been proposed to account for repetition suppression (RS). We focus primarily on studies using visually presented objects and their effects on the ventral object processing stream, to maximize overlap between monkey and human studies. We evaluate the neural models in terms ...
Repetition and the brain: neural models of stimulus
... of neural models that have been proposed to account for repetition suppression (RS). We focus primarily on studies using visually presented objects and their effects on the ventral object processing stream, to maximize overlap between monkey and human studies. We evaluate the neural models in terms ...
... of neural models that have been proposed to account for repetition suppression (RS). We focus primarily on studies using visually presented objects and their effects on the ventral object processing stream, to maximize overlap between monkey and human studies. We evaluate the neural models in terms ...
Brain and Nervous System Overview
... The simple version Pre-synaptic Action potential initiates at synapse (through allowing passage of Ca++) - unidirectional Causes vesicle passage ~300 vesicles per action potential containing chemical transmitter (excitatory or inhibitory) (i.e. ACH acetylcholine or GABA) Each vesicle contains ~10,00 ...
... The simple version Pre-synaptic Action potential initiates at synapse (through allowing passage of Ca++) - unidirectional Causes vesicle passage ~300 vesicles per action potential containing chemical transmitter (excitatory or inhibitory) (i.e. ACH acetylcholine or GABA) Each vesicle contains ~10,00 ...
Leap 2 - Teacher - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... 4. be reabsorbed back into the “sending” neuron - this reabsorption will signal cells to STOP releasing additional neurotransmitter, until the next stimulus occurs. This signaling to STOP releasing additional neurotransmitter is an example of a negative feedback loop. In a negative feedback loop, an ...
... 4. be reabsorbed back into the “sending” neuron - this reabsorption will signal cells to STOP releasing additional neurotransmitter, until the next stimulus occurs. This signaling to STOP releasing additional neurotransmitter is an example of a negative feedback loop. In a negative feedback loop, an ...
The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions
... • NO is a diffusible bioactive gas produced from arginine by nitric oxide synthase • NO is widely distributed in brain and peripheral tissues • NO is not stored and synthesis is regulated by the enzyme activity ...
... • NO is a diffusible bioactive gas produced from arginine by nitric oxide synthase • NO is widely distributed in brain and peripheral tissues • NO is not stored and synthesis is regulated by the enzyme activity ...
The Information Processing Mechanism of the Brain
... in essence, the neural network is a unit that performs processing of activity patterns.) There is reason to recap the central properties of a neural network. A neural network can be modelled in a simple physical mechanism, which can be studied in computer simulations. This model captures the essenti ...
... in essence, the neural network is a unit that performs processing of activity patterns.) There is reason to recap the central properties of a neural network. A neural network can be modelled in a simple physical mechanism, which can be studied in computer simulations. This model captures the essenti ...
Ascending Projections
... • Autonomic responses and visceral sensations accompany most emotion. The earliest theory hypothesized that emotion is the result of basic sensations: – Aristotle (350 BCE) - pain is an emotion – James-Lange (1884-85) – emotions result from physical changes - “we feel sorry because we cry, ... afrai ...
... • Autonomic responses and visceral sensations accompany most emotion. The earliest theory hypothesized that emotion is the result of basic sensations: – Aristotle (350 BCE) - pain is an emotion – James-Lange (1884-85) – emotions result from physical changes - “we feel sorry because we cry, ... afrai ...
Effects of Correlated Input on Development of Structure in an
... the neuron, forming connections with the neurites of other neurons. This growth and connection is dependent on the levels of activity within the neuron and the activity of neighbouring neurons. This activity dependent connection formation was theorised by Hebb and can be summarised with the statemen ...
... the neuron, forming connections with the neurites of other neurons. This growth and connection is dependent on the levels of activity within the neuron and the activity of neighbouring neurons. This activity dependent connection formation was theorised by Hebb and can be summarised with the statemen ...
39_LectureSlides
... The role of early experience in human development has become a political issue: “Fifteen years ago, we thought that a baby’s brain structure was virtually complete at birth. Now we understand that it is a work in progress, and that everything we do with a child has some kind of potential physical i ...
... The role of early experience in human development has become a political issue: “Fifteen years ago, we thought that a baby’s brain structure was virtually complete at birth. Now we understand that it is a work in progress, and that everything we do with a child has some kind of potential physical i ...
P312 Ch05_PerceivingObjectsII
... New Way – Spatial Frequency Representation. The external stimulus is considered to be a collection of alternating patterns of light and dark across the whole visual field. In this theory, each neuron responds not to what’s at a particular place, but instead to what’s happening across the whole visu ...
... New Way – Spatial Frequency Representation. The external stimulus is considered to be a collection of alternating patterns of light and dark across the whole visual field. In this theory, each neuron responds not to what’s at a particular place, but instead to what’s happening across the whole visu ...
3._Biological_Basis_of_Behavior_objectives
... 8. Define polarization and refractory period. Explain how they affect signal transduction in the nervous system. 9. Define neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. Describe their role in nervous system activity. 10. Describe the role of excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. Describe their r ...
... 8. Define polarization and refractory period. Explain how they affect signal transduction in the nervous system. 9. Define neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. Describe their role in nervous system activity. 10. Describe the role of excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. Describe their r ...
The Fine Structure of Slow-Wave Sleep Oscillations: from Single
... cats. Wake/sleep states were identified using the following criteria: Wake: lowamplitude fast activity in LFPs, high electrooculogram (EOG) and high electromyogram (EMG) activity; Slow-wave sleep: LFPs dominated by high-amplitude slowwaves, low EOG activity and EMG activity present; REM sleep: low-a ...
... cats. Wake/sleep states were identified using the following criteria: Wake: lowamplitude fast activity in LFPs, high electrooculogram (EOG) and high electromyogram (EMG) activity; Slow-wave sleep: LFPs dominated by high-amplitude slowwaves, low EOG activity and EMG activity present; REM sleep: low-a ...
Ch. 3 S. 1
... The spinal cord is also involved in spinal reflexes. A spinal reflex is a simple, automatic response to something. For example, if a person touches a hot stove, a message goes immediately from his or her hand to the spinal cord. A message to remove the hand is then sent back to motor neurons in the ...
... The spinal cord is also involved in spinal reflexes. A spinal reflex is a simple, automatic response to something. For example, if a person touches a hot stove, a message goes immediately from his or her hand to the spinal cord. A message to remove the hand is then sent back to motor neurons in the ...
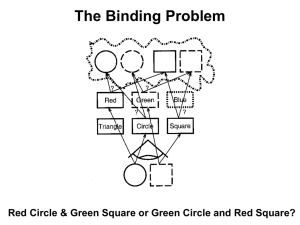
Optional extra slides on the Binding Problem
... Synchronization of pre-synaptic neuron inputs upon postsynaptic cells is increased with increased attention. (Fries, Reynolds, Rorie, and Desimone, 2001). ...
... Synchronization of pre-synaptic neuron inputs upon postsynaptic cells is increased with increased attention. (Fries, Reynolds, Rorie, and Desimone, 2001). ...
Glia Ç more than just brain glue
... glia maintained in vitro. Although such analysis is useful and has taught us much about the basic properties of glia, it cannot tell us how glia interact with other cell types. Electrophysiological and calcium imaging studies using mammalian brain slices have begun to provide insight into both glia– ...
... glia maintained in vitro. Although such analysis is useful and has taught us much about the basic properties of glia, it cannot tell us how glia interact with other cell types. Electrophysiological and calcium imaging studies using mammalian brain slices have begun to provide insight into both glia– ...
Increased leak conductance alters ISI variability.
... CV = standard deviation of ISI distribution/mean ISI ...
... CV = standard deviation of ISI distribution/mean ISI ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.