Dr. Ghassan The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): After studying
... ganglion chain without synapsing with a postganglionic neuron. Instead, the axons of these neurons travel more peripherally and synapse with postganglionic neurons in one of the sympathetic collateral ganglia. These include the celiac, superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric ganglia. Postganglio ...
... ganglion chain without synapsing with a postganglionic neuron. Instead, the axons of these neurons travel more peripherally and synapse with postganglionic neurons in one of the sympathetic collateral ganglia. These include the celiac, superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric ganglia. Postganglio ...
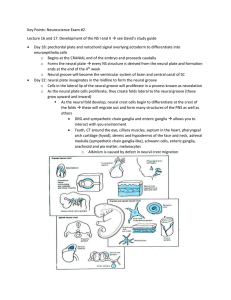
Key Points: Neuroscience Exam #2 Lecture 16 and 17: Development of
... complex sequences of voluntary movements. Receive projections from: Prefrontal cortex (decision making) Parietal association areas (spatial relationships between body & external world) o The brainstem also comes into play through a collective group of tracts that give inputs to body movements ...
... complex sequences of voluntary movements. Receive projections from: Prefrontal cortex (decision making) Parietal association areas (spatial relationships between body & external world) o The brainstem also comes into play through a collective group of tracts that give inputs to body movements ...
Identified nerve cells and insect behavior
... Studies of insect identified neurons over the past 25 years have provided some of the very best data on sensorimotor integration; tracing information flow from sensory to motor networks. General principles have emerged that have increased the sophistication with which we now understand both sensory ...
... Studies of insect identified neurons over the past 25 years have provided some of the very best data on sensorimotor integration; tracing information flow from sensory to motor networks. General principles have emerged that have increased the sophistication with which we now understand both sensory ...
Inferring spike-timing-dependent plasticity from spike train data
... For τ− > τ+ this corresponds to a more general Hebbian rule, where synapses are strengthened whenever pre- and post-synaptic spikes occur in close proximity. When spikes do not occur in close proximity the synapse is weakened. In this case, the parameters A+ , A− , τ+ , and τ− determine the magnitud ...
... For τ− > τ+ this corresponds to a more general Hebbian rule, where synapses are strengthened whenever pre- and post-synaptic spikes occur in close proximity. When spikes do not occur in close proximity the synapse is weakened. In this case, the parameters A+ , A− , τ+ , and τ− determine the magnitud ...
A4a - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... dendritic spines (small knobs projecting from dendrites), but some also end directly on shafts of dendrites; spines on apical dendrites of large pyramidal neurons in cerebral cortex; numbers of spines increase rapidly from birth to 8 months of age (in Down's syndrome, spines are thin and small): ...
... dendritic spines (small knobs projecting from dendrites), but some also end directly on shafts of dendrites; spines on apical dendrites of large pyramidal neurons in cerebral cortex; numbers of spines increase rapidly from birth to 8 months of age (in Down's syndrome, spines are thin and small): ...
neuron models and basic learning rules
... • In general, there are many different kinds of activation functions. • The step function used in the McCulloch-Pitts model is simply one of them. • Because the activation function takes only two values, this model is called discrete neuron. • To make the neuron learnable, some kind of continuous fu ...
... • In general, there are many different kinds of activation functions. • The step function used in the McCulloch-Pitts model is simply one of them. • Because the activation function takes only two values, this model is called discrete neuron. • To make the neuron learnable, some kind of continuous fu ...
Rules relating connections to cortical structure in primate prefrontal cortex H. Barbas
... architecture, and can be applied to the sensory and motor cortical systems as well, because their structure also varies systematically in primates (for review see [16]). Within the conceptual framework of the structural model, feedforward projections in sensory areas always originate in areas with h ...
... architecture, and can be applied to the sensory and motor cortical systems as well, because their structure also varies systematically in primates (for review see [16]). Within the conceptual framework of the structural model, feedforward projections in sensory areas always originate in areas with h ...
Poulet etal - Cornell University
... Fig. 4 Responses of auditory neurons to acoustic stimuli presented during silent singing. a Auditory afferents showed no modulation in their firing rate to acoustic stimuli and responded with a constant train of spikes during the chirp and chirp intervals. However, those spikes coinciding with PADs du ...
... Fig. 4 Responses of auditory neurons to acoustic stimuli presented during silent singing. a Auditory afferents showed no modulation in their firing rate to acoustic stimuli and responded with a constant train of spikes during the chirp and chirp intervals. However, those spikes coinciding with PADs du ...
An Introduction to the Nervous System
... mechanism involved in synaptic activity. • 12-8 Describe the major types of neurotransmitters and neuromodulators, and discuss their effects on postsynaptic membranes. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... mechanism involved in synaptic activity. • 12-8 Describe the major types of neurotransmitters and neuromodulators, and discuss their effects on postsynaptic membranes. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Understanding-Psychology-8th-Edition-Morris-Test-Bank
... b. Transmission of information at synapses occurs by means of direct physical contact between the nerve cells. c. The size and speed of the neural impulse is the same for a particular axon regardless of the strength of the stimulus that sets it off. d. None of the above are true. ...
... b. Transmission of information at synapses occurs by means of direct physical contact between the nerve cells. c. The size and speed of the neural impulse is the same for a particular axon regardless of the strength of the stimulus that sets it off. d. None of the above are true. ...
Kandel ch. 42 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Two deep transverse fissures divide the cerebellum into three lobes. The primary fissure on the dorsal surface separates the anterior and posterior lobes, which together form the body of the cerebellum. The posterolateral fissure on the ventral surface separates the body from the much smaller floccu ...
... Two deep transverse fissures divide the cerebellum into three lobes. The primary fissure on the dorsal surface separates the anterior and posterior lobes, which together form the body of the cerebellum. The posterolateral fissure on the ventral surface separates the body from the much smaller floccu ...
Mirror Neurons: Fire to Inspire
... MSH, our ancestors (but not those of other apes) developed brain mechanisms that supports the ability to recognize others performance and complex imitation mechanisms to approximate the performance with the increasing skill. Studies recommended that brain supporting complex imitation started from ol ...
... MSH, our ancestors (but not those of other apes) developed brain mechanisms that supports the ability to recognize others performance and complex imitation mechanisms to approximate the performance with the increasing skill. Studies recommended that brain supporting complex imitation started from ol ...
A mathematical model on REM-NREM cycle
... amplifying and one resonant current. Some mechanisms have one resonant and one amplifying current. So, many models focused on system of equations where the variables involved are these currents. They made correspondences between resting, excitable, and periodic spiking activity to a stable equilibri ...
... amplifying and one resonant current. Some mechanisms have one resonant and one amplifying current. So, many models focused on system of equations where the variables involved are these currents. They made correspondences between resting, excitable, and periodic spiking activity to a stable equilibri ...
Neurotransmission in the rat amygdala related to fear and anxiety
... inhibitory avoidance, Izquierdo and colieagues:J'> found that immediate posttraining infusion of APV into either the amygdala, medial septum, or hippocampus, blocked memory measured 18 h after training. lJ-2-Amino-5-phosphonovalerate caused amnesia when infused into either the hippocampus or amygdal ...
... inhibitory avoidance, Izquierdo and colieagues:J'> found that immediate posttraining infusion of APV into either the amygdala, medial septum, or hippocampus, blocked memory measured 18 h after training. lJ-2-Amino-5-phosphonovalerate caused amnesia when infused into either the hippocampus or amygdal ...
Chapter 13
... 7. The white matter is divided into columns. a. Each column contains distinct bundles of nerve axons that have a common origin or destination and carry similar information. b. These bundles are called tracts. 1) Sensory (ascending) tracts conduct nerve impulses toward the brain. 2) Motor (descending ...
... 7. The white matter is divided into columns. a. Each column contains distinct bundles of nerve axons that have a common origin or destination and carry similar information. b. These bundles are called tracts. 1) Sensory (ascending) tracts conduct nerve impulses toward the brain. 2) Motor (descending ...
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF VISUAL-SACCADIC DECISION MAKING
... to physiological study. For the second class, behaviors in which no deterministic connection was obvious between sensation and action, he followed Aristotle’s lead, identifying the source of these actions as the nonmaterial soul. Descartes’ dualist proposal was a tremendous advance for physiologists ...
... to physiological study. For the second class, behaviors in which no deterministic connection was obvious between sensation and action, he followed Aristotle’s lead, identifying the source of these actions as the nonmaterial soul. Descartes’ dualist proposal was a tremendous advance for physiologists ...
Mirror Neurons and Mirror Systems in Monkeys and Humans
... Motor acts that are richly represented in the observer’s motor repertoire determine a strong activation of the mirror system. This has been shown by a series of brain imaging studies that examined the mirror activations in persons expert in specific motor skills and comparing them with the activatio ...
... Motor acts that are richly represented in the observer’s motor repertoire determine a strong activation of the mirror system. This has been shown by a series of brain imaging studies that examined the mirror activations in persons expert in specific motor skills and comparing them with the activatio ...
An oscillation-based model for the neuronal basis
... neurons representing all stimulus features and sharing similar receptive fields). Thus, in the presence of multiple stimuli, the neurons responding to the different stimuli will compete against each other. Because we assume that attention “labels” neurons in VI within a particular spatial location, ...
... neurons representing all stimulus features and sharing similar receptive fields). Thus, in the presence of multiple stimuli, the neurons responding to the different stimuli will compete against each other. Because we assume that attention “labels” neurons in VI within a particular spatial location, ...
Complementary roles of basal ganglia and cerebellum in learning
... direction [62,63•]. Recently, Kawagoe and colleagues performed delayed-saccade experiments in which reward was given in only one of four possible saccade directions [64]. Surprisingly, the direction tuning of caudate neurons was strongly modulated by the reward condition. In some neurons, direction ...
... direction [62,63•]. Recently, Kawagoe and colleagues performed delayed-saccade experiments in which reward was given in only one of four possible saccade directions [64]. Surprisingly, the direction tuning of caudate neurons was strongly modulated by the reward condition. In some neurons, direction ...