Theoretical Result: References: II: Improving the Basic Model (BMS)
... the minimal average distance to the firing threshold singularity set is measured, as proposed and discussed in Cessac 2007. Huge simulations have been conducted on the INRIA cluster to carefully study the network behaviour. ...
... the minimal average distance to the firing threshold singularity set is measured, as proposed and discussed in Cessac 2007. Huge simulations have been conducted on the INRIA cluster to carefully study the network behaviour. ...
Notes Intro to Nervous System and Neurons
... Mainly function between neurons and capillaries • Bridging the two • Communication between the two • Barrier between the two – Control the chemical environment of the brain (taking in extra K+ or neurotransmitters) ...
... Mainly function between neurons and capillaries • Bridging the two • Communication between the two • Barrier between the two – Control the chemical environment of the brain (taking in extra K+ or neurotransmitters) ...
Neuroembryology II_UniTsNeurosciAY1415_06a
... (expressing EGFP under the control of a promoter which specifically fires in CR-cells) into the E11.5 telencephalon, at different locations. After a few days, they studied the resulting distribution of the two markers and could prove that: (1) CR-cells are specifically generated by the cortical hem ...
... (expressing EGFP under the control of a promoter which specifically fires in CR-cells) into the E11.5 telencephalon, at different locations. After a few days, they studied the resulting distribution of the two markers and could prove that: (1) CR-cells are specifically generated by the cortical hem ...
Neurons_and_Neurotranmission
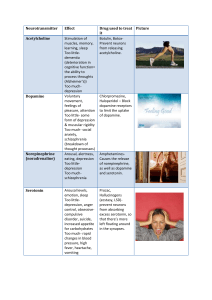
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
Airgas template
... assistance to maintain breathing. Autonomic dysreflexia represents an acute episode of exaggerated sympathetic reflex responses that occur in persons with some types of spinal cord injuries. The pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis involves the demyelination and subsequent degeneration of nerve fib ...
... assistance to maintain breathing. Autonomic dysreflexia represents an acute episode of exaggerated sympathetic reflex responses that occur in persons with some types of spinal cord injuries. The pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis involves the demyelination and subsequent degeneration of nerve fib ...
Neurotransmitter - Pamoja Education Blogs
... form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
... form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
Biology of Humans 2/e
... The signal passes across the synaptic cleft as a chemical called neurotransmitter which is released from vesicles by exocytosis. Neurotransmitter is a chemical that is secreted into a synaptic cleft by a neuron that affects another neuron or an effector by binding with receptors on it. The sending c ...
... The signal passes across the synaptic cleft as a chemical called neurotransmitter which is released from vesicles by exocytosis. Neurotransmitter is a chemical that is secreted into a synaptic cleft by a neuron that affects another neuron or an effector by binding with receptors on it. The sending c ...
Unit 3A Nervous System - Teacher Version
... action potential (excitatory neurotransmitters binding to receptors) must ...
... action potential (excitatory neurotransmitters binding to receptors) must ...
Title: Nervous System
... and each activated enzyme can regulate many target proteins (amplification). Second-messengers may activate certain enzymes that catalyze the phosphorylation of certain proteins, which in turn produce the physiological response of the cell to the extracellular signal (first messenger) ...
... and each activated enzyme can regulate many target proteins (amplification). Second-messengers may activate certain enzymes that catalyze the phosphorylation of certain proteins, which in turn produce the physiological response of the cell to the extracellular signal (first messenger) ...
Sample Take-home Final Exam
... receptor cell(s) that transduce the stimulus into a neural signal. Indicate whether this cell is a neuron or is not a neuron. Indicate what type of receptor it is: photoreceptor, mechanoreceptor, free nerve ending, thermoreceptor, nociceptor, chemoreceptor. What is the lifespan of that cell type? ...
... receptor cell(s) that transduce the stimulus into a neural signal. Indicate whether this cell is a neuron or is not a neuron. Indicate what type of receptor it is: photoreceptor, mechanoreceptor, free nerve ending, thermoreceptor, nociceptor, chemoreceptor. What is the lifespan of that cell type? ...
The Brainstem
... Forms transverse fibers that give pons its shape Superior (SCP) - To red nucleus & thalamus to correct motor actions OUTPUT (fix bad motor plan) ...
... Forms transverse fibers that give pons its shape Superior (SCP) - To red nucleus & thalamus to correct motor actions OUTPUT (fix bad motor plan) ...
KKDP 3: The role of the neuron (dendrites, axon, myelin and
... (excluding details related to signal transduction) ROLE OF THE NEURON ...
... (excluding details related to signal transduction) ROLE OF THE NEURON ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... The general objective of this subject is for students to acquire a basic knowledge of the structural, molecular and functional aspects of the mechanisms that control the working of the nervous system, the skin and the senses. This basic knowledge will allow students at a later stage to understand th ...
... The general objective of this subject is for students to acquire a basic knowledge of the structural, molecular and functional aspects of the mechanisms that control the working of the nervous system, the skin and the senses. This basic knowledge will allow students at a later stage to understand th ...
Neuroscience Course Conference
... 2. In demyelinating syndromes such as multiple sclerosis, an action potential propagating into a demyelinated zone from a normally myelinated zone may fail. a. What could cause this failure? b. What type of drug might you try to overcome this conduction failure? c. What might be the side effects of ...
... 2. In demyelinating syndromes such as multiple sclerosis, an action potential propagating into a demyelinated zone from a normally myelinated zone may fail. a. What could cause this failure? b. What type of drug might you try to overcome this conduction failure? c. What might be the side effects of ...
Nerve Cell Signaling - Mr. Moore`s Web Page
... 2. Describe the sequence of events that lead to an action potential and a depolarization of the neuron. 3. Describe the passage of neurotransmitter across a synaptic cleft. 4. Identify what a motor neuron and sensory neurons do and where they are located in the body. ...
... 2. Describe the sequence of events that lead to an action potential and a depolarization of the neuron. 3. Describe the passage of neurotransmitter across a synaptic cleft. 4. Identify what a motor neuron and sensory neurons do and where they are located in the body. ...
m5zn_363798b57fd4c88
... Function of the spinal cord The main functions of the spinal cord are: 1. The spinal cord communicates through nerve fibers, its nervous pathways, with various parts of the brain and through spinal nerves with organs. The spinal cord contains two kinds of nervous pathway: ascending (sensory) and d ...
... Function of the spinal cord The main functions of the spinal cord are: 1. The spinal cord communicates through nerve fibers, its nervous pathways, with various parts of the brain and through spinal nerves with organs. The spinal cord contains two kinds of nervous pathway: ascending (sensory) and d ...