The Autonomic Nervous System
... Parasympathetic neurons: The parasympathetic preganglionic fibers arise from the cranium (from cranialnerves III, VII, IX, and X) and from the sacral region of the spinal cord and synapse in ganglia near or on theeffector organs. Thus, in contrast to the sympathetic system, the preganglionic fibers ...
... Parasympathetic neurons: The parasympathetic preganglionic fibers arise from the cranium (from cranialnerves III, VII, IX, and X) and from the sacral region of the spinal cord and synapse in ganglia near or on theeffector organs. Thus, in contrast to the sympathetic system, the preganglionic fibers ...
consciousness
... Cerebrum: divided into two hemispheres (left and right), each consists of four lobes (frontal [at the front], parietal [in the middle], occipital [at the back], and temporal [at the bottom]). The outer layer of the brain is known as the cerebral cortex or the ‘grey matter.’ It covers the nuclei dee ...
... Cerebrum: divided into two hemispheres (left and right), each consists of four lobes (frontal [at the front], parietal [in the middle], occipital [at the back], and temporal [at the bottom]). The outer layer of the brain is known as the cerebral cortex or the ‘grey matter.’ It covers the nuclei dee ...
General classification of peripheral nervous system
... and motor neurons. All our conscious awareness of the external environment and all our motor activity to cope with it operate through the sensory-somatic division of the PNS. b) The Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system consists of sensory neurons and motor neurons that run between t ...
... and motor neurons. All our conscious awareness of the external environment and all our motor activity to cope with it operate through the sensory-somatic division of the PNS. b) The Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system consists of sensory neurons and motor neurons that run between t ...
PDF of article - Janelia Research Campus
... the tibiae, followed by co-contraction of both flexor and extensor muscles, followed by a rapid extension of its legs [54]. The schematized activity of flexor and extensor motor neurons is shown. (d) This motor output can be represented in a motor coordinate system where the position along each axis ...
... the tibiae, followed by co-contraction of both flexor and extensor muscles, followed by a rapid extension of its legs [54]. The schematized activity of flexor and extensor motor neurons is shown. (d) This motor output can be represented in a motor coordinate system where the position along each axis ...
10-21-09
... dissociated, and abstract math predicts math achievement. The two conditions in this experiment involved exact calculation (3+4= 6 or 7?) or approximate calculation (3+4= 6 or 9?). Exact involves rote memory retrieval, learning does not generalize, and involves left IFG. How does social power affect ...
... dissociated, and abstract math predicts math achievement. The two conditions in this experiment involved exact calculation (3+4= 6 or 7?) or approximate calculation (3+4= 6 or 9?). Exact involves rote memory retrieval, learning does not generalize, and involves left IFG. How does social power affect ...
Document
... Arousal and sleep – one section of reticular formation controls consciousness and alertness reticular activating system controls both sleep and waking state sleep not a loss of consciousness ...
... Arousal and sleep – one section of reticular formation controls consciousness and alertness reticular activating system controls both sleep and waking state sleep not a loss of consciousness ...
Artificial Intelligence CSC 361
... transmit messages A synapse is called excitatory if it raises the local membrane potential of the post synaptic cell. Inhibitory if the potential is lowered. ...
... transmit messages A synapse is called excitatory if it raises the local membrane potential of the post synaptic cell. Inhibitory if the potential is lowered. ...
Chapter 13 - PNS
... • Plexuses are found in the cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral regions • Each resulting branch of a plexus contains fibers from several spinal nerves • Each muscle receives a nerve supply from more than one spinal nerve • Damage to one spinal segment (gray matter) cannot completely paralyze a mu ...
... • Plexuses are found in the cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral regions • Each resulting branch of a plexus contains fibers from several spinal nerves • Each muscle receives a nerve supply from more than one spinal nerve • Damage to one spinal segment (gray matter) cannot completely paralyze a mu ...
GBA deficiency promotes SNCA/α-synuclein accumulation through
... Figure S4. C2-ceramide treatment conditions for maximal PPP2A activity. Optimal C2 concentration and application time (5 μM for 8 h) were determined according to the peak increase in PPP2A activity. *P<0.05 vs. control group, #P<0.05 vs. other C2 treatment groups; n=6. ...
... Figure S4. C2-ceramide treatment conditions for maximal PPP2A activity. Optimal C2 concentration and application time (5 μM for 8 h) were determined according to the peak increase in PPP2A activity. *P<0.05 vs. control group, #P<0.05 vs. other C2 treatment groups; n=6. ...
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... As a result of a viral infection, a patient has suffered destruction to the anterior gray horns in the lumbar region. What manifestations would you expect from this neurologic damage: a. Numbness in the feet b. Intense leg pain c. Deterioration of motor activity in the legs and feet d. Inability to ...
... As a result of a viral infection, a patient has suffered destruction to the anterior gray horns in the lumbar region. What manifestations would you expect from this neurologic damage: a. Numbness in the feet b. Intense leg pain c. Deterioration of motor activity in the legs and feet d. Inability to ...
File
... Neurons release neurotransmitters to influence other neurons. This opens a specific ion channel Neurotransmitter? ...
... Neurons release neurotransmitters to influence other neurons. This opens a specific ion channel Neurotransmitter? ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an action potential, or nerve impulse. They follow the all or none law!!! • The membrane will repolarize when K+ ...
... depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an action potential, or nerve impulse. They follow the all or none law!!! • The membrane will repolarize when K+ ...
11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... A. A synapse is a junction that mediates information transfer between neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell (p. 406; Fig. 11.16). B. Neurons conducting impulses toward the synapse are presynaptic cells, and neurons carrying impulses away from the synapse are postsynaptic cells (p. 406). C ...
... A. A synapse is a junction that mediates information transfer between neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell (p. 406; Fig. 11.16). B. Neurons conducting impulses toward the synapse are presynaptic cells, and neurons carrying impulses away from the synapse are postsynaptic cells (p. 406). C ...
Chapter 14
... Outer layers of neurons that contribute to optic nerve called ganglion cells. Neurons receive synaptic input from bipolar cells, which receive input from rods and cones. Horizontal cells synapse with photoreceptors. Amacrine cells synapse with several ganglion cells. ...
... Outer layers of neurons that contribute to optic nerve called ganglion cells. Neurons receive synaptic input from bipolar cells, which receive input from rods and cones. Horizontal cells synapse with photoreceptors. Amacrine cells synapse with several ganglion cells. ...
Artificial Intelligence
... part of the Mobile Servicing System on the International Space Station (ISS), and extends the function of this system to replace some ...
... part of the Mobile Servicing System on the International Space Station (ISS), and extends the function of this system to replace some ...
Histology of Nervous Tissue
... • Amount of voltage change (graded) dependent on # of gates open at one time and how long – Change is localized (not conducted) – Change may be depolarization or hyperpolarization • Usually limited to dendrites and cell body of neurons, and many sensory cells • Synapse - postsynaptic potential, Sens ...
... • Amount of voltage change (graded) dependent on # of gates open at one time and how long – Change is localized (not conducted) – Change may be depolarization or hyperpolarization • Usually limited to dendrites and cell body of neurons, and many sensory cells • Synapse - postsynaptic potential, Sens ...
Chapters 31 and 34 - Nervous Endocrine
... • Type of neuron that sends message from sense organ to spinal cord/brain – Sensory neuron ...
... • Type of neuron that sends message from sense organ to spinal cord/brain – Sensory neuron ...
File
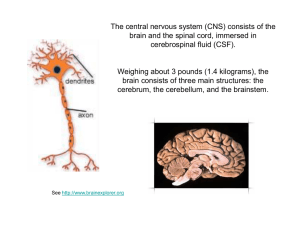
... The dendrites receive the information from sensory cells which then is passed down to the cell body where the information is evaluated and on to the axon. Once the information is at axon it travel downs length of axon in form of electrical signal known as action potential. Once the electrical impuls ...
... The dendrites receive the information from sensory cells which then is passed down to the cell body where the information is evaluated and on to the axon. Once the information is at axon it travel downs length of axon in form of electrical signal known as action potential. Once the electrical impuls ...
3 Types of Muscle Tissue SKELETAL MUSCLE CARDIAC MUSCLE
... Multinucleated due to being very active Cylindrical shape Voluntary control ...
... Multinucleated due to being very active Cylindrical shape Voluntary control ...
PNS
... legs spinal &stomach cord c. Receptive field Nociceptors are sensitized by various lemniscus to the thalamus (VP) of a single spinal segment is a dermatome information and projects to the changes in temperature as small as 0.01C. which nerves emerge (cervical: C1 C8, ii. Golgi tendon organs-distribu ...
... legs spinal &stomach cord c. Receptive field Nociceptors are sensitized by various lemniscus to the thalamus (VP) of a single spinal segment is a dermatome information and projects to the changes in temperature as small as 0.01C. which nerves emerge (cervical: C1 C8, ii. Golgi tendon organs-distribu ...