Chapter 8 THE ENERGY CONSUMING PROCESS OF RESPIRATION
... The direction H+ ion diffusion is indicated by the location of ATP synthase proteins (lollipops). Mictochondria and some bacteria use chemiosmosis to make ATP during cell respiration. Chloroplasts use chemiosmosis to make ATP as part of photosynthsis. ...
... The direction H+ ion diffusion is indicated by the location of ATP synthase proteins (lollipops). Mictochondria and some bacteria use chemiosmosis to make ATP during cell respiration. Chloroplasts use chemiosmosis to make ATP as part of photosynthsis. ...
Respiration: ATP - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... The process of respiration begins with the splitting of glucose in the cytoplasm (cytosol) of a cell. After many steps, the 6-carbon (hexose) glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, each with three carbon atoms. Energy from ATP is needed in the first two steps, called phosphorylation, b ...
... The process of respiration begins with the splitting of glucose in the cytoplasm (cytosol) of a cell. After many steps, the 6-carbon (hexose) glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, each with three carbon atoms. Energy from ATP is needed in the first two steps, called phosphorylation, b ...
Cellular Respiration - Kawameeh Middle School
... Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis • Notice that the cellular respiration equation is the breakdown of those molecules made through photosynthesis and that it also uses the waste products of photosynthesis. • Notice that photosynthesis uses those products made by cellular respiration. • This i ...
... Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis • Notice that the cellular respiration equation is the breakdown of those molecules made through photosynthesis and that it also uses the waste products of photosynthesis. • Notice that photosynthesis uses those products made by cellular respiration. • This i ...
Identification, Purification, and Molecular Cloning of
... because the cDNA sequence was not translated from the first ATG within this sequence. Translation of this cDNA from the first ATG revealed the presence of a putative plastid targeting sequence in this protein also. To determine whether the predicted chloroplast-targeting sequence in the spinach pGlc ...
... because the cDNA sequence was not translated from the first ATG within this sequence. Translation of this cDNA from the first ATG revealed the presence of a putative plastid targeting sequence in this protein also. To determine whether the predicted chloroplast-targeting sequence in the spinach pGlc ...
03-232 Biochemistry ... Name:________________________ or the back of the preceding page. In questions... Instructions:
... Choice B: Cholesterol keeps the membrane fluid, permitting conformational changes to occur in membrane enzymes and the diffusion of electron carriers, such as CoQ. Choice C: Both convert substrate to product. A soluble enzyme will typically cause a change in the chemical structure of the substrate. ...
... Choice B: Cholesterol keeps the membrane fluid, permitting conformational changes to occur in membrane enzymes and the diffusion of electron carriers, such as CoQ. Choice C: Both convert substrate to product. A soluble enzyme will typically cause a change in the chemical structure of the substrate. ...
Antigenic Properties of Mycoplasma Organisms and Membranes
... were analysed. In immunodiffusion tests they showed a serological specificity similar to the soluble cell proteins. This specificity was not found in lipids of M. laidlawii membranes extracted with chloroform methanol. In gel diffusion tests the hydrophobic protein fraction isolated from M. laidlawi ...
... were analysed. In immunodiffusion tests they showed a serological specificity similar to the soluble cell proteins. This specificity was not found in lipids of M. laidlawii membranes extracted with chloroform methanol. In gel diffusion tests the hydrophobic protein fraction isolated from M. laidlawi ...
"Dot and Slot Blotting of DNA". In: Current Protocols in Molecular
... into ice on removal from the incubator. Blotting, whether manual or with a manifold, takes time, with some samples being blotted more quickly than others, so differential renaturation is a possibility. The second denaturation step, when the membrane is placed on a filter paper soaked in alkali, is i ...
... into ice on removal from the incubator. Blotting, whether manual or with a manifold, takes time, with some samples being blotted more quickly than others, so differential renaturation is a possibility. The second denaturation step, when the membrane is placed on a filter paper soaked in alkali, is i ...
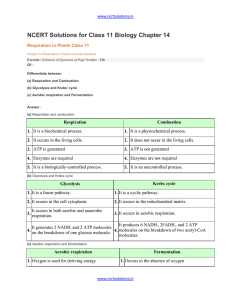
chapter_14_respiration_in_plants
... value is one for carbohydrates. However, it is always less than one for fats as fats consume more oxygen for respiration than carbohydrates. It can be illustrated through the example of tripalmitin fatty acid, which consumes 145 molecules of O2for respiration while 102 molecules of CO2are evolved. T ...
... value is one for carbohydrates. However, it is always less than one for fats as fats consume more oxygen for respiration than carbohydrates. It can be illustrated through the example of tripalmitin fatty acid, which consumes 145 molecules of O2for respiration while 102 molecules of CO2are evolved. T ...
Plastid degeneration in Tillandsia (Bromeliaceae) provides
... thus a MLB. However, it is not known how long these membranes might persist in such an autolytic vacuole. Plant macroautophagy tends to results in rather rapid breakdown of the sequestered material (van Doorn and Papini, 2013). If this is true, it would mean that plant ...
... thus a MLB. However, it is not known how long these membranes might persist in such an autolytic vacuole. Plant macroautophagy tends to results in rather rapid breakdown of the sequestered material (van Doorn and Papini, 2013). If this is true, it would mean that plant ...
10-3 Getting Energy to Make ATP
... d. Anaerobic Respiration i. Occurs when no oxygen is present ii. Not very efficient---only produces 2 ATP molecules from one glucose iii. There are different types of anaerobic respiration ...
... d. Anaerobic Respiration i. Occurs when no oxygen is present ii. Not very efficient---only produces 2 ATP molecules from one glucose iii. There are different types of anaerobic respiration ...
The Biochemical Machinery of Plastid Envelope
... AND PLASTID GENOMES Plastids rely mostly on the nucleus for their development, and the coordination between the expression of plastid and nuclear genes requires an exchange of information between the nucleus and the organelle. Envelope membranes at the border between plastids and the cytosol play a ...
... AND PLASTID GENOMES Plastids rely mostly on the nucleus for their development, and the coordination between the expression of plastid and nuclear genes requires an exchange of information between the nucleus and the organelle. Envelope membranes at the border between plastids and the cytosol play a ...
CHAPTER 6 - Richsingiser.com
... The β-Turn (aka β-bend, or tight turn) • Allows the peptide chain to reverse direction • Carbonyl C of one residue is H-bonded to the amide proton of a residue three residues away • Proline and glycine are prevalent in β-turns • There are two principal forms of β-turns ...
... The β-Turn (aka β-bend, or tight turn) • Allows the peptide chain to reverse direction • Carbonyl C of one residue is H-bonded to the amide proton of a residue three residues away • Proline and glycine are prevalent in β-turns • There are two principal forms of β-turns ...
cellular-respiration 1
... protein mobile carriers that transport electrons. b. The three protein complexes include NADH-Q reductase complex, the cytochrome reductase complex, and the cytochrome oxidase complex; the two protein mobile carriers are coenzyme Q and cytochrome c. c. Energy released from the flow of electrons down ...
... protein mobile carriers that transport electrons. b. The three protein complexes include NADH-Q reductase complex, the cytochrome reductase complex, and the cytochrome oxidase complex; the two protein mobile carriers are coenzyme Q and cytochrome c. c. Energy released from the flow of electrons down ...
Cellular Respiration
... *potential energy = stored kinetic energy = being used *can be transformed from one type to another – -battery - chemical to electrical -roll downhill - potential to kinetic -flip light switch –mechanical to electrical to light & heat *it is the ability to do work! ...
... *potential energy = stored kinetic energy = being used *can be transformed from one type to another – -battery - chemical to electrical -roll downhill - potential to kinetic -flip light switch –mechanical to electrical to light & heat *it is the ability to do work! ...
Towards an Analysis of the Rice Mitochondrial Proteome
... purification of the isolated compartment away from other cellular contaminants. We have adapted a twoPercoll gradient density separation technique to the isolation of these organelles from dark-grown rice shoots that yields mitochondria largely free of contamination by cytosol, peroxisomes, plastids ...
... purification of the isolated compartment away from other cellular contaminants. We have adapted a twoPercoll gradient density separation technique to the isolation of these organelles from dark-grown rice shoots that yields mitochondria largely free of contamination by cytosol, peroxisomes, plastids ...
Transport of primary metabolites across the plant vacuolar membrane
... accumulation of solutes, including sugars, in Arabidopsis leaves [55–57] and since most of the sugars in mesophyll cells accumulate in the vacuole [1,25], it is very likely that AtTMT proteins contribute to the molecular response of Arabidopsis upon osmotic stress. The observation that vacuoles isol ...
... accumulation of solutes, including sugars, in Arabidopsis leaves [55–57] and since most of the sugars in mesophyll cells accumulate in the vacuole [1,25], it is very likely that AtTMT proteins contribute to the molecular response of Arabidopsis upon osmotic stress. The observation that vacuoles isol ...
Ch8_CellularRespiration
... • 2 molecules of ATP are required for glycolysis, while 4 are produced, for a net gain of 2 ATPs. • Glycolysis supplies some energy, its product (pyruvate) can be broken down ...
... • 2 molecules of ATP are required for glycolysis, while 4 are produced, for a net gain of 2 ATPs. • Glycolysis supplies some energy, its product (pyruvate) can be broken down ...
Theoretical studies of Membrane Proteins
... Despite their importance it has not been possible to study their structure and organization in much detail because of the difficulty to obtain 3D structures. In this thesis theoretical studies of membrane protein sequences and structures have been carried out by analyzing existing experimental data. ...
... Despite their importance it has not been possible to study their structure and organization in much detail because of the difficulty to obtain 3D structures. In this thesis theoretical studies of membrane protein sequences and structures have been carried out by analyzing existing experimental data. ...
TCA Cycle
... • They diffuse across the membrane and pick up protons from one side and release then on the other side 2. Ionophores • Hydrophobic molecules that disspate osmotic gradients by inserting them selves into the membrane and form a channel ...
... • They diffuse across the membrane and pick up protons from one side and release then on the other side 2. Ionophores • Hydrophobic molecules that disspate osmotic gradients by inserting them selves into the membrane and form a channel ...
Plant and Soil
... about the structure and composition of the symbiotic interfaces is presented below. Two different types of symbiotic interfaces can be found, depending on whether the fungus grows interor intracellularly in the root system. Intercellular interfaces are created when the fungal hyphae grows within the ...
... about the structure and composition of the symbiotic interfaces is presented below. Two different types of symbiotic interfaces can be found, depending on whether the fungus grows interor intracellularly in the root system. Intercellular interfaces are created when the fungal hyphae grows within the ...
23. electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation
... member and transfer them to the following one, in a specific sequence. The electrons entering the electron-transport chain are energy-rich, but as they pass down the chain step-by-step to oxygen, they lose free energy. Much of this energy is conserved in the form of ATP in the inner mitochondrial me ...
... member and transfer them to the following one, in a specific sequence. The electrons entering the electron-transport chain are energy-rich, but as they pass down the chain step-by-step to oxygen, they lose free energy. Much of this energy is conserved in the form of ATP in the inner mitochondrial me ...
Cellular Process Test w/answers
... 4. In the presence of oxygen, cells can generate as many as 36 to 38 molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from the metabolism of one molecule of glucose. Which cellular process results in this amount of ATP production? (4B) a. Anaerobic cellular respiration b. Protein synthesis c. Aerobic cellu ...
... 4. In the presence of oxygen, cells can generate as many as 36 to 38 molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from the metabolism of one molecule of glucose. Which cellular process results in this amount of ATP production? (4B) a. Anaerobic cellular respiration b. Protein synthesis c. Aerobic cellu ...
UNIT 5 I. Energy and the Cell Module 5.1 Energy is the capacity to
... C. Proteins must first be digested to their constituent amino acids. The amino acids are then transformed into various compounds, which enter the middle of glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. Toxic parts of amino acids are stripped off and eliminated in urine (urea) or used to synthesize other comp ...
... C. Proteins must first be digested to their constituent amino acids. The amino acids are then transformed into various compounds, which enter the middle of glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. Toxic parts of amino acids are stripped off and eliminated in urine (urea) or used to synthesize other comp ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.