basic principles of isoelectric focusing in biomedical engineering
... electrical charge or the negative and positive charges are equal. Surfaces naturally charge to form a double layer. In the common case when the surface chargedetermining ions are H+/OH-, the net surface charge is affected by the pH of the liquid in which the solid is submerged. Again, the pI is the ...
... electrical charge or the negative and positive charges are equal. Surfaces naturally charge to form a double layer. In the common case when the surface chargedetermining ions are H+/OH-, the net surface charge is affected by the pH of the liquid in which the solid is submerged. Again, the pI is the ...
aerobic respiration
... Pyruvate not moved into mitochondria (stays in cytosol & is converted into waste products that can be transported out of cells) Waste product depends on type of cell e.g. ethanol in yeast e.g. lactate in skeletal muscles, bacteria ...
... Pyruvate not moved into mitochondria (stays in cytosol & is converted into waste products that can be transported out of cells) Waste product depends on type of cell e.g. ethanol in yeast e.g. lactate in skeletal muscles, bacteria ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... What is a coenzyme? (If you have forgotten, look back to a few pages in Chapter 8.) ...
... What is a coenzyme? (If you have forgotten, look back to a few pages in Chapter 8.) ...
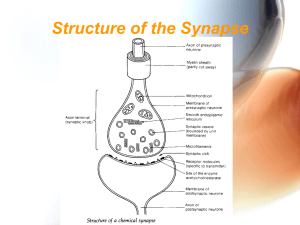
Structure of the Synapse
... threshold is reached then action potential is initated • Inhibitory ion channels - neuroreceptors are Cl- channels. When Cl- channels open, hyperpolarisation occurs, making action potential less likely • Non channel synapses - neuroreceptors are membrane-bound enzymes. When activated, they catalyse ...
... threshold is reached then action potential is initated • Inhibitory ion channels - neuroreceptors are Cl- channels. When Cl- channels open, hyperpolarisation occurs, making action potential less likely • Non channel synapses - neuroreceptors are membrane-bound enzymes. When activated, they catalyse ...
Learning Objectives, test #2 BIO105 Mark S. Wilson Topic: Cell
... - trace electron flow from water through photosystems 1 and 2 - compare cyclic and noncyclic electron flow and explain the relationship between these components of the light reaction - compare and contrast mitochondrial and chloroplast structures, particularly with reference to the compartments tha ...
... - trace electron flow from water through photosystems 1 and 2 - compare cyclic and noncyclic electron flow and explain the relationship between these components of the light reaction - compare and contrast mitochondrial and chloroplast structures, particularly with reference to the compartments tha ...
Respiration - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
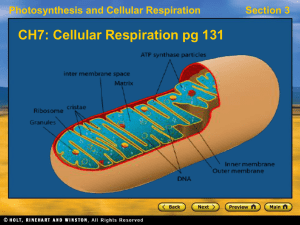
... • Process of extracting to energy from NADH and FADH2 to form ATP. • Function: Convert NADH and FADH2 into ATP. • Location: Mitochondria cristae. ...
... • Process of extracting to energy from NADH and FADH2 to form ATP. • Function: Convert NADH and FADH2 into ATP. • Location: Mitochondria cristae. ...
Cellular Respiration
... – 2 molecules NADH are created • Important because NADH are Hydrogen ion/proton and e- carriers ...
... – 2 molecules NADH are created • Important because NADH are Hydrogen ion/proton and e- carriers ...
Fatty acid
... 1. Lipids: These are water insoluble biomolecules that readily dissolve in organic solvents like chloroform and have a wide range of biological functions. They are important components of membranes, serve as fuel reserves and signalling molecules. Three important membrane lipids include phospholipid ...
... 1. Lipids: These are water insoluble biomolecules that readily dissolve in organic solvents like chloroform and have a wide range of biological functions. They are important components of membranes, serve as fuel reserves and signalling molecules. Three important membrane lipids include phospholipid ...
Next Question
... A. Incorrect – chloroplasts make ATP to use during photosynthesis using light energy B. Correct – chloroplasts use light energy to create chemical energy in the form of glucose. C. Incorrect – heat energy is not a part of photosynthesis D. Incorrect – the energy coming in to photosynthesis is light ...
... A. Incorrect – chloroplasts make ATP to use during photosynthesis using light energy B. Correct – chloroplasts use light energy to create chemical energy in the form of glucose. C. Incorrect – heat energy is not a part of photosynthesis D. Incorrect – the energy coming in to photosynthesis is light ...
Mycobacterium tuberculosis evades macrophage defenses by
... • comprise Prostaglandins and related compounds • Mostly produced from arachidonic acid (a 20-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid) • considered "local hormones" • effects on target cells close to their site of formation • Are rapidly degraded, so they are not transported to distal sites within the bod ...
... • comprise Prostaglandins and related compounds • Mostly produced from arachidonic acid (a 20-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid) • considered "local hormones" • effects on target cells close to their site of formation • Are rapidly degraded, so they are not transported to distal sites within the bod ...
Cell Location
... If oxygen is not available, some types of cells have a back-up mechanism for glucose metabolism called _fermentation___. If a cell cannot switch to fermentation, it cannot survive without oxygen. A. General Description In fermentation, the pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis does not enter the _ ...
... If oxygen is not available, some types of cells have a back-up mechanism for glucose metabolism called _fermentation___. If a cell cannot switch to fermentation, it cannot survive without oxygen. A. General Description In fermentation, the pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis does not enter the _ ...
1 All cells can harvest energy from organic molecules. To do this
... theoretical yield of ATP from the breakdown of one molecule of glucose by aerobic respiration is 38. In eukaryotes, this is reduced to 36 ATP because NADH generated by glycolysis in the cytoplasm has to be actively transported into the mitochondria. This costs the cell 1 ATP per NADH transported. ...
... theoretical yield of ATP from the breakdown of one molecule of glucose by aerobic respiration is 38. In eukaryotes, this is reduced to 36 ATP because NADH generated by glycolysis in the cytoplasm has to be actively transported into the mitochondria. This costs the cell 1 ATP per NADH transported. ...
Chapter 8
... When oxygen is unavailable, cells cannot follow glycolysis with the aerobic respiration (Krebs cycle and electron transport). The anaerobic process that follows glycolysis is anaerobic respiration, or ...
... When oxygen is unavailable, cells cannot follow glycolysis with the aerobic respiration (Krebs cycle and electron transport). The anaerobic process that follows glycolysis is anaerobic respiration, or ...
Cell Membrane Properties
... mosaic of protein molecules bobbing in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids. These proteins determine most of the membrane’s specific functions. ...
... mosaic of protein molecules bobbing in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids. These proteins determine most of the membrane’s specific functions. ...
The Citric Acid Cycle - Rubin Risto Gulaboski
... Kreb’s Cycle Summary • Remember, we get 3NADH from TCA along with the one we got from the Pyruvate DH reaction and then an FADH2 (a lot like NADH, but less reducing power) and an ATP and this is just from ...
... Kreb’s Cycle Summary • Remember, we get 3NADH from TCA along with the one we got from the Pyruvate DH reaction and then an FADH2 (a lot like NADH, but less reducing power) and an ATP and this is just from ...
Adv. Bio. Ch 9 Glyco and Resp
... How does this work? 1.) carboxyl group on pyruvate is removed & released as ...
... How does this work? 1.) carboxyl group on pyruvate is removed & released as ...
endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipid metabolism
... Ino2p/Ino4p pathway by binding directly to Ino2p and recruiting a transcriptional repressor (Sin3p) to the promoter. Opi1p activity is, in turn, regulated by ER protein Scs2p and increased ...
... Ino2p/Ino4p pathway by binding directly to Ino2p and recruiting a transcriptional repressor (Sin3p) to the promoter. Opi1p activity is, in turn, regulated by ER protein Scs2p and increased ...
Unit F214/01 - Communication, homeostasis and energy
... The liver is an organ that is metabolically very active, carrying out over 500 different functions. Some of its important functions include converting chemicals including toxins, into other compounds. Fig. 2.1 outlines some of the reaction pathways that take place in the liver cells. ...
... The liver is an organ that is metabolically very active, carrying out over 500 different functions. Some of its important functions include converting chemicals including toxins, into other compounds. Fig. 2.1 outlines some of the reaction pathways that take place in the liver cells. ...
Photosynthesis Research
... phase or bright field microscopy to be in the living condition, as evidenced by vigorous cytoplasmic streaming. These observations confirmed the widespread occurrence of strings of grana in all the species examined. A selection of these CLSM images for six different plant species is shown in Figure 4. ...
... phase or bright field microscopy to be in the living condition, as evidenced by vigorous cytoplasmic streaming. These observations confirmed the widespread occurrence of strings of grana in all the species examined. A selection of these CLSM images for six different plant species is shown in Figure 4. ...
d21af95090a6323
... • It is a light activated proton pump • Each contains a light absorbing chromophore called retinal (vitamin A) • Light causes a change in conformation of the protein and H+ goes from inside to outside of the cell • In bright light each molecule pumps several hundred protons per second • The H+ gradi ...
... • It is a light activated proton pump • Each contains a light absorbing chromophore called retinal (vitamin A) • Light causes a change in conformation of the protein and H+ goes from inside to outside of the cell • In bright light each molecule pumps several hundred protons per second • The H+ gradi ...
Chloroplasts in living cells and the string-of
... phase or bright field microscopy to be in the living condition, as evidenced by vigorous cytoplasmic streaming. These observations confirmed the widespread occurrence of strings of grana in all the species examined. A selection of these CLSM images for six different plant species is shown in Figure ...
... phase or bright field microscopy to be in the living condition, as evidenced by vigorous cytoplasmic streaming. These observations confirmed the widespread occurrence of strings of grana in all the species examined. A selection of these CLSM images for six different plant species is shown in Figure ...
Sec14p-like proteins regulate phosphoinositide homoeostasis and
... Sec9p t-SNARE (target membrane soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein attachment protein receptor) function Stt4p and Mss4p reside in the yeast plasma membrane [22]. This raises the possibility that SFH proteins modulate exocytic and/or endocytic events at the plasma membrane. To investig ...
... Sec9p t-SNARE (target membrane soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein attachment protein receptor) function Stt4p and Mss4p reside in the yeast plasma membrane [22]. This raises the possibility that SFH proteins modulate exocytic and/or endocytic events at the plasma membrane. To investig ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.