Lipid II: A central component in bacterial cell wall synthesis and a
... type, which strikingly resembles the bactoprenol chain. Thus in both peptidoglycan synthesis and N-glycosylation the precursors are minor-polyprenol-anchored (pyro)phosphate-coupled membrane components. These examples suggest that building a carbohydrate containing biopolymer from a membrane is best ...
... type, which strikingly resembles the bactoprenol chain. Thus in both peptidoglycan synthesis and N-glycosylation the precursors are minor-polyprenol-anchored (pyro)phosphate-coupled membrane components. These examples suggest that building a carbohydrate containing biopolymer from a membrane is best ...
The Lamin B Receptor of the Nuclear Envelope Inner Membrane: A
... integral membrane proteins that may be involved in the anchorage of these structures. In support of this notion, several integral membrane proteins associated with these structures have been identified and localized to specific nuclear envelope membrane domains. An integral membrane glycoprotein (gp ...
... integral membrane proteins that may be involved in the anchorage of these structures. In support of this notion, several integral membrane proteins associated with these structures have been identified and localized to specific nuclear envelope membrane domains. An integral membrane glycoprotein (gp ...
University of Groningen Sugar transport in
... over the membrane in symport with protons or sodium ions, thus utilizing the electrochemical gradient of protons or sodium ions; (ii) phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)-dependent phosphotransferase systems (PTS), in which sugar transport is coupled to phosphorylation of the substrate at the expense of PEP; ( ...
... over the membrane in symport with protons or sodium ions, thus utilizing the electrochemical gradient of protons or sodium ions; (ii) phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)-dependent phosphotransferase systems (PTS), in which sugar transport is coupled to phosphorylation of the substrate at the expense of PEP; ( ...
Chapter 7A- Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis - TJ
... Glycolysis is the first of 3 steps in cellular respiration. Review glycolysis by matching each phrase on the left with a term on the right. Some terms are used twice, some questions may have more than 1 answer. 1. Compound formed as glucose is changed to pyruvic acid. ...
... Glycolysis is the first of 3 steps in cellular respiration. Review glycolysis by matching each phrase on the left with a term on the right. Some terms are used twice, some questions may have more than 1 answer. 1. Compound formed as glucose is changed to pyruvic acid. ...
Soft Palate
... vertical groove seen in the midline on the outer surface of the upper lip. Median folds of mucous membrane-the labial frenulaconnect the inner surface of the lips to the gums. ...
... vertical groove seen in the midline on the outer surface of the upper lip. Median folds of mucous membrane-the labial frenulaconnect the inner surface of the lips to the gums. ...
Glycolysis Quiz
... 7. Enzymes involved in the oxidation reduction of a substance can not operate without NAD+. What is NAD+ known as? (a) co-enzyme (b) co-factor (c) amino acid (d) protein ...
... 7. Enzymes involved in the oxidation reduction of a substance can not operate without NAD+. What is NAD+ known as? (a) co-enzyme (b) co-factor (c) amino acid (d) protein ...
Document
... inorganic molecules as well as organic molecules can serve as electron donors for electron transport and ATP synthesis. Microbial catabolism is unique in the diversity of nutrients and mechanisms employed to make energy available. 6. In photosynthesis trapped light energy boosts electrons to more ne ...
... inorganic molecules as well as organic molecules can serve as electron donors for electron transport and ATP synthesis. Microbial catabolism is unique in the diversity of nutrients and mechanisms employed to make energy available. 6. In photosynthesis trapped light energy boosts electrons to more ne ...
Supplement
... Figure S4. EELS signal to monitor material composition at nanopore. The EELS signal can be used not only to monitor the progress of the nanopore drilling as Figure 1f of the main manuscript shows but also to characterize the chemistry of the membrane surrounding the nanopore. The EELS spectrum shows ...
... Figure S4. EELS signal to monitor material composition at nanopore. The EELS signal can be used not only to monitor the progress of the nanopore drilling as Figure 1f of the main manuscript shows but also to characterize the chemistry of the membrane surrounding the nanopore. The EELS spectrum shows ...
Inactivation of Photosystems I and II in Response
... under high-salt conditions of compatible solutes such as Suc, trehalose, Gly betaine, and glucosylglycerol has often been found in association with tolerance to salt stress in cyanobacteria (Reed and Stewart, 1988; Joset et al., 1996; Hagemann and Erdmann, 1997; Hayashi and Murata, 1998; Papageorgio ...
... under high-salt conditions of compatible solutes such as Suc, trehalose, Gly betaine, and glucosylglycerol has often been found in association with tolerance to salt stress in cyanobacteria (Reed and Stewart, 1988; Joset et al., 1996; Hagemann and Erdmann, 1997; Hayashi and Murata, 1998; Papageorgio ...
Initial characterization of ayrRABC
... of transcriptional regulators (16), and Cro regulates its own transcription by binding such a palindrome (17, 18). To determine if AyrR binds its upstream palindrome, a gel shift assay was employed using various DNA fragments (Fig. 1D). The data clearly demonstrate that AyrR selectively binds the pa ...
... of transcriptional regulators (16), and Cro regulates its own transcription by binding such a palindrome (17, 18). To determine if AyrR binds its upstream palindrome, a gel shift assay was employed using various DNA fragments (Fig. 1D). The data clearly demonstrate that AyrR selectively binds the pa ...
Photosynthesis: CO assimilation and sugar metabolism
... • Stomata close during the day, and CO2 is released from organic acids and used in the Calvin cycle • Thus, in C4, CO2 uptake is spatially separated form RUBISCO. In CAM plants, it is temporally ...
... • Stomata close during the day, and CO2 is released from organic acids and used in the Calvin cycle • Thus, in C4, CO2 uptake is spatially separated form RUBISCO. In CAM plants, it is temporally ...
Structure and function of basement membranes
... changed dramatically in recent years is the definition of a basement membrane. The definition used to be very strict and was based on the appearance of the basement membrane in the elec~ tron microscope as a distinct structure with a lamina lucida and a lamina den sa. However, with the realization t ...
... changed dramatically in recent years is the definition of a basement membrane. The definition used to be very strict and was based on the appearance of the basement membrane in the elec~ tron microscope as a distinct structure with a lamina lucida and a lamina den sa. However, with the realization t ...
Full Text - BioTechniques
... tion, the syringes had to be washed four times. This process takes a total of 11 min. To produce a similar membrane (with 384 spots) using a Hydra-PP equipped with 384 syringes, the same procedure takes approximately 3 min because only one wash step is required. To produce higher-density membranes o ...
... tion, the syringes had to be washed four times. This process takes a total of 11 min. To produce a similar membrane (with 384 spots) using a Hydra-PP equipped with 384 syringes, the same procedure takes approximately 3 min because only one wash step is required. To produce higher-density membranes o ...
The Structure and Hydrolysis of ATP
... chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phos ...
... chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phos ...
Slide 1
... To used the energy banked in NADH and FADH2 The cell must shuttle their electrons to the Electron Transport Chain Where energy from the oxidation of organic fuel will power the oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP ...
... To used the energy banked in NADH and FADH2 The cell must shuttle their electrons to the Electron Transport Chain Where energy from the oxidation of organic fuel will power the oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... Oxidation of 2 isocitrate (2NADH) 6 ATP Oxidation of 2 -ketoglutarate (2NADH) 6 ATP 2 Direct substrate phosphorylations (2GTP) 2 ATP Oxidation of 2 succinate (2FADH2) 4 ATP Oxidation of 2 malate (2NADH) 6 ATP 24 ATP Summary: 2Acetyl CoA + 24 ADP + 24 Pi 4CO2 + 2H2O + 24 ATP + 2 CoASH ...
... Oxidation of 2 isocitrate (2NADH) 6 ATP Oxidation of 2 -ketoglutarate (2NADH) 6 ATP 2 Direct substrate phosphorylations (2GTP) 2 ATP Oxidation of 2 succinate (2FADH2) 4 ATP Oxidation of 2 malate (2NADH) 6 ATP 24 ATP Summary: 2Acetyl CoA + 24 ADP + 24 Pi 4CO2 + 2H2O + 24 ATP + 2 CoASH ...
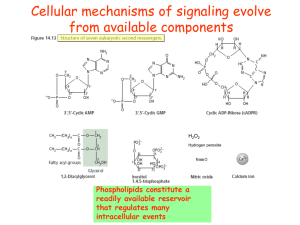
Phospholipid signaling
... PLA2 generates lyso-phospholipids (LPL) and FFAs that stimulate the plasma membrane H+ATPase, and free fatty acids can be metabolised via octadecanoid pathway to JA. PLC hydrolyses PIP2 into IP3 and DAG. IP3 diffuses into the cytosol, where it could release Ca2+ from intracellular stores, or is meta ...
... PLA2 generates lyso-phospholipids (LPL) and FFAs that stimulate the plasma membrane H+ATPase, and free fatty acids can be metabolised via octadecanoid pathway to JA. PLC hydrolyses PIP2 into IP3 and DAG. IP3 diffuses into the cytosol, where it could release Ca2+ from intracellular stores, or is meta ...
Document
... ALEK and phloem loading from the hollow petioles of adult Ricinus leaves (M BAKER, 1977). In our own laboratory l!TovaCmY and ULLRICH-EBERIUS found correlations between membrane potential and active glucose transport in fronds of the angiosperm water plant Lemna gibba (fig. 5). We have also -sucrose ...
... ALEK and phloem loading from the hollow petioles of adult Ricinus leaves (M BAKER, 1977). In our own laboratory l!TovaCmY and ULLRICH-EBERIUS found correlations between membrane potential and active glucose transport in fronds of the angiosperm water plant Lemna gibba (fig. 5). We have also -sucrose ...
Chapter 12 (part 1) - University of Nevada, Reno
... • Only step in TCA cycle that involves the formation of a C-C bond ...
... • Only step in TCA cycle that involves the formation of a C-C bond ...
MOLECULAR BASIS FOR MEMBRANE PHOSPHOLIPID
... Their primary function is to define the permeability barrier of cells and organelles by forming a phospholipid bilayer. This bilayer serves as the matrix and support for a vast array of proteins involved in important functions of the cell such as energy transduction, signal transduction, solute tran ...
... Their primary function is to define the permeability barrier of cells and organelles by forming a phospholipid bilayer. This bilayer serves as the matrix and support for a vast array of proteins involved in important functions of the cell such as energy transduction, signal transduction, solute tran ...
Chapter 4 Microbial Metabolism
... Anaerobic respiration: energy-yielding process in which terminal electron acceptor is oxidized inorganic compound other than oxygen •Major electron acceptors = Nitrate, sulfate, CO2, Iron •Anaerobic respiration produces less ATP •Anaerobic respiration is more efficient than fermentation •Uses ETC & ...
... Anaerobic respiration: energy-yielding process in which terminal electron acceptor is oxidized inorganic compound other than oxygen •Major electron acceptors = Nitrate, sulfate, CO2, Iron •Anaerobic respiration produces less ATP •Anaerobic respiration is more efficient than fermentation •Uses ETC & ...
Fatty Acid Catabolism
... B) Fatty acyl CoA. C) Acetoacetyl CoA. D) Lysophospholipid CoA. 2. There are four steps in the β‐oxidation pathway. Some reaction types are listed below. Give the proper reaction types in the order that they occur in the β‐oxidation pathway. 1. Condensation 2. Oxidation 3. Reduction 4. Thiolysi ...
... B) Fatty acyl CoA. C) Acetoacetyl CoA. D) Lysophospholipid CoA. 2. There are four steps in the β‐oxidation pathway. Some reaction types are listed below. Give the proper reaction types in the order that they occur in the β‐oxidation pathway. 1. Condensation 2. Oxidation 3. Reduction 4. Thiolysi ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.