Active and Passive Transport
... Sodium-Potassium Pump- a membrane protein that plays a role in transporting 3 Na+ outside and 2 K+ inside as in axon, while utilizing ATP. https://sp.yimg.com/xj/th?id=OIP.Mf69dc0c6bdeb6cbb5fb11e057650443co0&pid=15.1 &P=0&w=288&h=163 Proton Pump- during photosynthesis, a proton gradient is establish ...
... Sodium-Potassium Pump- a membrane protein that plays a role in transporting 3 Na+ outside and 2 K+ inside as in axon, while utilizing ATP. https://sp.yimg.com/xj/th?id=OIP.Mf69dc0c6bdeb6cbb5fb11e057650443co0&pid=15.1 &P=0&w=288&h=163 Proton Pump- during photosynthesis, a proton gradient is establish ...
Quiz5ch5new.doc
... 10. Two types of connections between cells called "gap junctions" and "plasmodesmata" are specialized to __________. a. prevent the movement of molecules between cells that are tightly joined along ribbons of cell membrane b. tightly hold one cell against another at focal points, almost like a spot ...
... 10. Two types of connections between cells called "gap junctions" and "plasmodesmata" are specialized to __________. a. prevent the movement of molecules between cells that are tightly joined along ribbons of cell membrane b. tightly hold one cell against another at focal points, almost like a spot ...
Photosynthesis
... 2. The stomata is bounded by two half moon shaped guard cells. 3. Found on the bottom surface of the leaf because the guard cells are partially light activated, plants under direct light would constantly have their stomata open and would thus lose much water and the plant would die. 4. Guard cells E ...
... 2. The stomata is bounded by two half moon shaped guard cells. 3. Found on the bottom surface of the leaf because the guard cells are partially light activated, plants under direct light would constantly have their stomata open and would thus lose much water and the plant would die. 4. Guard cells E ...
Document
... acetyl-CoA(C2H3O-CoA) + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H2O CoA-SH + 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH2 + GTP ...
... acetyl-CoA(C2H3O-CoA) + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H2O CoA-SH + 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH2 + GTP ...
TYPES OF PASSIVE TRANSPORT DIFFUSION
... Main electrogenic pump in PLANTS ATP provides energy to pump H+ ions across a membrane Stored H+ = potential energy to do work EX: COTRANSPORT (see below) ATP PRODUCTION during cellular respiration/photosynthesis ...
... Main electrogenic pump in PLANTS ATP provides energy to pump H+ ions across a membrane Stored H+ = potential energy to do work EX: COTRANSPORT (see below) ATP PRODUCTION during cellular respiration/photosynthesis ...
Cell Biology - rci.rutgers.edu
... A. Cytoplasm—cellular material inside cell 1. Most cellular activities occur here 2. Comprised of: a. Cytosol—fluid in which other components are suspended b. Organelles (see below) c. Inclusions—non-functioning chemicals substances that may be unique to a given cell type B. Ribosomes—site of protei ...
... A. Cytoplasm—cellular material inside cell 1. Most cellular activities occur here 2. Comprised of: a. Cytosol—fluid in which other components are suspended b. Organelles (see below) c. Inclusions—non-functioning chemicals substances that may be unique to a given cell type B. Ribosomes—site of protei ...
Bacterial Cell Walls Contain Peptidoglycans
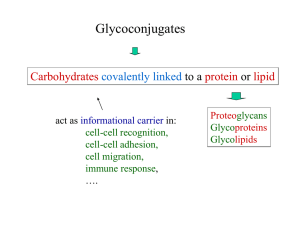
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
Friday`s presentation.
... protons) across the inner membrane, which is relatively impermeable to H+. b. The H+ ions tend to move down their concentration gradient toward the matrix of the mitochondrion. Movement through the ATP synthase is used to generate the ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. ...
... protons) across the inner membrane, which is relatively impermeable to H+. b. The H+ ions tend to move down their concentration gradient toward the matrix of the mitochondrion. Movement through the ATP synthase is used to generate the ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. ...
Slide 1
... protons) across the inner membrane, which is relatively impermeable to H+. b. The H+ ions tend to move down their concentration gradient toward the matrix of the mitochondrion. Movement through the ATP synthase is used to generate the ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. ...
... protons) across the inner membrane, which is relatively impermeable to H+. b. The H+ ions tend to move down their concentration gradient toward the matrix of the mitochondrion. Movement through the ATP synthase is used to generate the ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. ...
Cell Membrane
... lipids cannot pass through • Most water molecules, and ions such as H+, NA+, K+, and Ca+ cannot pass through ...
... lipids cannot pass through • Most water molecules, and ions such as H+, NA+, K+, and Ca+ cannot pass through ...
Chapter 5 - Ellis Benjamin
... • 10 steps all in the cytoplasm • First 5 steps “activate” glucose – invest 2 ATP to get the process going • Last 5 steps produce 4 ATP • ATP produced through phosphorylation – donor molecule transfers P to ADP • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Net gain of 2 ATPs • Results in 2 pyruvate and 2 ...
... • 10 steps all in the cytoplasm • First 5 steps “activate” glucose – invest 2 ATP to get the process going • Last 5 steps produce 4 ATP • ATP produced through phosphorylation – donor molecule transfers P to ADP • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Net gain of 2 ATPs • Results in 2 pyruvate and 2 ...
general biology syllabus
... 2) Energy (ATP, high-energy electrons) C) Coupled channels: active transport followed by facilitated diffusion 1) Proton pump (proton = H+) a) In photosynthesis and cellular respiration, high-energy e– power first transport protein in active transport of H+ through membrane b) As H+ passes through s ...
... 2) Energy (ATP, high-energy electrons) C) Coupled channels: active transport followed by facilitated diffusion 1) Proton pump (proton = H+) a) In photosynthesis and cellular respiration, high-energy e– power first transport protein in active transport of H+ through membrane b) As H+ passes through s ...
Mitochondria: Energy Conversion
... can be converted to chemical energy in ATP 3. To realize how the structural organizations of mitochondria have allowed the above electrochemical reactions to be carried out effectively ...
... can be converted to chemical energy in ATP 3. To realize how the structural organizations of mitochondria have allowed the above electrochemical reactions to be carried out effectively ...
Biology Study Guide
... A membrane is selectively permeable if it lets only some materials pass through. Shrinking of a human red blood cell would occur if the cell were in a hypertonic solution. Ion channels aid in the movement of ions across a cell membrane. The sodium-potassium pump transports NA+ out of the cell and K+ ...
... A membrane is selectively permeable if it lets only some materials pass through. Shrinking of a human red blood cell would occur if the cell were in a hypertonic solution. Ion channels aid in the movement of ions across a cell membrane. The sodium-potassium pump transports NA+ out of the cell and K+ ...
Biology-1 Sample Questions for Exam Two Facilitated diffusion
... d. is embedded in the outer membrane of the mitochondrion. e. helps transport H+ against the concentration gradient. ...
... d. is embedded in the outer membrane of the mitochondrion. e. helps transport H+ against the concentration gradient. ...
Name
... 11) Which molecule is least able to cross a plasma membrane by simple diffusion due to its sphere of hydration? a) Water b) Bicarbonate c) Carbon dioxide d) Triglyceride 12) There are four types of transmembrane ATP-ase, which one is most important for moving very large molecules across the membrane ...
... 11) Which molecule is least able to cross a plasma membrane by simple diffusion due to its sphere of hydration? a) Water b) Bicarbonate c) Carbon dioxide d) Triglyceride 12) There are four types of transmembrane ATP-ase, which one is most important for moving very large molecules across the membrane ...
Chapter 10: Photosynthesis
... B. Internal membranes organized into flattened sacs called C. Numerous thylakoids stacked in arrangements called D. Photosynthetic pigments bound to membranes in thylakoids E. Architecture of the Chloroplast 1. Membrane is impermeable to most 2. Proton transit occurs through transmembrane channels 3 ...
... B. Internal membranes organized into flattened sacs called C. Numerous thylakoids stacked in arrangements called D. Photosynthetic pigments bound to membranes in thylakoids E. Architecture of the Chloroplast 1. Membrane is impermeable to most 2. Proton transit occurs through transmembrane channels 3 ...
Cellular Respiration
... One gram of the sugar glucose (C6H12O6) when burned in the presence of oxygen, releases 3,811 calories of heat energy. ...
... One gram of the sugar glucose (C6H12O6) when burned in the presence of oxygen, releases 3,811 calories of heat energy. ...
Biology-1 Sample Questions for Exam Two Facilitated diffusion
... d. is embedded in the outer membrane of the mitochondrion. e. helps transport H+ against the concentration gradient. ...
... d. is embedded in the outer membrane of the mitochondrion. e. helps transport H+ against the concentration gradient. ...
Chapter 4b
... • Functions for membranes • Selective permeability allows passage of some molecules • Movement through the membrane • Active - requires energy ...
... • Functions for membranes • Selective permeability allows passage of some molecules • Movement through the membrane • Active - requires energy ...
Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of cellulose
... anchors organelles and serves as a “track” for organelles to move on. ...
... anchors organelles and serves as a “track” for organelles to move on. ...
Learning Guide: Origins of Life
... Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins o Describe why the cell membrane exhibits selective permeability o Explain why a phospholipid is considered amphipathic (use a sketch in your answer). o Describe the fluidity of cell membranes. o Using the components of the cell membrane, ...
... Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins o Describe why the cell membrane exhibits selective permeability o Explain why a phospholipid is considered amphipathic (use a sketch in your answer). o Describe the fluidity of cell membranes. o Using the components of the cell membrane, ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.