Name
... and can even burst. 16. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmotic pressure? ___________ 17. What happens to a plant when plasmolysis occurs? ...
... and can even burst. 16. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmotic pressure? ___________ 17. What happens to a plant when plasmolysis occurs? ...
Updated Power Point
... Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed. Also known as the law of “Conservation of Energy” ...
... Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed. Also known as the law of “Conservation of Energy” ...
Chapter Outline
... In a hypertonic solution there is a higher percentage of solute outside than inside the cell, which can cause the cells to shrink or shrivel. Transport by Carrier Proteins Carrier proteins are specific; each can combine only with a certain type of molecule or ion, which is then transported through ...
... In a hypertonic solution there is a higher percentage of solute outside than inside the cell, which can cause the cells to shrink or shrivel. Transport by Carrier Proteins Carrier proteins are specific; each can combine only with a certain type of molecule or ion, which is then transported through ...
Solutions to 7.014 Quiz I
... Cyclic photophosphorylation produces glucose from CO2 but uses the redox reaction H2S Æ S as a source of electrons for the production of NADPH, Thus O2 is not released as a waste product. ii) Cyclic photophosphorylation converts CO2 into glucose. Briefly describe how these organisms use ATP synthase ...
... Cyclic photophosphorylation produces glucose from CO2 but uses the redox reaction H2S Æ S as a source of electrons for the production of NADPH, Thus O2 is not released as a waste product. ii) Cyclic photophosphorylation converts CO2 into glucose. Briefly describe how these organisms use ATP synthase ...
Bacterial Cell Structure (continued)
... surfaces. •Rotate like propellers. •Different from eukaryotic flagella. Arrangements on cells: polar, Lophotrichous, amphitrichous, peritrichous. ...
... surfaces. •Rotate like propellers. •Different from eukaryotic flagella. Arrangements on cells: polar, Lophotrichous, amphitrichous, peritrichous. ...
Organelles 3
... store pigments for fruits & flowers chloroplasts store chlorophyll & function in photosynthesis in leaves, other green structures of plants & in eukaryotic algae ...
... store pigments for fruits & flowers chloroplasts store chlorophyll & function in photosynthesis in leaves, other green structures of plants & in eukaryotic algae ...
Summary of Endomembrane
... 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures (organelles) are found in all eukaryotic cells,such as plasma membrane, the nucleus, peroxisome,the endoplasmic reticulum, t ...
... 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures (organelles) are found in all eukaryotic cells,such as plasma membrane, the nucleus, peroxisome,the endoplasmic reticulum, t ...
Cell Membrane PPT - Gulfport School District
... All biological membranes contain proteins; the ratio of proteins to phospholipids varies. Not all amino acid R groups are the same. Peripheral membrane proteins lack hydrophobic groups and are not embedded in the bilayer. Integral membrane proteins are at least partly embedded in the phospholipid b ...
... All biological membranes contain proteins; the ratio of proteins to phospholipids varies. Not all amino acid R groups are the same. Peripheral membrane proteins lack hydrophobic groups and are not embedded in the bilayer. Integral membrane proteins are at least partly embedded in the phospholipid b ...
Regulation of Photochemical Energy Transfer Accompanied
... membranes in higher plants are mainly composed of two regions called appressed grana stacks and non-appressed stroma lamellae. Thylakoid membranes in L25 seedlings formed well-distinguished appressed grana stacks and stroma lamella (Figure 1c). However, many grana clearly unstacked after L40 treatme ...
... membranes in higher plants are mainly composed of two regions called appressed grana stacks and non-appressed stroma lamellae. Thylakoid membranes in L25 seedlings formed well-distinguished appressed grana stacks and stroma lamella (Figure 1c). However, many grana clearly unstacked after L40 treatme ...
Virtual Cell Worksheet
... has a ____________________ membrane. Cut the outer membrane and move to next page. The white folded structure is the _________________________. The inner membrane is where most _______________ respiration occurs. Cut the inner membrane and move to the next page. The inner membrane is __________ with ...
... has a ____________________ membrane. Cut the outer membrane and move to next page. The white folded structure is the _________________________. The inner membrane is where most _______________ respiration occurs. Cut the inner membrane and move to the next page. The inner membrane is __________ with ...
Homeostasis and Cell Transport
... to another and some proteins are embedded only half-way Proteins are utilized for both PASSIVE AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT Carbohydrate chains are located on the outer surface of the membrane. If they are attached to phospholipids they are known as GLYCOLIPIDS. If they are attached to proteins they are ...
... to another and some proteins are embedded only half-way Proteins are utilized for both PASSIVE AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT Carbohydrate chains are located on the outer surface of the membrane. If they are attached to phospholipids they are known as GLYCOLIPIDS. If they are attached to proteins they are ...
Homeostasis and Cell Transport
... to another and some proteins are embedded only half-way Proteins are utilized for both PASSIVE AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT Carbohydrate chains are located on the outer surface of the membrane. If they are attached to phospholipids they are known as GLYCOLIPIDS. If they are attached to proteins they are ...
... to another and some proteins are embedded only half-way Proteins are utilized for both PASSIVE AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT Carbohydrate chains are located on the outer surface of the membrane. If they are attached to phospholipids they are known as GLYCOLIPIDS. If they are attached to proteins they are ...
photosynthesis - Northwest ISD Moodle
... using sun’s energy to make ATP using CO2 & water to make sugar in chloroplasts (leaf) allows plants to grow makes a waste product ...
... using sun’s energy to make ATP using CO2 & water to make sugar in chloroplasts (leaf) allows plants to grow makes a waste product ...
Biophysical methods New approaches to study macromolecular
... advances are required to obtain a molecular understanding of these important biological processes. Cryo-electron microscopy provides another way of studying macromolecular assemblies, including assemblies that are associated with biological membranes. Tao and Zhang (pp 616–622) review techniques tha ...
... advances are required to obtain a molecular understanding of these important biological processes. Cryo-electron microscopy provides another way of studying macromolecular assemblies, including assemblies that are associated with biological membranes. Tao and Zhang (pp 616–622) review techniques tha ...
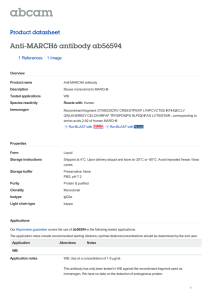
Anti-MARCH6 antibody ab56594 Product datasheet 1 References 1 Image
... The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
... The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
Co-ordinated Synthesis of Membrane Phospholipids with the
... The brain is an organ that, unlike the liver, does not secrete phospholipids. Consequently phospholipid synthesis at the termination of growth is required only for turnover and replacement of the cerebral membranes. Synthesis of the membrane phospholipids de novo largely occurs in the endoplasmic re ...
... The brain is an organ that, unlike the liver, does not secrete phospholipids. Consequently phospholipid synthesis at the termination of growth is required only for turnover and replacement of the cerebral membranes. Synthesis of the membrane phospholipids de novo largely occurs in the endoplasmic re ...
1.4 Membrane Transport
... from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration. OR from a region of higher water potential to a region of low water potential. ...
... from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration. OR from a region of higher water potential to a region of low water potential. ...
Mathematics Semester 1 Study Guide
... 8. What are polymers and how are they made? 9. What is a condensation or dehydration synthesis reaction? 10. What is a hydrolysis reaction? How is water involved in this type of reaction? 11. What are the four major classes of organic compounds? 12. What organic compound class includes the sugars an ...
... 8. What are polymers and how are they made? 9. What is a condensation or dehydration synthesis reaction? 10. What is a hydrolysis reaction? How is water involved in this type of reaction? 11. What are the four major classes of organic compounds? 12. What organic compound class includes the sugars an ...
Bio102 Problems
... occur and write the name of this compartment below. Stroma 6B. During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, protons (H+) are actively transported across a membrane. Draw a star in the compartment that becomes more acidic and write the name of that compartment below. Thylakoid Lumen 7. Eac ...
... occur and write the name of this compartment below. Stroma 6B. During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, protons (H+) are actively transported across a membrane. Draw a star in the compartment that becomes more acidic and write the name of that compartment below. Thylakoid Lumen 7. Eac ...
cytology - Citrus College
... Cytosol • The semi-fluid medium found in the cytoplasm. • This does not include the organelles. ...
... Cytosol • The semi-fluid medium found in the cytoplasm. • This does not include the organelles. ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.