Translation
... Evolutionary significance of intron existence: • Possibility of alternative splicing (more proteins from one gene). • Increased probability of genetic recombination between exons of ...
... Evolutionary significance of intron existence: • Possibility of alternative splicing (more proteins from one gene). • Increased probability of genetic recombination between exons of ...
Translation
... Evolutionary significance of intron existence: • Possibility of alternative splicing (more proteins from one gene). • Increased probability of genetic recombination between exons of ...
... Evolutionary significance of intron existence: • Possibility of alternative splicing (more proteins from one gene). • Increased probability of genetic recombination between exons of ...
Translation
... Evolutionary significance of intron existence: • Possibility of alternative splicing (more proteins from one gene). • Increased probability of genetic recombination between exons of ...
... Evolutionary significance of intron existence: • Possibility of alternative splicing (more proteins from one gene). • Increased probability of genetic recombination between exons of ...
File
... sequence but often has the sequence CAT •The position of the start site is determined not by the sequences located there but by the location of the consensus sequences •If the consensus sequences are artificially moved upstream or downstream, the location of the starting point of transcription corre ...
... sequence but often has the sequence CAT •The position of the start site is determined not by the sequences located there but by the location of the consensus sequences •If the consensus sequences are artificially moved upstream or downstream, the location of the starting point of transcription corre ...
12-Transcription-The Relationship Between Genes and Proteins
... Shortly after RNA polymerase II initiates transcription at the first nucleotide of the first exon of a gene, the 5′ end of the nascent RNA is capped with 7-methylguanylate. Transcription by RNA polymerase II terminates at any one of multiple termination sites downstream from the poly(A) site, which ...
... Shortly after RNA polymerase II initiates transcription at the first nucleotide of the first exon of a gene, the 5′ end of the nascent RNA is capped with 7-methylguanylate. Transcription by RNA polymerase II terminates at any one of multiple termination sites downstream from the poly(A) site, which ...
genetic code
... 1 nucleotide clearly not sufficient-- that gives on 4 amino acids 2 nucleotides is better, but not enough-- 42 gives 16 amino acids 3 nucleotides is the minimum-- 43 gives 64 possible amino acids, enough early 1960's, Crick, Brenner and students used acridine dyes to generate mutants defective for v ...
... 1 nucleotide clearly not sufficient-- that gives on 4 amino acids 2 nucleotides is better, but not enough-- 42 gives 16 amino acids 3 nucleotides is the minimum-- 43 gives 64 possible amino acids, enough early 1960's, Crick, Brenner and students used acridine dyes to generate mutants defective for v ...
Human Primary Cell cDNA
... The single-strand cDNA is designed for studying gene expression or cloning genes by PCR amplification for various types of purified human cells. RNA is purified from the cells by using an optimized procedure to ensure that the RNA is of highest quality and free of genomic DNA contamination. Full-len ...
... The single-strand cDNA is designed for studying gene expression or cloning genes by PCR amplification for various types of purified human cells. RNA is purified from the cells by using an optimized procedure to ensure that the RNA is of highest quality and free of genomic DNA contamination. Full-len ...
Non-coding RNA | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... enhancer RNA (eRNA) is made by enhancer regions in genes and appears to amplify protein production when the genes associated with the enhancers are expressed. Scientists have long known that enhancer regions bind with transcription factors to enhance the transcription of targeted genes by interacti ...
... enhancer RNA (eRNA) is made by enhancer regions in genes and appears to amplify protein production when the genes associated with the enhancers are expressed. Scientists have long known that enhancer regions bind with transcription factors to enhance the transcription of targeted genes by interacti ...
RNA processing
... – mRNA modifications create an open reading frame and permit it to be translated • Splicing removes non-functional regions of the primary transcript yielding mature message • Capping and polyadenylation characterize mRNA processing ...
... – mRNA modifications create an open reading frame and permit it to be translated • Splicing removes non-functional regions of the primary transcript yielding mature message • Capping and polyadenylation characterize mRNA processing ...
•MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
... consequence of the size, shape and chemical composition, by base pair interaction (A-T and C-G) There are two major forces that contribute to stability of helix formation: Hydrogen bonding in base-pairing Hydrophobic interactions in base stacking (堆) ...
... consequence of the size, shape and chemical composition, by base pair interaction (A-T and C-G) There are two major forces that contribute to stability of helix formation: Hydrogen bonding in base-pairing Hydrophobic interactions in base stacking (堆) ...
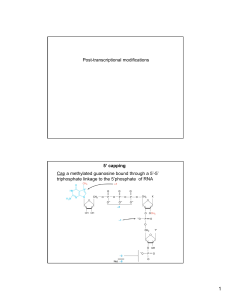
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... Gene silencing is probably often the result of more than one mechanism. Transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) is often associated with methylation of the gene, which may inhibit transcription. In posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS), high levels of normal mRNA can cause activation of RNA-depende ...
... Gene silencing is probably often the result of more than one mechanism. Transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) is often associated with methylation of the gene, which may inhibit transcription. In posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS), high levels of normal mRNA can cause activation of RNA-depende ...
RNA Processing in Eukaryotes
... of these molecules interacts by complementary base pairing with some of the nucleotides in the pre-mRNA transcript. However, the guide RNA has more A nucleotides than the pre-mRNA has U nucleotides to bind with. In these regions, the guide RNA loops out. The 3' ends of guide RNAs have a long poly-U ...
... of these molecules interacts by complementary base pairing with some of the nucleotides in the pre-mRNA transcript. However, the guide RNA has more A nucleotides than the pre-mRNA has U nucleotides to bind with. In these regions, the guide RNA loops out. The 3' ends of guide RNAs have a long poly-U ...
$doc.title
... The mode of control of sigma54 (the gene product of ntrA or rpoN) is achieved, because (unlike sigma70) sigma54 cannot function alone -it requires interaction with another protein NtrC (NRI), which is the gene product of the ntrC gene. Moreover, it is not just the NtrC (NRI) that is required, becau ...
... The mode of control of sigma54 (the gene product of ntrA or rpoN) is achieved, because (unlike sigma70) sigma54 cannot function alone -it requires interaction with another protein NtrC (NRI), which is the gene product of the ntrC gene. Moreover, it is not just the NtrC (NRI) that is required, becau ...
Exam 2 practice questions organized by lecture topic
... 10. During transcription, the following RNA(s) will be involved in the process A. ribosomal RNA D. B and C are correct B. transfer RNA E. A, B, and C are correct C. message RNA 11. Are any of the statements below incorrect? If yes, which one? A. DNA is composed of A,T,C,G nucleotides B. RNA is compo ...
... 10. During transcription, the following RNA(s) will be involved in the process A. ribosomal RNA D. B and C are correct B. transfer RNA E. A, B, and C are correct C. message RNA 11. Are any of the statements below incorrect? If yes, which one? A. DNA is composed of A,T,C,G nucleotides B. RNA is compo ...
Biol120 Mock Final Examination
... c) It has a guanine cap on its 3’ end and a poly-A tail on its 5’ end d) It is a polymer of adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine bases 45. Where are electrons donated to from photosystem I? a) A complex located on the lumen face of the thylakoid membrane called NADP+ reductase where NADP+ is redu ...
... c) It has a guanine cap on its 3’ end and a poly-A tail on its 5’ end d) It is a polymer of adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine bases 45. Where are electrons donated to from photosystem I? a) A complex located on the lumen face of the thylakoid membrane called NADP+ reductase where NADP+ is redu ...
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN
... Transcription proceeds until after the RNA polymerase transcribes a terminator sequence in the DNA. ° In prokaryotes, RNA polymerase stops transcription right at the end of the terminator. Both the RNA and DNA are then released. ° In eukaryotes, the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain w ...
... Transcription proceeds until after the RNA polymerase transcribes a terminator sequence in the DNA. ° In prokaryotes, RNA polymerase stops transcription right at the end of the terminator. Both the RNA and DNA are then released. ° In eukaryotes, the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain w ...
chapter 17 from gene to protein
... The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is the nucleic acid RNA. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the nitrogenous base uracil for thymine. An RNA molecule almost always consists of a single strand. In DNA or RNA, the four nucleotide ...
... The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is the nucleic acid RNA. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the nitrogenous base uracil for thymine. An RNA molecule almost always consists of a single strand. In DNA or RNA, the four nucleotide ...
Access Slides
... Structure of RNAPII and interaction of the enzyme with promoter DNA. This schematic representation of the polymerase (shown in orange) emphasizes the way in which the clamp and wall domains restrict access to the active site. Subunits Rpb4 and Rpb7 form a complex (shown in blue) that can dissociate ...
... Structure of RNAPII and interaction of the enzyme with promoter DNA. This schematic representation of the polymerase (shown in orange) emphasizes the way in which the clamp and wall domains restrict access to the active site. Subunits Rpb4 and Rpb7 form a complex (shown in blue) that can dissociate ...
Review Questions for Ch 1
... 5. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. DNA and RNA are both nucleotides made up of a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a Nitrogen containing base. The polymers of both are built by the bonding of the sugar of one nucleotide to the phosphate group of the next, and both play a role in the building ...
... 5. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. DNA and RNA are both nucleotides made up of a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a Nitrogen containing base. The polymers of both are built by the bonding of the sugar of one nucleotide to the phosphate group of the next, and both play a role in the building ...
Describe the central dogma of molecular biology.
... information in cells is from DNA, to RNA, to proteins. Basically, genes control the traits of organisms by controlling which proteins are made. Although there are exceptions, in general, each gene codes for the production of one polypeptide. ...
... information in cells is from DNA, to RNA, to proteins. Basically, genes control the traits of organisms by controlling which proteins are made. Although there are exceptions, in general, each gene codes for the production of one polypeptide. ...
Biol115 The Thread of Life
... Split genes and RNA splicing • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually express ...
... Split genes and RNA splicing • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually express ...
mv-lect-06-virus-repl-stratigies
... • Replication of genetic information is the single most distinctive characteristic of living organisms, which is accomplished with great economy and simplicity among viruses. • To achieve the expression, replication, and spread of their genes, different families of viruses have evolved diverse genet ...
... • Replication of genetic information is the single most distinctive characteristic of living organisms, which is accomplished with great economy and simplicity among viruses. • To achieve the expression, replication, and spread of their genes, different families of viruses have evolved diverse genet ...
G - AP Bio Take 5
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
RNA world

The RNA world refers to the self-replicating ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules that were precursors to all current life on Earth. It is generally accepted that current life on Earth descends from an RNA world, although RNA-based life may not have been the first life to exist.RNA stores genetic information like DNA, and catalyzes chemical reactions like an enzyme protein. It may, therefore, have played a major step in the evolution of cellular life. The RNA world would have eventually been replaced by the DNA, RNA and protein world of today, likely through an intermediate stage of ribonucleoprotein enzymes such as the ribosome and ribozymes, since proteins large enough to self-fold and have useful activities would only have come about after RNA was available to catalyze peptide ligation or amino acid polymerization. DNA is thought to have taken over the role of data storage due to its increased stability, while proteins, through a greater variety of monomers (amino acids), replaced RNA's role in specialized biocatalysis.The RNA world hypothesis is supported by many independent lines of evidence, such as the observations that RNA is central to the translation process and that small RNAs can catalyze all of the chemical group and information transfers required for life. The structure of the ribosome has been called the ""smoking gun,"" as it showed that the ribosome is a ribozyme, with a central core of RNA and no amino acid side chains within 18 angstroms of the active site where peptide bond formation is catalyzed. Many of the most critical components of cells (those that evolve the slowest) are composed mostly or entirely of RNA. Also, many critical cofactors (ATP, Acetyl-CoA, NADH, etc.) are either nucleotides or substances clearly related to them. This would mean that the RNA and nucleotide cofactors in modern cells are an evolutionary remnant of an RNA-based enzymatic system that preceded the protein-based one seen in all extant life.Evidence suggests chemical conditions (including the presence of boron, molybdenum and oxygen) for initially producing RNA molecules may have been better on the planet Mars than those on the planet Earth. If so, life-suitable molecules, originating on Mars, may have later migrated to Earth via panspermia or similar process.