The Function & Anatomy of Neurons What is a Neuron?
... Association- Carry impulses between neurons within the central nervous system(multipolar). Motor(Efferent)- Carry impulses from the central nervous system to any part of the body capable of responding. (most are multipolar). ...
... Association- Carry impulses between neurons within the central nervous system(multipolar). Motor(Efferent)- Carry impulses from the central nervous system to any part of the body capable of responding. (most are multipolar). ...
Lessons 1
... The chemical synapse In the presynaptic membrane there are numerous synaptic vesicles, containing neurotransmitters (chemical substances which ultimately cause postsynaptic changes in the receiving neuron) The 2 most common neurotransmitters in the brain are the amino acids glutamate and GABA The p ...
... The chemical synapse In the presynaptic membrane there are numerous synaptic vesicles, containing neurotransmitters (chemical substances which ultimately cause postsynaptic changes in the receiving neuron) The 2 most common neurotransmitters in the brain are the amino acids glutamate and GABA The p ...
Chapter 48 Nervous System
... The nervous, endocrine and immune systems often cooperate and interact in regulating internal body functions to maintain homeostasis. The ability of an organism to survive and maintain homeostasis depends largely on how it responds to internal and external stimuli. A stimulus is an agent or a change ...
... The nervous, endocrine and immune systems often cooperate and interact in regulating internal body functions to maintain homeostasis. The ability of an organism to survive and maintain homeostasis depends largely on how it responds to internal and external stimuli. A stimulus is an agent or a change ...
Chapter Two - Texas Christian University
... due to the concentration of positive ions on the outside and negative ions on the inside. Due to negative electrical charge, the neuron at rest is said to be in a state of polarization. Incoming signals from other neurons stimulate receiving neurons at the dendrites through binding of Neurotransmitt ...
... due to the concentration of positive ions on the outside and negative ions on the inside. Due to negative electrical charge, the neuron at rest is said to be in a state of polarization. Incoming signals from other neurons stimulate receiving neurons at the dendrites through binding of Neurotransmitt ...
CHAPTER 9 MUSCULAR SYSTEM: HISTOLOGY
... the microfilaments. Have them draw these structures in their notes or as a homework assignment. Membrane Potentials, Ion Channels, Action Potentials Stress the fact that muscles are excitable tissue and have resting membrane potentials that can be altered. Students must understand the resting membra ...
... the microfilaments. Have them draw these structures in their notes or as a homework assignment. Membrane Potentials, Ion Channels, Action Potentials Stress the fact that muscles are excitable tissue and have resting membrane potentials that can be altered. Students must understand the resting membra ...
Reflexes
... -sensory neurons monitor the degree (type Ia fibers and type II fibers) and rate of stretch (type Ia fibers) of the intrafusal muscle fibers -the whole production (receptor cells and sensory neuron endings) is called a muscle spindle -when the muscle is stretched, sensory neurons send impulses and “ ...
... -sensory neurons monitor the degree (type Ia fibers and type II fibers) and rate of stretch (type Ia fibers) of the intrafusal muscle fibers -the whole production (receptor cells and sensory neuron endings) is called a muscle spindle -when the muscle is stretched, sensory neurons send impulses and “ ...
Exam - McLoon Lab
... B. the initial segment of the axon becomes sufficiently depolarized. C. the voltage-gated sodium (Na+) channels in the initial segment of the axon close. D. the membrane potential for most neurons reaches approximately -65mV. E. More than one of the above is true. 27. The refractory period for a neu ...
... B. the initial segment of the axon becomes sufficiently depolarized. C. the voltage-gated sodium (Na+) channels in the initial segment of the axon close. D. the membrane potential for most neurons reaches approximately -65mV. E. More than one of the above is true. 27. The refractory period for a neu ...
Functions of the Nervous System
... When the central neuron is excited, the efferent impulse is conducted outward along the axon, at the same time, also can excite a inhibitory interneuron though its collateral branch, then cause the release of inhibitory neurotransmitter, which inhibit the previously excited neurons, this kind of inh ...
... When the central neuron is excited, the efferent impulse is conducted outward along the axon, at the same time, also can excite a inhibitory interneuron though its collateral branch, then cause the release of inhibitory neurotransmitter, which inhibit the previously excited neurons, this kind of inh ...
Document
... • Opening other types of ion channels triggers a depolarization, a reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential • For example, depolarization occurs if gated Na+ channels open and Na+ diffuses into the cell ...
... • Opening other types of ion channels triggers a depolarization, a reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential • For example, depolarization occurs if gated Na+ channels open and Na+ diffuses into the cell ...
Chapter 17:
... • insecticides interfere with enzymes that break down neurotransmitters causing their hearts to remain contracted, • whereas LSD and other hallucinogens are believed to bind to the receptor sites for neurotransmitters ...
... • insecticides interfere with enzymes that break down neurotransmitters causing their hearts to remain contracted, • whereas LSD and other hallucinogens are believed to bind to the receptor sites for neurotransmitters ...
Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... ● rhodopsin absorbs light, and breaks apart, as its retinal component changes shape; opsin is now ACTIVE; ● this triggers a chain of metabolic events (signal-transduction pathway!) that makes the rod cell membrane less permeable to sodium and therefore hyperpolarizes the rod cell membrane; ● the rod ...
... ● rhodopsin absorbs light, and breaks apart, as its retinal component changes shape; opsin is now ACTIVE; ● this triggers a chain of metabolic events (signal-transduction pathway!) that makes the rod cell membrane less permeable to sodium and therefore hyperpolarizes the rod cell membrane; ● the rod ...
A1990DD76100001
... showed that the receptor protein undergoes transitions between discrete confoemationai states, some of which present before thebinding of acetykholine In other words, the acetylcholine receptor exhibits several properties typical of allostenc proteins but withdistinctive features associated with its ...
... showed that the receptor protein undergoes transitions between discrete confoemationai states, some of which present before thebinding of acetykholine In other words, the acetylcholine receptor exhibits several properties typical of allostenc proteins but withdistinctive features associated with its ...
file - Athens Academy
... In addition to helping us maintain our sanity, having an imbalance in this neurotransmitter plays a role in the development of Parkinson’s Disease. ...
... In addition to helping us maintain our sanity, having an imbalance in this neurotransmitter plays a role in the development of Parkinson’s Disease. ...
Nervous System
... • If membrane potential becomes less negative, it has depolarized • Graded (or proportional) to intensity of stimulation, meaning the greater the stimulation, the greater the depolarization • if the depolarization is great enough, reach threshold potential ...
... • If membrane potential becomes less negative, it has depolarized • Graded (or proportional) to intensity of stimulation, meaning the greater the stimulation, the greater the depolarization • if the depolarization is great enough, reach threshold potential ...
02biologya
... • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter. • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. • Neurotransmitter binds to receptors that it fits. ...
... • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter. • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. • Neurotransmitter binds to receptors that it fits. ...
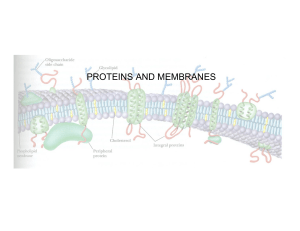
PROTEINS AND MEMBRANES
... faulty versions of the gene and suffer crippling pain because their sodium channels open too easily or can't close. In the third disorder, which leaves patients unable to feel pain at all, SCN9A produces a protein that can't function. "We wondered if more common, apparently harmless [changes] in the ...
... faulty versions of the gene and suffer crippling pain because their sodium channels open too easily or can't close. In the third disorder, which leaves patients unable to feel pain at all, SCN9A produces a protein that can't function. "We wondered if more common, apparently harmless [changes] in the ...
Chapter 17: Nervous System - Johnston Community College
... is close to a dendrite or cell body of another neuron; this region of close proximity is called the synapse. Transmission of a nerve impulse takes place when a neurotransmitter molecule stored in synaptic vesicles in the axon bulb is released into a synaptic cleft between the axon and the receiving ...
... is close to a dendrite or cell body of another neuron; this region of close proximity is called the synapse. Transmission of a nerve impulse takes place when a neurotransmitter molecule stored in synaptic vesicles in the axon bulb is released into a synaptic cleft between the axon and the receiving ...
Ch48(2) - ISpatula
... A) cause the membrane to hyperpolarize and then depolarize. B) can undergo temporal and spatial summation. C) are triggered by a depolarization that reaches the threshold. D) move at the same speed along all axons. E) result from the diffusion of Na+ and K+ through ligand-gated channels. Answer: C ...
... A) cause the membrane to hyperpolarize and then depolarize. B) can undergo temporal and spatial summation. C) are triggered by a depolarization that reaches the threshold. D) move at the same speed along all axons. E) result from the diffusion of Na+ and K+ through ligand-gated channels. Answer: C ...
08 Electrophysiology of muscles
... This influx of calcium from the outside of the cell occurs during the cardiac muscle action potential – part of the mechanism of the action potential – especially in the plateau phase. Thus even though the calcium enters as part of the action potential mechanism–it is also important for the contract ...
... This influx of calcium from the outside of the cell occurs during the cardiac muscle action potential – part of the mechanism of the action potential – especially in the plateau phase. Thus even though the calcium enters as part of the action potential mechanism–it is also important for the contract ...
Neural Tissue
... Damage and Repair • PNS neurons have a greater capacity for repair and regeneration than CNS neurons – Axons and dendrites of PNS neurons that are associated with a neurolemma may undergo repair if the cell body remains intact, if the schwann cells are functions, and if scar tissue formation does n ...
... Damage and Repair • PNS neurons have a greater capacity for repair and regeneration than CNS neurons – Axons and dendrites of PNS neurons that are associated with a neurolemma may undergo repair if the cell body remains intact, if the schwann cells are functions, and if scar tissue formation does n ...
Responses to stimulating multiple inputs
... synapses that neuron 1 makes onto neuron 2 show facilitation if presynaptic action potentials occur within 10 ms of each other; if at least 4 such occurrences are required for eliciting spiking in neuron 2. Synaptic depression, however, occurs at the synapse between neuron 2 and 3 when action potent ...
... synapses that neuron 1 makes onto neuron 2 show facilitation if presynaptic action potentials occur within 10 ms of each other; if at least 4 such occurrences are required for eliciting spiking in neuron 2. Synaptic depression, however, occurs at the synapse between neuron 2 and 3 when action potent ...
Nervous System I
... Nearby neuroglia secrete growth factors that guide developing sprouts from the cell body into a tube formed by the remaining Schwann Cells. ...
... Nearby neuroglia secrete growth factors that guide developing sprouts from the cell body into a tube formed by the remaining Schwann Cells. ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.