Local Anesthetics
... Local anesthetics work in general by binding to sodium channel receptors inside the cell and thereby inhibiting action potentials in a given axon. They work the best when the axon is firing. The Cell membrane consists of ion pumps, most notably the Na/K pump that create a negative 70mV resting poten ...
... Local anesthetics work in general by binding to sodium channel receptors inside the cell and thereby inhibiting action potentials in a given axon. They work the best when the axon is firing. The Cell membrane consists of ion pumps, most notably the Na/K pump that create a negative 70mV resting poten ...
Neural-Ville
... 3. It may bind to the first cell's autoreceptors, which tell that cell not to release any more of the neurotransmitter molecules, then leave the autoreceptor and continue trying to bind again somewhere until its activity is ended by step 4, 5 or 6. ...
... 3. It may bind to the first cell's autoreceptors, which tell that cell not to release any more of the neurotransmitter molecules, then leave the autoreceptor and continue trying to bind again somewhere until its activity is ended by step 4, 5 or 6. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Named according to their vertebrae Each spinal nerve has 2 roots: dorsal and ventral ...
... Named according to their vertebrae Each spinal nerve has 2 roots: dorsal and ventral ...
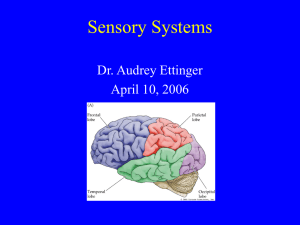
Sensory Systems - Cedar Crest College
... the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
... the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
Neural Anatomy and Function
... press • For his first lift, 50 pounds is put on the bar • He will be using his pectoralis major muscle with has 500 motor units (300 slow twitch and 200 fast twitch) and his triceps muscle • His CNS stimulates 280 motor units leading to his pectoralis major muscle (180 slow twitch and 100 fast twitc ...
... press • For his first lift, 50 pounds is put on the bar • He will be using his pectoralis major muscle with has 500 motor units (300 slow twitch and 200 fast twitch) and his triceps muscle • His CNS stimulates 280 motor units leading to his pectoralis major muscle (180 slow twitch and 100 fast twitc ...
BIOL 273 Midterm #1 Notes
... takes for the Na gates to get to their original “starting positions”, from where they can open again and let more Na into the cell ...
... takes for the Na gates to get to their original “starting positions”, from where they can open again and let more Na into the cell ...
9.5 & 9.11 PP - Mrs. heninger
... Real-world connection How drugs interact with the nervous system. Vocabulary nerve pathways, synapse, synaptic cleft, synaptic transmission, neurotransmitters, resting potential, action potential, reflex arc, receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, effector. ...
... Real-world connection How drugs interact with the nervous system. Vocabulary nerve pathways, synapse, synaptic cleft, synaptic transmission, neurotransmitters, resting potential, action potential, reflex arc, receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, effector. ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neurons take information from the CNS to muscles or glands. ...
... integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neurons take information from the CNS to muscles or glands. ...
control systems of the body - chapter 11
... nervous system is by far the more rapid acting & complex. Nervous cells communicate by means of electrochemical signals, which are rapid & specific, usually causing almost immediate responses. It involves ions like Na+ (sodium) and K+ (potassium) crossing the membrane of neurons. An action potential ...
... nervous system is by far the more rapid acting & complex. Nervous cells communicate by means of electrochemical signals, which are rapid & specific, usually causing almost immediate responses. It involves ions like Na+ (sodium) and K+ (potassium) crossing the membrane of neurons. An action potential ...
Lab 11 Nervous System I
... 4. The binding of a neurotransmitter to a ligand-gated channel results in the outflow of potassium from the cell. What effect does this have on the post-synaptic membrane? ...
... 4. The binding of a neurotransmitter to a ligand-gated channel results in the outflow of potassium from the cell. What effect does this have on the post-synaptic membrane? ...
AP Psychology - Ms. Hofmann`s Website
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name
... dendrite of another neuron (or an organ). The entire region is called a __________________. Transmission of nerve impulses across a Synaptic clef is carried out by chemicals Page 6 of 20 ...
... dendrite of another neuron (or an organ). The entire region is called a __________________. Transmission of nerve impulses across a Synaptic clef is carried out by chemicals Page 6 of 20 ...
A1992HX83800001
... motivation to switch to more simple systems that could be put under complete experimental control. Then, in 1964,1 was joined by tw o young biologists— V. Gerasimov and V. Maisky—who also were looking for more simple structures to study nerve cell functions. We turned to snails (Helix pomatia), whic ...
... motivation to switch to more simple systems that could be put under complete experimental control. Then, in 1964,1 was joined by tw o young biologists— V. Gerasimov and V. Maisky—who also were looking for more simple structures to study nerve cell functions. We turned to snails (Helix pomatia), whic ...
Neuron Stations
... 4. The list below is what happens when a neuron fires and sends a signal along to another neuron. Fill in the missing blanks in each statement. (Remember to use the Pause button!) a. When an ___________ ________________ begins in a neuron, it travels down the ______________. b. When the action poten ...
... 4. The list below is what happens when a neuron fires and sends a signal along to another neuron. Fill in the missing blanks in each statement. (Remember to use the Pause button!) a. When an ___________ ________________ begins in a neuron, it travels down the ______________. b. When the action poten ...
Chapter 9 A and B Questions
... Beginning with the arrival of an action potential in a motor axon terminal, list the events that lead to the release of Ca++ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum? What is a T-tubule? What are the roles of DHP receptors and ryanodine receptors? What role does ATP have in myofibers regarding Ca++? How is t ...
... Beginning with the arrival of an action potential in a motor axon terminal, list the events that lead to the release of Ca++ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum? What is a T-tubule? What are the roles of DHP receptors and ryanodine receptors? What role does ATP have in myofibers regarding Ca++? How is t ...
here
... Action potential: a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are used by the nervous system to transmit information between neurons, and between neurons and effectors. ...
... Action potential: a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are used by the nervous system to transmit information between neurons, and between neurons and effectors. ...
Topic 9
... 1. An ion-channel receptor (the Amiloridesensitive sodium channel) allows EITHER sodium or hydrogen ions to pass into the taste bud. 2. This ion movement will lead to a depolarization which leads to the influx of calcium ions, stimulating the release of neurotrasmitter agents. 3. The hydrogen ions w ...
... 1. An ion-channel receptor (the Amiloridesensitive sodium channel) allows EITHER sodium or hydrogen ions to pass into the taste bud. 2. This ion movement will lead to a depolarization which leads to the influx of calcium ions, stimulating the release of neurotrasmitter agents. 3. The hydrogen ions w ...
Effects of Alcohol Concentration on Beet Membranes--Pre
... Just one observation of a drunken person is enough to convince you that alcohol directly affects the brain. People who drink enough to get drunk often end up with slurred speech and impaired motor skills and judgment, among other side effects. Many of them suffer from headaches, nausea and other unp ...
... Just one observation of a drunken person is enough to convince you that alcohol directly affects the brain. People who drink enough to get drunk often end up with slurred speech and impaired motor skills and judgment, among other side effects. Many of them suffer from headaches, nausea and other unp ...
SENSORY AND MOTOR SYSTEMS: REFLEXES
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
Chp 9: NERVOUS TISSUE
... OBJ: Describe how a nerve impulse is generated and conducted. What is another name for action potentials? ___________________________ What two features of plasma membrane do action potentials in muscle fibers and in neurons depend on? (1) ___________________________________________________________ ( ...
... OBJ: Describe how a nerve impulse is generated and conducted. What is another name for action potentials? ___________________________ What two features of plasma membrane do action potentials in muscle fibers and in neurons depend on? (1) ___________________________________________________________ ( ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 7: PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Receptor cells constantly replaced; only neurons known that do this d) 5 million receptors of 1000 different kinds (compared to only 3 receptor types for color vision and 4 for taste) ...
... Receptor cells constantly replaced; only neurons known that do this d) 5 million receptors of 1000 different kinds (compared to only 3 receptor types for color vision and 4 for taste) ...
unit 3 study sheet - El Camino College
... synaptic potential, receptor, neurotransmitter, calcium, gated channels (3-types), threshold. 14. How do the following terms relate to each other: potential propagation, refractory period, salutatory conduction, hyperporlarization 15. What is the role of calcium in the nervous system? How does this ...
... synaptic potential, receptor, neurotransmitter, calcium, gated channels (3-types), threshold. 14. How do the following terms relate to each other: potential propagation, refractory period, salutatory conduction, hyperporlarization 15. What is the role of calcium in the nervous system? How does this ...
resting potential
... • Opening other types of ion channels triggers a depolarization, a reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential • For example, depolarization occurs if gated Na+ channels open and Na+ diffuses into the cell ...
... • Opening other types of ion channels triggers a depolarization, a reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential • For example, depolarization occurs if gated Na+ channels open and Na+ diffuses into the cell ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.