Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
The Nervous System WS-11A Review Quest
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
Chapter 13
... As a result of this active transport, the cytoplasm of the neuron contains more ___ ions and fewer ____ ions than the surrounding medium The cell membrane also has 2 other separate protein channels, one that ‘leaks’ K+ ions and one that ‘leaks’ Na+ ions down their ________________________ There are ...
... As a result of this active transport, the cytoplasm of the neuron contains more ___ ions and fewer ____ ions than the surrounding medium The cell membrane also has 2 other separate protein channels, one that ‘leaks’ K+ ions and one that ‘leaks’ Na+ ions down their ________________________ There are ...
HBNervous
... terminus; the location of the synapse. Action potential develops in the axon. axon depends upon the cell body for everything: organelles, proteins, and enzymes for synthesis of neurotransmitter In humans, neurons can grow up to a meter long. All the functions of the nervous system involve neurons co ...
... terminus; the location of the synapse. Action potential develops in the axon. axon depends upon the cell body for everything: organelles, proteins, and enzymes for synthesis of neurotransmitter In humans, neurons can grow up to a meter long. All the functions of the nervous system involve neurons co ...
Unit 8 - Perry Local Schools
... Distribution of Ions Potential Difference (PD) = the difference in electrical charge between 2 points (across cell membrane) Resting Membrane Potential (RMP) = results from the distribution of ions across the cell membrane Resting neuron’s cell membrane – polarized ...
... Distribution of Ions Potential Difference (PD) = the difference in electrical charge between 2 points (across cell membrane) Resting Membrane Potential (RMP) = results from the distribution of ions across the cell membrane Resting neuron’s cell membrane – polarized ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... to our biology), this chapter will focus on the neuron, the nervous system, and how these physiological components of our being interact, respond to, and influence our psychological health. ...
... to our biology), this chapter will focus on the neuron, the nervous system, and how these physiological components of our being interact, respond to, and influence our psychological health. ...
Biology 231
... neuromuscular junction – synapse between neuron and muscle fiber neuroglandular junction – synapse between neuron and gland most synapses are between one neuron and another neuron Synapses Between Neurons presynaptic neuron – sending neuron (axon terminal) postsynaptic neuron – receiving neuron (den ...
... neuromuscular junction – synapse between neuron and muscle fiber neuroglandular junction – synapse between neuron and gland most synapses are between one neuron and another neuron Synapses Between Neurons presynaptic neuron – sending neuron (axon terminal) postsynaptic neuron – receiving neuron (den ...
Anat3_01_Nervous_Tissue
... excitable cell cannot generate another action potential. Absolute refractory period – a second action potential ...
... excitable cell cannot generate another action potential. Absolute refractory period – a second action potential ...
Document
... due to Na+ and K+ ions o Greater concentration of sodium ions outside and potassium ions inside. o Potassium ions pass through more easily o Active transport (sodium/potassium pump) maintains balance ...
... due to Na+ and K+ ions o Greater concentration of sodium ions outside and potassium ions inside. o Potassium ions pass through more easily o Active transport (sodium/potassium pump) maintains balance ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Tamalpais Union High School District
... • Dopamine also sends signals that help coordinate your skeletal muscle movements • Parkinson’s Disease – deficient dopamine production – tremors ...
... • Dopamine also sends signals that help coordinate your skeletal muscle movements • Parkinson’s Disease – deficient dopamine production – tremors ...
Slide ()
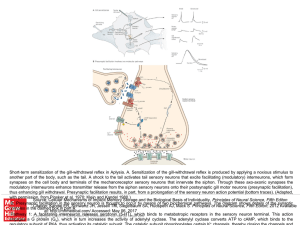
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
last lecture neurophysiology - Evans Laboratory: Environmental
... TRANSMISSION AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION • when an action potential reaches the axon terminal of the neuromuscular junction it triggers calcium (Ca+2) channels to open • the concentration of Ca+2 inside the neuron is much lower than outside, so Ca+2 moves into the neuron along its concentration gr ...
... TRANSMISSION AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION • when an action potential reaches the axon terminal of the neuromuscular junction it triggers calcium (Ca+2) channels to open • the concentration of Ca+2 inside the neuron is much lower than outside, so Ca+2 moves into the neuron along its concentration gr ...
Lecture 1 st week
... Action of the transmitter substance on the postsynaptic neuron • The membrane of the postsynaptic neuron contains large numbers of receptor proteins with two components: – 1) a binding component (outward into the synaptic cleft—here it binds the neurotransmitter) – 2) an ionophore component (that p ...
... Action of the transmitter substance on the postsynaptic neuron • The membrane of the postsynaptic neuron contains large numbers of receptor proteins with two components: – 1) a binding component (outward into the synaptic cleft—here it binds the neurotransmitter) – 2) an ionophore component (that p ...
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 2 Week 9/28 – 10/2 The following
... D. They are made to run four three-mile sprints/day, uphill both ways E. They have a mutant form of the gene somatostatin, which produces a protein that competes for myostatin receptors, altering growth patterns 2. Botox is a neurotoxin that prevents the release of acetylcholine, effectively paralyz ...
... D. They are made to run four three-mile sprints/day, uphill both ways E. They have a mutant form of the gene somatostatin, which produces a protein that competes for myostatin receptors, altering growth patterns 2. Botox is a neurotoxin that prevents the release of acetylcholine, effectively paralyz ...
Passive Conduction - Cable Theory
... Now for an example modeled to be more relevant to physical systems, take a system which includes a dendrite and connecting soma at the far end of the cable. The other end of the dendrite can be only be excited by a -70 mV pulse once every 5 ms. To make the example even a little more concrete, employ ...
... Now for an example modeled to be more relevant to physical systems, take a system which includes a dendrite and connecting soma at the far end of the cable. The other end of the dendrite can be only be excited by a -70 mV pulse once every 5 ms. To make the example even a little more concrete, employ ...
12-2cut
... – 4) Receptor proteins cause start of action potential in postsynaptic membrane – 5) Enzymes ______________ neurotransmitters when transmission is completed. Prepares synapse for the next impulse. ...
... – 4) Receptor proteins cause start of action potential in postsynaptic membrane – 5) Enzymes ______________ neurotransmitters when transmission is completed. Prepares synapse for the next impulse. ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... If you are unsure about the precise mode of action of neurotransmission and neuromodulation, you might like to consult Chapter 3, where these terms are explained. Neurotransmitter would be employed where ballistic action is called for as in the brain rapidly instigating a response or in inhibiting a ...
... If you are unsure about the precise mode of action of neurotransmission and neuromodulation, you might like to consult Chapter 3, where these terms are explained. Neurotransmitter would be employed where ballistic action is called for as in the brain rapidly instigating a response or in inhibiting a ...
The nervous system - Sonoma Valley High School
... outside is positive Na+ and K+ ions move across the cell Membrane via the sodium-potassium pump ...
... outside is positive Na+ and K+ ions move across the cell Membrane via the sodium-potassium pump ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... called (neurotransmitters) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
... called (neurotransmitters) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
Psychopharmacology
... – 1. Nigrostratal tract (movement) • Starts in A9 – substantia nigra (in mesencephalon) • projects to the striatum (caudate and putamen). ...
... – 1. Nigrostratal tract (movement) • Starts in A9 – substantia nigra (in mesencephalon) • projects to the striatum (caudate and putamen). ...
The Nervous System
... because it resists the free movement of ions. So whenever +ve & -ve ions are separated by a resistance (cell membrane) a potential difference exists. The potential difference is measured in volts or mV (the resting potential or transmembrane potential is -0.07V for a neuron cell membrane) ...
... because it resists the free movement of ions. So whenever +ve & -ve ions are separated by a resistance (cell membrane) a potential difference exists. The potential difference is measured in volts or mV (the resting potential or transmembrane potential is -0.07V for a neuron cell membrane) ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.