Flipped Classroom - "C. Marchesi" – Mascalucia
... Class activities may include: using math manipulatives and emerging mathematical technologies, in-depth laboratory experiments, original document analysis, debate or speech presentation, current event discussions, project-based learning, and skill development or concept practice. ...
... Class activities may include: using math manipulatives and emerging mathematical technologies, in-depth laboratory experiments, original document analysis, debate or speech presentation, current event discussions, project-based learning, and skill development or concept practice. ...
Powerpoint
... Linear Classifiers Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation ...
... Linear Classifiers Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation ...
Probabilistic Models for Unsupervised Learning
... We can still work with such models by using approximate inference techniques to estimate the latent variables. ...
... We can still work with such models by using approximate inference techniques to estimate the latent variables. ...
Snap-drift ADaptive FUnction Neural Network (SADFUNN) for Optical and Pen-Based Handwritten Digit Recognition
... An ADaptive Function Neural Network (ADFUNN) is combined with the on-line snap-drift learning method in this paper to solve an Optical Recognition of Handwritten Digits problem and a Pen-Based Recognition of Handwritten Digits problem. SnapDrift [1] employs the complementary concepts of minimalist l ...
... An ADaptive Function Neural Network (ADFUNN) is combined with the on-line snap-drift learning method in this paper to solve an Optical Recognition of Handwritten Digits problem and a Pen-Based Recognition of Handwritten Digits problem. SnapDrift [1] employs the complementary concepts of minimalist l ...
Making New Memories
... the hippocampus and other related medial temporal lobe structures in a recent human fMRI study using a variant of our location–scene association task.37 These findings suggest that associative learning signals can be studied in parallel in both human and nonhuman primate systems. What are the implic ...
... the hippocampus and other related medial temporal lobe structures in a recent human fMRI study using a variant of our location–scene association task.37 These findings suggest that associative learning signals can be studied in parallel in both human and nonhuman primate systems. What are the implic ...
Formative Evaluation
... What would they use it for? Is there a perceived benefit of having the OLM? 3-May-17 ...
... What would they use it for? Is there a perceived benefit of having the OLM? 3-May-17 ...
Developing Effective Robot Teammates for Human
... focus within Human-Robot Interaction and involves underlying research questions deeply relevant to the Artificial Intelligence community. Especially in domains where modern robots are ineffective, we wish to leverage human-robot teaming to improve the efficiency, ability, and safety of human workers ...
... focus within Human-Robot Interaction and involves underlying research questions deeply relevant to the Artificial Intelligence community. Especially in domains where modern robots are ineffective, we wish to leverage human-robot teaming to improve the efficiency, ability, and safety of human workers ...
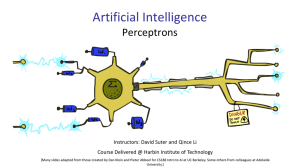
Artificial Intelligence
... • NPCs (non-player characters) can have goals, plans, emotions • NPCs use path finding • NPCs respond to sounds, lights, signals • NPCs co-ordinate with each other; squad tactics • Some natural language processing ...
... • NPCs (non-player characters) can have goals, plans, emotions • NPCs use path finding • NPCs respond to sounds, lights, signals • NPCs co-ordinate with each other; squad tactics • Some natural language processing ...
Instrumental Conditioning Driven by Apparently Neutral Stimuli: A
... (a) phasic DA responses have been recorded following stimuli with no apparent rewarding value, if these stimuli have not been previously shown to the organism: novelty causes phasic DA independently of the appetitive value of the stimulus; (b) while the time required to establish an association vari ...
... (a) phasic DA responses have been recorded following stimuli with no apparent rewarding value, if these stimuli have not been previously shown to the organism: novelty causes phasic DA independently of the appetitive value of the stimulus; (b) while the time required to establish an association vari ...
Revision Lectures - School of Computer Science
... Suggestion: 10-15 minutes for initial read-through and thinking, then up to about 15 minutes for answering each question, leaving about 15 minutes for final checking/refining. Some questions have several parts. Some questions broadly be similar in style to some questions in formative Exercise ...
... Suggestion: 10-15 minutes for initial read-through and thinking, then up to about 15 minutes for answering each question, leaving about 15 minutes for final checking/refining. Some questions have several parts. Some questions broadly be similar in style to some questions in formative Exercise ...
issues, results and the LLL challenge
... In both cases, follow up studies [13, 4] have shown that these ILP approaches to natural language problems extend with relative ease to various languages other than English. The area of Learning Language in Logic (LLL) is producing a number of challenges to existing ILP theory and implementations. I ...
... In both cases, follow up studies [13, 4] have shown that these ILP approaches to natural language problems extend with relative ease to various languages other than English. The area of Learning Language in Logic (LLL) is producing a number of challenges to existing ILP theory and implementations. I ...
LeCun - NYU Computer Science
... • MKL only gets few % gain over averaging features Features are ...
... • MKL only gets few % gain over averaging features Features are ...
Neural networks.
... Neural networks are adaptive statistical devices. This means that they can change iteratively the values of their parameters (i.e., the synaptic weights) as a function of their performance. These changes are made according to learning rules which can be characterized as supervised (when a desired ou ...
... Neural networks are adaptive statistical devices. This means that they can change iteratively the values of their parameters (i.e., the synaptic weights) as a function of their performance. These changes are made according to learning rules which can be characterized as supervised (when a desired ou ...
PDF
... In this talk, we introduce our robot learning framework which follows a similar timeline with human infant development. In the initial stages of the development, the robot organizes its action parameter space to form behavior primitives, and explore the environment with these primitives to learn bas ...
... In this talk, we introduce our robot learning framework which follows a similar timeline with human infant development. In the initial stages of the development, the robot organizes its action parameter space to form behavior primitives, and explore the environment with these primitives to learn bas ...
ppt
... encode complex grammatical knowledge such as humans use to assemble sentences, recognize errors and make corrections” ...
... encode complex grammatical knowledge such as humans use to assemble sentences, recognize errors and make corrections” ...
Learning from learning curves: Item Response Theory
... Cognitive Tutor. 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. 2007. ...
... Cognitive Tutor. 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. 2007. ...
Learning as a phenomenon occurring in a critical state
... rules, where again a single neuron fires at each step of the iteration, together with a uniform negative feedback plastic adaptation acting on time scales slower than the neuron firing time scale, enables learning the XOR rule without error backpropagation [17]. Both results suggest that the system ...
... rules, where again a single neuron fires at each step of the iteration, together with a uniform negative feedback plastic adaptation acting on time scales slower than the neuron firing time scale, enables learning the XOR rule without error backpropagation [17]. Both results suggest that the system ...
Com1005: Machines and Intelligence
... Brain can extract meaning from sentence, or recognise visual pattern in 1/10th of a second. Means program should only be 100 instructions long. But AI programs contain 1000s of instructions ...
... Brain can extract meaning from sentence, or recognise visual pattern in 1/10th of a second. Means program should only be 100 instructions long. But AI programs contain 1000s of instructions ...
Lecture 7A
... one cybernetics machine that would combine all the knowledge of all the galaxies. Dwar Reyn spoke briefly to the watching and listening trillions. Then after a moment’s silence he said, “Now, Dwar Ev.” Dwar Ev threw the switch. There was a mighty hum, the surge of power from ninety-six billion plane ...
... one cybernetics machine that would combine all the knowledge of all the galaxies. Dwar Reyn spoke briefly to the watching and listening trillions. Then after a moment’s silence he said, “Now, Dwar Ev.” Dwar Ev threw the switch. There was a mighty hum, the surge of power from ninety-six billion plane ...
daniel lowd - CIS Users web server
... June 2010 – Present: Assistant Professor, Department of Computer and Information Science, University of Oregon September 2009 – June 2010: Acting Assistant Professor, Department of Computer and Information Science, University of Oregon September 2003 – August 2009: Research assistant for Pedro Domin ...
... June 2010 – Present: Assistant Professor, Department of Computer and Information Science, University of Oregon September 2009 – June 2010: Acting Assistant Professor, Department of Computer and Information Science, University of Oregon September 2003 – August 2009: Research assistant for Pedro Domin ...
Meta-Learning
... progressively more sophisticated representations of patterns, invariants, correlations from data. Success in limited domains only … Meta-learning: learning how to learn. ...
... progressively more sophisticated representations of patterns, invariants, correlations from data. Success in limited domains only … Meta-learning: learning how to learn. ...
Machine Learning CSCI 5622 - University of Colorado Boulder
... know how to formalize (code) what makes her an expert! – For Example: I’m an expert on chairs but I can’t (and no one can!) write a program that identifies chairs in an image ...
... know how to formalize (code) what makes her an expert! – For Example: I’m an expert on chairs but I can’t (and no one can!) write a program that identifies chairs in an image ...
Igor Kiselev - University of Waterloo
... From dynamic programming approach: Qi(s,a): Long-run payoff to i from s on a then equilibrium University of Waterloo ...
... From dynamic programming approach: Qi(s,a): Long-run payoff to i from s on a then equilibrium University of Waterloo ...
Computational Natural Language Learning:±20years±Data
... architectures, and there is significant challenge associated with exploiting them for more ad hoc network structures. On the other hand high level modularity and multimodality naturally give rise to components that effectively run in parallel but need to coordinate efficiently. For example our HeadX ...
... architectures, and there is significant challenge associated with exploiting them for more ad hoc network structures. On the other hand high level modularity and multimodality naturally give rise to components that effectively run in parallel but need to coordinate efficiently. For example our HeadX ...
Approved Module Information for Introduction to Computational
... * Problem solving and reasoning using mathematical approaches (e.g. probabilities, logic, sets). * How humans think and reason, including introspection and meta-analysis. * Understanding of dynamic systems, emergent properties, and autonomous programming. ...
... * Problem solving and reasoning using mathematical approaches (e.g. probabilities, logic, sets). * How humans think and reason, including introspection and meta-analysis. * Understanding of dynamic systems, emergent properties, and autonomous programming. ...