attribute_selection
... selection is done using the learning algorithm as a black box. Ron Kohavi, George H. John (1997). Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artificial Intelligence. 97(1-2):273-324. N. Gagunashvili (UNAK & MPIK) ...
... selection is done using the learning algorithm as a black box. Ron Kohavi, George H. John (1997). Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artificial Intelligence. 97(1-2):273-324. N. Gagunashvili (UNAK & MPIK) ...
Refinement Planning: Status and Prospectus
... An attempt to deal with issues of semantic meaning as well as syntactic form. Answers that are neither exact nor optimal, but are in some sense “sufficient.” This is a result of the essential reliance on heuristic problem-solving methods in situations where optimal or exact results are either too ex ...
... An attempt to deal with issues of semantic meaning as well as syntactic form. Answers that are neither exact nor optimal, but are in some sense “sufficient.” This is a result of the essential reliance on heuristic problem-solving methods in situations where optimal or exact results are either too ex ...
幻灯片 1 - Peking University
... formal rules are extracted from a set of observations. The rules extracted may represent a full scientific model of the data, or merely represent local patterns in the data. Labeled examples: training & testing data Admissible rules (hypotheses space) Search strategy ...
... formal rules are extracted from a set of observations. The rules extracted may represent a full scientific model of the data, or merely represent local patterns in the data. Labeled examples: training & testing data Admissible rules (hypotheses space) Search strategy ...
Refinement Planning: Status and Prospectus
... An attempt to deal with issues of semantic meaning as well as syntactic form. Answers that are neither exact nor optimal, but are in some sense “sufficient.” This is a result of the essential reliance on heuristic problem-solving methods in situations where optimal or exact results are either too ex ...
... An attempt to deal with issues of semantic meaning as well as syntactic form. Answers that are neither exact nor optimal, but are in some sense “sufficient.” This is a result of the essential reliance on heuristic problem-solving methods in situations where optimal or exact results are either too ex ...
Unsupervised Learning
... In contrast to supervised learning, unsupervised or self-organised learning does not require an external teacher. During the training session, the neural network receives a number of different input patterns, discovers significant features in these patterns and learns how to classify input data i ...
... In contrast to supervised learning, unsupervised or self-organised learning does not require an external teacher. During the training session, the neural network receives a number of different input patterns, discovers significant features in these patterns and learns how to classify input data i ...
Artificial Neural Networks - Introduction -
... These units are also referred to as neurons or nodes. The Neural Network has a natural propensity for storing experiential knowledge and making it available for use. ...
... These units are also referred to as neurons or nodes. The Neural Network has a natural propensity for storing experiential knowledge and making it available for use. ...
Learning objects and Learning styles
... Motivation and problem statement Each learner has his own individual needs and characteristics Most of LMSs do not consider learners’ needs and preferences the need for providing learners with adaptive courses While adaptive systems support adaptivity, they support only few functions of web- ...
... Motivation and problem statement Each learner has his own individual needs and characteristics Most of LMSs do not consider learners’ needs and preferences the need for providing learners with adaptive courses While adaptive systems support adaptivity, they support only few functions of web- ...
Sequence Learning: From Recognition and Prediction to
... Let us briefly examine several major approaches to sequence learning, while keeping in mind these dimensions. Several neural network models deal with sequences; one example is recurrent backpropagation networks. These networks computer.org/intelligent ...
... Let us briefly examine several major approaches to sequence learning, while keeping in mind these dimensions. Several neural network models deal with sequences; one example is recurrent backpropagation networks. These networks computer.org/intelligent ...
Artificial Intelligence
... • NPCs use path finding • NPCs respond to sounds, lights, signals • NPCs co-ordinate with each other; squad tactics • Some natural language processing • Randomness can be useful ...
... • NPCs use path finding • NPCs respond to sounds, lights, signals • NPCs co-ordinate with each other; squad tactics • Some natural language processing • Randomness can be useful ...
Climate setting
... • Report presentation • Discussion/question on every report • Conclusion of the reports should be linked up with the subject matter through ...
... • Report presentation • Discussion/question on every report • Conclusion of the reports should be linked up with the subject matter through ...
"Abstractions and Hierarchies for Learning and Planning
... Based on Subgoal Discovery. NCI 2004. 13. Amy McGovern: Autonomous Discovery of Abstractions through Interaction with an Environment. SARA 2002: 338-339. 14. Ozgür Simsek, Alicia P. Wolfe, and Andrew G. Barto: Identifying useful subgoals in reinforcement learning by local graph partitioning. In ICML ...
... Based on Subgoal Discovery. NCI 2004. 13. Amy McGovern: Autonomous Discovery of Abstractions through Interaction with an Environment. SARA 2002: 338-339. 14. Ozgür Simsek, Alicia P. Wolfe, and Andrew G. Barto: Identifying useful subgoals in reinforcement learning by local graph partitioning. In ICML ...
Lifelong learning: overcoming the language barrier at the Vaal
... implementation of these teaching methods. Empirical data relating to the success of the teaching method outlined in this paper are presented in the poster entitled ‘Demonstration of the relationship between meaningful lifelong learning, English language proficiency and teaching methods.’ In conclusi ...
... implementation of these teaching methods. Empirical data relating to the success of the teaching method outlined in this paper are presented in the poster entitled ‘Demonstration of the relationship between meaningful lifelong learning, English language proficiency and teaching methods.’ In conclusi ...
Artificial Intelligence
... which lie in the domain of Artificial Intelligence (AI). But what exactly is AI? Defining AI: The phrase AI, which was coined by John McCarthy three decades ago,evades a concise and formal definition to date. One representative definition is pivoted around the comparison of intelligence of computing ...
... which lie in the domain of Artificial Intelligence (AI). But what exactly is AI? Defining AI: The phrase AI, which was coined by John McCarthy three decades ago,evades a concise and formal definition to date. One representative definition is pivoted around the comparison of intelligence of computing ...
CS607_Current_Subjective
... Answer:- (Page 187) It resembles the brain in two respects • Knowledge is acquired by the network through a learning process (called training) • Interneuron connection strengths known as synaptic weights are used to store the knowledge Elaborate the goal state of STRIPS. 2 Answer: Goal is also repre ...
... Answer:- (Page 187) It resembles the brain in two respects • Knowledge is acquired by the network through a learning process (called training) • Interneuron connection strengths known as synaptic weights are used to store the knowledge Elaborate the goal state of STRIPS. 2 Answer: Goal is also repre ...
2 . The Role of Learning in the Task Domain
... Outcome feedback (Hogarth 1981) was purported to be insufficient for users to learn how to improve the accuracy of decision-making. In a decision making task involving uncertainty, outcome feedback was found to be ineffective in fostering learning and improving judgmental performance (Brehmer 1980; ...
... Outcome feedback (Hogarth 1981) was purported to be insufficient for users to learn how to improve the accuracy of decision-making. In a decision making task involving uncertainty, outcome feedback was found to be ineffective in fostering learning and improving judgmental performance (Brehmer 1980; ...
Development of the Patient Safety Incident
... We have a further mapping session in December for users who cannot map their local systems to the NRLS (including eForm users, patients, and organisations who cannot currently participate in national learning at all). This will generate further User Stories to add to the case. We’re also procuring a ...
... We have a further mapping session in December for users who cannot map their local systems to the NRLS (including eForm users, patients, and organisations who cannot currently participate in national learning at all). This will generate further User Stories to add to the case. We’re also procuring a ...
Presentation
... – mathematical laws governing emotional involvement into thinking process have not been well known – there is a long-standing cultural belief that emotions are opposite to thinking and intellectually inferior • Socrates, Plato, Aristotle • reiterated by founders of Artificial Intelligence [Newell] ...
... – mathematical laws governing emotional involvement into thinking process have not been well known – there is a long-standing cultural belief that emotions are opposite to thinking and intellectually inferior • Socrates, Plato, Aristotle • reiterated by founders of Artificial Intelligence [Newell] ...
Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
... – Require a number of parameters typically best determined empirically, e.g., the network topology or ``structure." – Poor interpretability: Difficult to interpret the symbolic meaning behind the learned weights and of ``hidden units" in the network ...
... – Require a number of parameters typically best determined empirically, e.g., the network topology or ``structure." – Poor interpretability: Difficult to interpret the symbolic meaning behind the learned weights and of ``hidden units" in the network ...
Principles of writing learning objectives
... drop in the “organ container” all images that constitute the prompted body region. Principle 5: Write a separate statement for each objective. Multiple statements can clarify your instructional objectives. ...
... drop in the “organ container” all images that constitute the prompted body region. Principle 5: Write a separate statement for each objective. Multiple statements can clarify your instructional objectives. ...
Presentation 5 JAN 16
... will get lighter as they grow I think the seeds will get heavier as they grow ...
... will get lighter as they grow I think the seeds will get heavier as they grow ...
Machine Learning
... udacity - intro to machine learning explores pattern recognition during data analysis through computer science and statistics using the popular python language, amazon machine learning predictive analytics with aws - amazon machine learning helps developers create predictive models to build smart ap ...
... udacity - intro to machine learning explores pattern recognition during data analysis through computer science and statistics using the popular python language, amazon machine learning predictive analytics with aws - amazon machine learning helps developers create predictive models to build smart ap ...
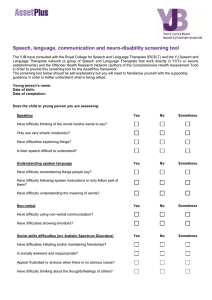
2) Speech, Language, Communication and Neuro
... Speech, language, communication and neuro-disability screening tool The YJB have consulted with the Royal College for Speech and Language Therapists (RCSLT) and the YJ Speech and Language Therapists network (a group of Speech and Language Therapists that work directly in YOTs or secure establishment ...
... Speech, language, communication and neuro-disability screening tool The YJB have consulted with the Royal College for Speech and Language Therapists (RCSLT) and the YJ Speech and Language Therapists network (a group of Speech and Language Therapists that work directly in YOTs or secure establishment ...