The Biological Perspective
... Structures Under the Cortex Limbic system – involved in emotions, motivation, memory, and learning Thalamus – round structure in the center of the brain Hypothalamus – just below the front of the thalamus Hippocampus – in the temporal lobes on each side of the brain Amygdala – near the hi ...
... Structures Under the Cortex Limbic system – involved in emotions, motivation, memory, and learning Thalamus – round structure in the center of the brain Hypothalamus – just below the front of the thalamus Hippocampus – in the temporal lobes on each side of the brain Amygdala – near the hi ...
Organisation of the nervous system
... Brain, saggital section displaying hypothalamus and pituitary ...
... Brain, saggital section displaying hypothalamus and pituitary ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy - RIDDELL
... a. cell bodies range in diameter from 5 to 135 micrometers b. the pattern of dendritic branching is quite variable and distinctive for neurons in different regions of the nervous system c. a few small neurons lack an axon and many others have very short axons; long neurons have axons that may exceed ...
... a. cell bodies range in diameter from 5 to 135 micrometers b. the pattern of dendritic branching is quite variable and distinctive for neurons in different regions of the nervous system c. a few small neurons lack an axon and many others have very short axons; long neurons have axons that may exceed ...
File
... something with your left hand it is received by the right side of your brain. The corpus callosum helps get that information from one side to the other. The occipital lobe contains the primary visual area of the cerebral cortex. Damage can create unusual conditions. – They can recognize and object, ...
... something with your left hand it is received by the right side of your brain. The corpus callosum helps get that information from one side to the other. The occipital lobe contains the primary visual area of the cerebral cortex. Damage can create unusual conditions. – They can recognize and object, ...
15-1 Section Summary
... he nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps in maintaining stable internal conditions. A stimulus is any change or signal in the enviro ...
... he nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps in maintaining stable internal conditions. A stimulus is any change or signal in the enviro ...
Nervous Tissue
... • White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) ...
... • White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) ...
Chapt13 Lecture 13ed Pt 1
... insulation, and regeneration in the PNS • _____________ – neuroglia that make up the myelin sheath in the PNS • _____________ – gaps between myelination on the axons • Saltatory conduction – conduction of the nerve impulse from node to node ...
... insulation, and regeneration in the PNS • _____________ – neuroglia that make up the myelin sheath in the PNS • _____________ – gaps between myelination on the axons • Saltatory conduction – conduction of the nerve impulse from node to node ...
Chapter 7
... Control of Motor Function • Subcortical and cortical motivation areas – Sends a “rough draft” of the movement • Cerebellum and basal ganglia ...
... Control of Motor Function • Subcortical and cortical motivation areas – Sends a “rough draft” of the movement • Cerebellum and basal ganglia ...
Body Systems - Nervous System
... your body d. The somatic nervous system allows you to feel hot and cold sensations 7. If an area of your body is particularly sensitive, what can you conclude about that area? a. It contains more skin cells than other areas of your body b. It contains more nerve endings than other areas of your body ...
... your body d. The somatic nervous system allows you to feel hot and cold sensations 7. If an area of your body is particularly sensitive, what can you conclude about that area? a. It contains more skin cells than other areas of your body b. It contains more nerve endings than other areas of your body ...
Name
... d. cauda equina 12) Which neuroglia myelinate axons of the PNS? a. astrocytes b. Schwann cells c. oligodendrocytes d. microglia 13) Which statement is correct regarding resting membrane potential? a. The Na+/K+ pump moves potassium out of the cell. b. The membrane is highly permeable to sodium. c. T ...
... d. cauda equina 12) Which neuroglia myelinate axons of the PNS? a. astrocytes b. Schwann cells c. oligodendrocytes d. microglia 13) Which statement is correct regarding resting membrane potential? a. The Na+/K+ pump moves potassium out of the cell. b. The membrane is highly permeable to sodium. c. T ...
The Nervous System
... reproduction and circadian rhythms ▫ Larger in the sheep’s brain when compared to the human brain, that has less basic instinctual behavior controls. ...
... reproduction and circadian rhythms ▫ Larger in the sheep’s brain when compared to the human brain, that has less basic instinctual behavior controls. ...
Notes Chapter 50 Nervous and Sensory Systems
... The white matter surrounds a rigid inner core of gray matter, which is composed of the cell bodies of neurons. d) Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves, part of the peripheral nervous system, originate in the spinal cord and branch out to both sides of the body. i) Recall that neurons have long axons th ...
... The white matter surrounds a rigid inner core of gray matter, which is composed of the cell bodies of neurons. d) Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves, part of the peripheral nervous system, originate in the spinal cord and branch out to both sides of the body. i) Recall that neurons have long axons th ...
PowerPoint to accompany Hole’s Human Anatomy and
... • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
... • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
Nervous system and senses
... and decision making. Near the back of the head, beneath the cerebrum, is the cerebellum. The cerebellum coordinates and balances the actions of the voluntary muscles. It makes your muscles move smooth and helps you keep your balance. Bundles of nerves from the cerebrum and cerebellum come together a ...
... and decision making. Near the back of the head, beneath the cerebrum, is the cerebellum. The cerebellum coordinates and balances the actions of the voluntary muscles. It makes your muscles move smooth and helps you keep your balance. Bundles of nerves from the cerebrum and cerebellum come together a ...
Nervous System - Intermediate School Biology
... Central Nervous System: the brain and spinal cord. Describe the location and function of the following parts of the brain: cerebrum, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. Describe the cross section of the spinal cord indicating the following: white matter, grey matter cen ...
... Central Nervous System: the brain and spinal cord. Describe the location and function of the following parts of the brain: cerebrum, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. Describe the cross section of the spinal cord indicating the following: white matter, grey matter cen ...
Strategies for drug delivery through the blood
... • Active transport through a protein carrier: specific binding site that undergoes a change in affinity. Active transport requires ATP hydrolysis and conducts movement against the concentration gradient. ...
... • Active transport through a protein carrier: specific binding site that undergoes a change in affinity. Active transport requires ATP hydrolysis and conducts movement against the concentration gradient. ...
02Biology of the brain
... to his frontal lobe. She is perplexed by his behavior. Which of the following would you tell her is “normal behavior” for a person with frontal lobe damage? A. B. C. D. ...
... to his frontal lobe. She is perplexed by his behavior. Which of the following would you tell her is “normal behavior” for a person with frontal lobe damage? A. B. C. D. ...
Intro-biological
... and controls lower level functioning such as respiration and digestion. The spinal cord connects the brain and the body's main receptors, and serves as a conduit for sensory input and motor output. ...
... and controls lower level functioning such as respiration and digestion. The spinal cord connects the brain and the body's main receptors, and serves as a conduit for sensory input and motor output. ...
Chapter 12 Notes - Las Positas College
... A. The human body contains billions of nondividing neurons or nerve cells. B. Neurons are composed of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and an axon. (Figs. 12.4–12.5) 1. The cytoplasm of the cell body contains all the usual organelles and chromatophilic bodies. Most neuronal cell bo ...
... A. The human body contains billions of nondividing neurons or nerve cells. B. Neurons are composed of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and an axon. (Figs. 12.4–12.5) 1. The cytoplasm of the cell body contains all the usual organelles and chromatophilic bodies. Most neuronal cell bo ...
Slide 1
... Attaches neurons to nearby structures protects them Three main types of glial cells Astrocytes—anchor small blood vessels to neurons Microglia—in inflamed or degenerating brain tissue they act as phagocytes and remove this tissue Oligodendrocytes—form myelin sheaths on axons in the CNS ...
... Attaches neurons to nearby structures protects them Three main types of glial cells Astrocytes—anchor small blood vessels to neurons Microglia—in inflamed or degenerating brain tissue they act as phagocytes and remove this tissue Oligodendrocytes—form myelin sheaths on axons in the CNS ...
4/7
... Neurons are commonly connected to many other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron will do. ...
... Neurons are commonly connected to many other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron will do. ...
Slide ()
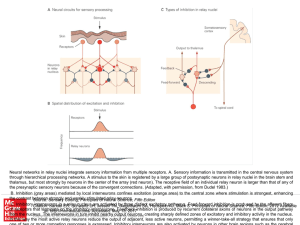
... thalamus, but most strongly by neurons in the center of the array (red neuron). The receptive field of an individual relay neuron is larger than that of any of the presynaptic sensory neurons because of the convergent connections. (Adapted, with permission, from Dudel 1983.) B. Inhibition (gray area ...
... thalamus, but most strongly by neurons in the center of the array (red neuron). The receptive field of an individual relay neuron is larger than that of any of the presynaptic sensory neurons because of the convergent connections. (Adapted, with permission, from Dudel 1983.) B. Inhibition (gray area ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.