The Central Nervous System
... Gray Matter: inside; contains neuron cell bodies & neuroglia…forms an H or butterfly shape White Matter: outside; contains axons of neurons Dorsal Roots: carry sensory info to spinal cord Ventral Roots: carry motor info to muscles and glands ...
... Gray Matter: inside; contains neuron cell bodies & neuroglia…forms an H or butterfly shape White Matter: outside; contains axons of neurons Dorsal Roots: carry sensory info to spinal cord Ventral Roots: carry motor info to muscles and glands ...
The Nervous System
... • 1. Sensory-receptors gather information and pass it on toward the CNS • 2. Integrative-in the spinal cord or brain, we put information together and make sense of it • 3. Motor-carry impulses to effectors such as muscles and glands ...
... • 1. Sensory-receptors gather information and pass it on toward the CNS • 2. Integrative-in the spinal cord or brain, we put information together and make sense of it • 3. Motor-carry impulses to effectors such as muscles and glands ...
Using POCS Method of Problem
... Nerve signals are constantly whizzing from neuron to neuron all around your body – yet no two neurons ever actually touch. Instead, there is a small gap between connecting neurons called a synapse. When a nerve signal is passed on from one neuron to the next, it is carried across the gap by special ...
... Nerve signals are constantly whizzing from neuron to neuron all around your body – yet no two neurons ever actually touch. Instead, there is a small gap between connecting neurons called a synapse. When a nerve signal is passed on from one neuron to the next, it is carried across the gap by special ...
The Central Nervous System
... Fine tunes most movements Links to brain stem, cerebrum, spinal cord • Communicates over cerebellar peduncles ...
... Fine tunes most movements Links to brain stem, cerebrum, spinal cord • Communicates over cerebellar peduncles ...
A&P Ch 8 PowerPoint(Nervous System)
... Fine tunes most movements Links to brain stem, cerebrum, spinal cord • Communicates over cerebellar peduncles ...
... Fine tunes most movements Links to brain stem, cerebrum, spinal cord • Communicates over cerebellar peduncles ...
Document
... _ Lacks rough endoplasmic reticulum and polysomes _ Smooth endoplasmic reticulum _ Mitochondria _ Axon hillock. Region of the cell body where axon originates _ Devoid of rough endoplasmic reticulum _ Continuous with initial segment of the axon that is a highly electrically excitable zone for initiat ...
... _ Lacks rough endoplasmic reticulum and polysomes _ Smooth endoplasmic reticulum _ Mitochondria _ Axon hillock. Region of the cell body where axon originates _ Devoid of rough endoplasmic reticulum _ Continuous with initial segment of the axon that is a highly electrically excitable zone for initiat ...
UNIT 2 REVIEW GUIDE *Be able to identify/label parts of the neuron
... incoming messages from the body to higher parts of the brain? ...
... incoming messages from the body to higher parts of the brain? ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Central and peripheral myelin also contain myelin basic proteins. Seven related proteins produced from a single gene by alternative splicing. ...
... Central and peripheral myelin also contain myelin basic proteins. Seven related proteins produced from a single gene by alternative splicing. ...
Brain, Body, and Behavior
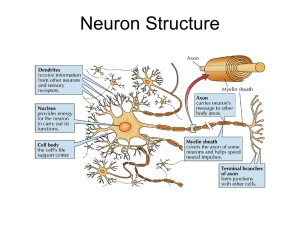
... Each nerve cell is separate from the others The body of the neuron has fibers sticking out from it Short fibers are called dendrites Look like branches Axons carry the message from the cell to other ...
... Each nerve cell is separate from the others The body of the neuron has fibers sticking out from it Short fibers are called dendrites Look like branches Axons carry the message from the cell to other ...
collinsnervoussystem (1)
... 11. When you are walking, the brain sends messages to the skeletal muscles in the legs by way of a) efferent fibers b) sensory fibers c) afferent fibers d) central fibers ...
... 11. When you are walking, the brain sends messages to the skeletal muscles in the legs by way of a) efferent fibers b) sensory fibers c) afferent fibers d) central fibers ...
The nervous system
... • Each branched end of an exon transmits information to another cell at a junction called a synapse. • The part of each axon branch that forms this specialized junction is a synaptic terminal. • Chemical messengers called neurotransmitters pass information from the transmitting neuron to the receivi ...
... • Each branched end of an exon transmits information to another cell at a junction called a synapse. • The part of each axon branch that forms this specialized junction is a synaptic terminal. • Chemical messengers called neurotransmitters pass information from the transmitting neuron to the receivi ...
Document
... " In development, guide neurons as they migrate to their destinations " Stimulate neuronal growth by secreting growth factors " Forms the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB), connecting neurons to blood vessels ...
... " In development, guide neurons as they migrate to their destinations " Stimulate neuronal growth by secreting growth factors " Forms the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB), connecting neurons to blood vessels ...
The Human Brain
... The human brain is probably the most complicated thing in the universe. It weights about 3lbs and has the texture of toothpaste. It is made up of 50 to 100 billion nerve cells called neurons as well as 500-1000 billion other cells. Neurons have a cell body with lots of branches coming off them calle ...
... The human brain is probably the most complicated thing in the universe. It weights about 3lbs and has the texture of toothpaste. It is made up of 50 to 100 billion nerve cells called neurons as well as 500-1000 billion other cells. Neurons have a cell body with lots of branches coming off them calle ...
Nervous System 1
... Because of its role, the nervous system is resistant to evolutionary change. Even if bones change shape, the nerves innervating the muscles must still work. The system is therefore an ideal comparative tool to help us understand the evolution of vertebrates. ...
... Because of its role, the nervous system is resistant to evolutionary change. Even if bones change shape, the nerves innervating the muscles must still work. The system is therefore an ideal comparative tool to help us understand the evolution of vertebrates. ...
8th Grade Information Processing
... the nervous systems, including structure, function, and disorders. • Neuroscience is a relatively new field. New information is always being discovered and there are still many unexplained mysteries of the brain. ...
... the nervous systems, including structure, function, and disorders. • Neuroscience is a relatively new field. New information is always being discovered and there are still many unexplained mysteries of the brain. ...
PsychSim 5 neural messages
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
The Endocrine System
... communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems. ...
... communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems. ...
KS4_nervous_models_Pupil_Sheets
... There is a small gap where the end of one neuron joins with another. Professor Charles Sherrington, who worked at the University of Oxford in the early 20th century, named this a synapse. ...
... There is a small gap where the end of one neuron joins with another. Professor Charles Sherrington, who worked at the University of Oxford in the early 20th century, named this a synapse. ...
Key Stage 4 – Nervous models Pupil worksheet
... There is a small gap where the end of one neuron joins with another. Professor Charles Sherrington, who worked at the University of Oxford in the early 20th century, named this a synapse. ...
... There is a small gap where the end of one neuron joins with another. Professor Charles Sherrington, who worked at the University of Oxford in the early 20th century, named this a synapse. ...
Chapter 2
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a ...
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a ...
Slide ()
... Internal capsule (A) and MRIs through internal capsule (B) and midbrain (C). The locations of the descending axons in the internal capsule and basis pedunculi are shown on the MRIs. The letters "FATL" abbreviate Face, Arm, Trunk, and Leg. In the midbrain, the descending cortical fibers (filled middl ...
... Internal capsule (A) and MRIs through internal capsule (B) and midbrain (C). The locations of the descending axons in the internal capsule and basis pedunculi are shown on the MRIs. The letters "FATL" abbreviate Face, Arm, Trunk, and Leg. In the midbrain, the descending cortical fibers (filled middl ...
Unit Two
... One of the best ways to find out whether or not a trait is inherited is to study twins. Identical Twins: Twins who come from one fertilized egg; in other words, twins having the same heredity. Fraternal Twins: Twins who come from 2 different eggs fertilized by 2 different sperm. How can studying twi ...
... One of the best ways to find out whether or not a trait is inherited is to study twins. Identical Twins: Twins who come from one fertilized egg; in other words, twins having the same heredity. Fraternal Twins: Twins who come from 2 different eggs fertilized by 2 different sperm. How can studying twi ...
Introduction to Psychology The Nervous System: Biological Control
... Neurons range in length from less than a millimeter to more than a meter in length. There are the same three parts in every neuron. 1) The cell body – contains a neuron’s nucleus and other parts essential for the cell’s preservation and nourishment. 2) Dendrites – braches that extend out and r ...
... Neurons range in length from less than a millimeter to more than a meter in length. There are the same three parts in every neuron. 1) The cell body – contains a neuron’s nucleus and other parts essential for the cell’s preservation and nourishment. 2) Dendrites – braches that extend out and r ...
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue
... increase in blood flow to skeletal & cardiac muscle airways dilate & respiratory rate increases ...
... increase in blood flow to skeletal & cardiac muscle airways dilate & respiratory rate increases ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.