Lecture 4 : Nervous System
... system, a semi-independent part of the nervous system whose function is to control the gastrointestinal system. At the cellular level, the nervous system is defined by the presence of a special type of cell, called the neuron, also known as a "nerve cell". Neurons have special structures that allow ...
... system, a semi-independent part of the nervous system whose function is to control the gastrointestinal system. At the cellular level, the nervous system is defined by the presence of a special type of cell, called the neuron, also known as a "nerve cell". Neurons have special structures that allow ...
the teenage brain webquest
... 1. How many parts make up the central nervous system? 2. How much does an adult brain weigh? 3. How many nerve cells are there in the brain? 4. Are there any other special cells in the brain? What are they? ...
... 1. How many parts make up the central nervous system? 2. How much does an adult brain weigh? 3. How many nerve cells are there in the brain? 4. Are there any other special cells in the brain? What are they? ...
Lecture 1
... Neurological – “what do different parts of the brain do?” do?” Useful in brain surgery. 2. Psychological – “what are the brain mechanisms of specific functions (e.g., ...
... Neurological – “what do different parts of the brain do?” do?” Useful in brain surgery. 2. Psychological – “what are the brain mechanisms of specific functions (e.g., ...
Platyhelminthes
... motile animals, implies that the nervous tissue is concentrated at the anterior end ___________________: Body wall consists of three cellular layers Acoelomate: No body cavity, spaces between internal organs are filled Digestion ___________________ Mouth, but no anal opening Nervous system Some spec ...
... motile animals, implies that the nervous tissue is concentrated at the anterior end ___________________: Body wall consists of three cellular layers Acoelomate: No body cavity, spaces between internal organs are filled Digestion ___________________ Mouth, but no anal opening Nervous system Some spec ...
PDF
... numbers of neurons are initially generated, before approximately half of them undergo programmed cell death (PCD), often during synapse formation. The factors that regulate central neuron survival and synaptic specificity remain largely unknown, but now, Joshua Sanes and colleagues (see p. 4141) rep ...
... numbers of neurons are initially generated, before approximately half of them undergo programmed cell death (PCD), often during synapse formation. The factors that regulate central neuron survival and synaptic specificity remain largely unknown, but now, Joshua Sanes and colleagues (see p. 4141) rep ...
PDF
... numbers of neurons are initially generated, before approximately half of them undergo programmed cell death (PCD), often during synapse formation. The factors that regulate central neuron survival and synaptic specificity remain largely unknown, but now, Joshua Sanes and colleagues (see p. 4141) rep ...
... numbers of neurons are initially generated, before approximately half of them undergo programmed cell death (PCD), often during synapse formation. The factors that regulate central neuron survival and synaptic specificity remain largely unknown, but now, Joshua Sanes and colleagues (see p. 4141) rep ...
The Nervous System
... – responsible for increasing activity in most systems (except GI) – adrenergic fibers release epinephrine ...
... – responsible for increasing activity in most systems (except GI) – adrenergic fibers release epinephrine ...
Brain growth, development and Autism
... occurs with experience and learning, but this outpaces synaptic growth, resulting in net pruning back of the “wires” from childhood through adolescence until it reaches the normal adult brain levels. This delicate process regulates the maturation of synapses and neural circuitry to form the brain’s ...
... occurs with experience and learning, but this outpaces synaptic growth, resulting in net pruning back of the “wires” from childhood through adolescence until it reaches the normal adult brain levels. This delicate process regulates the maturation of synapses and neural circuitry to form the brain’s ...
Slide ()
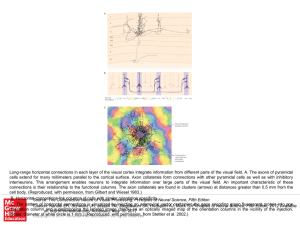
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
Nervous Tissue - Chiropractor Manhattan | Chiropractor New
... Each nerve contains a single axon. The axon propagates impulses toward another neuron, muscle fiber, or gland cell. ...
... Each nerve contains a single axon. The axon propagates impulses toward another neuron, muscle fiber, or gland cell. ...
File
... •Can be done at neuronal level, larger areas of brain tissue or at hemispheric level •Rerouting = an undamaged neuron that has lost a connection with an active neuron may seek a new active neuron and connect with it instead •Sprouting = the growth of new bushier nerve fibres with more branches to ma ...
... •Can be done at neuronal level, larger areas of brain tissue or at hemispheric level •Rerouting = an undamaged neuron that has lost a connection with an active neuron may seek a new active neuron and connect with it instead •Sprouting = the growth of new bushier nerve fibres with more branches to ma ...
EDP3004_ch2a
... Information processing: Spatial informationleft to right » Timeback to front » No such thing as right or left brain learningonly preferences » The left hemisphere process parts (sequentially) » The right hemisphere process wholes (randomly) » Both sides of the brain are involved in every human ac ...
... Information processing: Spatial informationleft to right » Timeback to front » No such thing as right or left brain learningonly preferences » The left hemisphere process parts (sequentially) » The right hemisphere process wholes (randomly) » Both sides of the brain are involved in every human ac ...
Neurotransmitters
... • Neurotransmitters are chemicals that relay and modulate messages between neurons. • Much of human behavior is mediated by the action of neurotransmitters in the brain. Researchers are also demonstrating that behavioral pathology is largely due to imbalances in one or more neurotransmitter systems. ...
... • Neurotransmitters are chemicals that relay and modulate messages between neurons. • Much of human behavior is mediated by the action of neurotransmitters in the brain. Researchers are also demonstrating that behavioral pathology is largely due to imbalances in one or more neurotransmitter systems. ...
Unit 1 Practice
... 3. Communication between neurons is _________________. a. electrical b. chemical c. magical d. genetic 4. Dopamine, serotonin, and histamine are examples of a. neuropeptides. b. nerves. c. neurotransmitters. d. neural pathways. 5. Ray is suffering from multiple sclerosis. When his doctor examines a ...
... 3. Communication between neurons is _________________. a. electrical b. chemical c. magical d. genetic 4. Dopamine, serotonin, and histamine are examples of a. neuropeptides. b. nerves. c. neurotransmitters. d. neural pathways. 5. Ray is suffering from multiple sclerosis. When his doctor examines a ...
Ch. 13 Central Nervous System
... Certain areas of the cortex engage in predominately one function. However, this can vary from person to person and at different times in an individual when the brain is damaged. (cerebral plasticity) The function of each region depends on the structures that is communicates with. No part of the brai ...
... Certain areas of the cortex engage in predominately one function. However, this can vary from person to person and at different times in an individual when the brain is damaged. (cerebral plasticity) The function of each region depends on the structures that is communicates with. No part of the brai ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... neurotransmitters are either Agonists or Antagonists. There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit ...
... neurotransmitters are either Agonists or Antagonists. There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Specialized tissue for rapid conduction of electrical impulses that convey information from one part of the body to another – 98% nervous tissue concentrated in brain and spinal cord Nervous tissue contains two basic cell types Neurons = functional units transmit information in the form of electrica ...
... Specialized tissue for rapid conduction of electrical impulses that convey information from one part of the body to another – 98% nervous tissue concentrated in brain and spinal cord Nervous tissue contains two basic cell types Neurons = functional units transmit information in the form of electrica ...
2014 chemical signal..
... between two neurons to change in strength including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitter released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitter -Since ...
... between two neurons to change in strength including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitter released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitter -Since ...
NOVEL APPROACHES TO TRAUMATIC BRAIN AND SPINAL
... UH0113 and -0213 restore neuronal growth and functions after injury. UH0113 increases the number of axons within (A) and crossing over (B) an injury site. Following SCI, UH0113 and -0213 enhance locomotor activity as measured by vertical grid climbing (C) and trauma assessment test (D). Following TB ...
... UH0113 and -0213 restore neuronal growth and functions after injury. UH0113 increases the number of axons within (A) and crossing over (B) an injury site. Following SCI, UH0113 and -0213 enhance locomotor activity as measured by vertical grid climbing (C) and trauma assessment test (D). Following TB ...
Slide ()
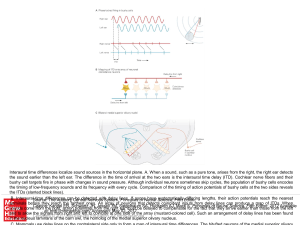
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.