Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous
... Nonselective; also affect sodium channels in muscles of area; causes temporary paralysis; reason for crooked smiles and drooling following dental work ...
... Nonselective; also affect sodium channels in muscles of area; causes temporary paralysis; reason for crooked smiles and drooling following dental work ...
Cheatsheet - Rapid Learning Center
... rest and digestion. The parasympathetic division innervation involves the cranial nerves, such as the facial nerve. Sympathetic Division: The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is active during times of physical or mental stress on the body. As the system`s activity increases, sk ...
... rest and digestion. The parasympathetic division innervation involves the cranial nerves, such as the facial nerve. Sympathetic Division: The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is active during times of physical or mental stress on the body. As the system`s activity increases, sk ...
Chapter 13
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
The Peripheral Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Question
... a dendritic process and an axon extending from the cell body, unipolar neurons which are large neurons that have a cell body lying to one side of the axonal-dendritic process, and multipolar neurons which many dendritic process off the cell body and also have a single axon extending from the cell bo ...
... a dendritic process and an axon extending from the cell body, unipolar neurons which are large neurons that have a cell body lying to one side of the axonal-dendritic process, and multipolar neurons which many dendritic process off the cell body and also have a single axon extending from the cell bo ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Neurons are classified by direction that they send information: 1. Sensory (afferent) neurons sends information from sensory receptors (e.g. skin, eyes, ears) 2. Motor (efferent) neurons sends information AWAY from the CNS to muscles or organs. 3. Inter-neurons: send information between sensory a ...
... Neurons are classified by direction that they send information: 1. Sensory (afferent) neurons sends information from sensory receptors (e.g. skin, eyes, ears) 2. Motor (efferent) neurons sends information AWAY from the CNS to muscles or organs. 3. Inter-neurons: send information between sensory a ...
the human brain
... hormones into the bloodstream for distribution to the rest of the body; the amygdala, which deals with emotion; and the hippocampus, which plays a major role in the formation of spatial memories. Among the most recently evolved parts are the basal ganglia, which regulate the speed and smoothness of ...
... hormones into the bloodstream for distribution to the rest of the body; the amygdala, which deals with emotion; and the hippocampus, which plays a major role in the formation of spatial memories. Among the most recently evolved parts are the basal ganglia, which regulate the speed and smoothness of ...
The Brain: Your Crowning Glory
... We begin our tour of the brain at the lowest level, the hindbrain — the part of the brain where the spinal cord enters the skull and widens. We then work our way upward, first to the midbrain, which lies above the hindbrain, and then to the forebrain, which lies in the highest part of the brain. Con ...
... We begin our tour of the brain at the lowest level, the hindbrain — the part of the brain where the spinal cord enters the skull and widens. We then work our way upward, first to the midbrain, which lies above the hindbrain, and then to the forebrain, which lies in the highest part of the brain. Con ...
LSUHSC N C E
... Remodeling requires ganglion cell action potentials, which are endogenously generated in utero long before rods and cones are present: ganglion cells fire spontaneously and synchronously, generating “waves” of activity that sweep across retinal domains. Waves are also required for regulation of gene ...
... Remodeling requires ganglion cell action potentials, which are endogenously generated in utero long before rods and cones are present: ganglion cells fire spontaneously and synchronously, generating “waves” of activity that sweep across retinal domains. Waves are also required for regulation of gene ...
Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: Neurons by
... ◊ 1 axon extends away from cell body ◊ 1 dendrite extends from axon ◊ Occur in afferent pathways of the visual, auditory and vestibular systems ∼ Unipolar: ◊ Possess a single process from the cell body ◊ This usually divides into dendritic and axonal branches ◊ Consists of primary afferents of the s ...
... ◊ 1 axon extends away from cell body ◊ 1 dendrite extends from axon ◊ Occur in afferent pathways of the visual, auditory and vestibular systems ∼ Unipolar: ◊ Possess a single process from the cell body ◊ This usually divides into dendritic and axonal branches ◊ Consists of primary afferents of the s ...
Step Up To: Psychology - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate the activation of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. D) control pain through the release of opiate-like chemicals into the brain. ...
... A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate the activation of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. D) control pain through the release of opiate-like chemicals into the brain. ...
Unit 3A Nervous System - Teacher Version
... • Neurotransmitters – the chemical messengers that carry information across the synapse between one neuron and then next are released from terminal buttons on the sending neuron ...
... • Neurotransmitters – the chemical messengers that carry information across the synapse between one neuron and then next are released from terminal buttons on the sending neuron ...
File
... Sara’s grandfather—Ach—Acetylcholine neurons have died off so there is less stimulation of his cortex. The Parasympathetic nervous system—the parasympathetic half of the autonomic nervous system takes care of normal body maintenance functions including slow normal breathing & heart rate. Amy—the Tha ...
... Sara’s grandfather—Ach—Acetylcholine neurons have died off so there is less stimulation of his cortex. The Parasympathetic nervous system—the parasympathetic half of the autonomic nervous system takes care of normal body maintenance functions including slow normal breathing & heart rate. Amy—the Tha ...
Plasticity and Functional Recovery of the Brain After
... Our increased understanding in this area has contributed to the field of neurorehabilitation. In other words, it has helped in the treatment of those who have suffered brain trauma. The fact that we know that spontaneous brain recovery slows down after a few weeks, means that we are aware of when it ...
... Our increased understanding in this area has contributed to the field of neurorehabilitation. In other words, it has helped in the treatment of those who have suffered brain trauma. The fact that we know that spontaneous brain recovery slows down after a few weeks, means that we are aware of when it ...
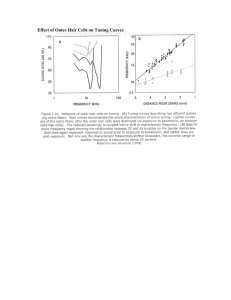
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
... Converting a complex sound wave into electrode-stimulus patterns requires several steps. At left is a 100-millisecond portion of the waveform for the syllable "sa," including the junction between the "s" and "a." In this example, the input wave is filtered into four frequency bands (the band with t ...
... Converting a complex sound wave into electrode-stimulus patterns requires several steps. At left is a 100-millisecond portion of the waveform for the syllable "sa," including the junction between the "s" and "a." In this example, the input wave is filtered into four frequency bands (the band with t ...
chapter_12 - The Anatomy Academy
... detect changes in body and external environment information transmitted into brain or spinal cord lie between sensory and motor pathways in CNS 90% of our neurons are interneurons process, store and retrieve information ...
... detect changes in body and external environment information transmitted into brain or spinal cord lie between sensory and motor pathways in CNS 90% of our neurons are interneurons process, store and retrieve information ...
Q1 (from chapter 1)
... Incorrect statement about brain-behavior relationship is: A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. O ...
... Incorrect statement about brain-behavior relationship is: A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. O ...
Cognitive Neuroscience - U
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All of the nerve cells except those of the brain and the spinal cord Consists of: – Somatic voluntary part (sensory and motor nerves) – Autonomic involuntary part • Sympathetic (activated under stress) • Parasympathetic (maintains body functions) ...
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All of the nerve cells except those of the brain and the spinal cord Consists of: – Somatic voluntary part (sensory and motor nerves) – Autonomic involuntary part • Sympathetic (activated under stress) • Parasympathetic (maintains body functions) ...
Development of the Brain
... Development of the Brain • At birth, the human brain weighs approximately 350 grams. • By the first year. the brain weighs approximately 1000 grams. • The adult brain weighs 1200-1400 grams. ...
... Development of the Brain • At birth, the human brain weighs approximately 350 grams. • By the first year. the brain weighs approximately 1000 grams. • The adult brain weighs 1200-1400 grams. ...
Vanderbilt neuroscientists identify “oops center” in the brain
... when human subjects made errors. They called this the “blunder blip” and attributed it to the brain’s error-recognition response. Then Jonathan Cohen at Princeton University conducted a series of fMRI experiments that mapped brain activity when human subjects were put in situations where they are li ...
... when human subjects made errors. They called this the “blunder blip” and attributed it to the brain’s error-recognition response. Then Jonathan Cohen at Princeton University conducted a series of fMRI experiments that mapped brain activity when human subjects were put in situations where they are li ...
Chapter 8 Nervous System
... 5. Median nerve – innervates most anterior forearm muscles, some intrinsic hand muscles, and skin covering the radial side of hand C. Lumbosacral Plexus – originates from spinal nerves L1 thru S4 – controls lower limbs – 4 major nerves 1. Obturator nerve – innervates the muscles of the medial thigh ...
... 5. Median nerve – innervates most anterior forearm muscles, some intrinsic hand muscles, and skin covering the radial side of hand C. Lumbosacral Plexus – originates from spinal nerves L1 thru S4 – controls lower limbs – 4 major nerves 1. Obturator nerve – innervates the muscles of the medial thigh ...
abstract english
... between inbred mouse lines that we found in chapter 2. By recording suppressing currents activated by GABA we found that variation in the duration of these GABA activated currents correlated with the frequency of fast network oscillations indicating that genes that influence the GABA activated curre ...
... between inbred mouse lines that we found in chapter 2. By recording suppressing currents activated by GABA we found that variation in the duration of these GABA activated currents correlated with the frequency of fast network oscillations indicating that genes that influence the GABA activated curre ...
Perception and Reality
... Computers are made of metal and use electricity to process information. Brains are made of organic cells and use a mix of electrical signals and chemicals to process information. If one part of a computer breaks it can do almost nothing. If one part of your brain gets damaged only certain things are ...
... Computers are made of metal and use electricity to process information. Brains are made of organic cells and use a mix of electrical signals and chemicals to process information. If one part of a computer breaks it can do almost nothing. If one part of your brain gets damaged only certain things are ...
Norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter
... • They have effects similar to that of THC • Short fatty acids produced in the dendrites and cell bodies and released directly from the plasma membrane (no vesicle) ...
... • They have effects similar to that of THC • Short fatty acids produced in the dendrites and cell bodies and released directly from the plasma membrane (no vesicle) ...
Nervous System Lect/96
... Nodes of Ranvier along a myelinated axon b) Unmyelinated axons lie in grooves or furrows formed by Schwann cells--however no myelin sheath is formed. These axons are generally 1 m in diameter or smaller. As is the case for myelinated axons, many Schwann cells aligned end-to-end surround these axon ...
... Nodes of Ranvier along a myelinated axon b) Unmyelinated axons lie in grooves or furrows formed by Schwann cells--however no myelin sheath is formed. These axons are generally 1 m in diameter or smaller. As is the case for myelinated axons, many Schwann cells aligned end-to-end surround these axon ...
Hormonal Control
... actually conduct the nerve impulses and the neuroglial cells (supporting cells) that function to support the neurons in various ways. Neurons have a cell body or cyton, where the nucleus is found, and several processes or extensions off this cell body. The processes that conduct the impulse toward t ...
... actually conduct the nerve impulses and the neuroglial cells (supporting cells) that function to support the neurons in various ways. Neurons have a cell body or cyton, where the nucleus is found, and several processes or extensions off this cell body. The processes that conduct the impulse toward t ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.