Nerve Impulse Transmission
... carry it toward the cell body, which contains the nucleus. • The axon carries the impulse from the cell body toward the synaptic knobs where it will be transferred to other neurons. ...
... carry it toward the cell body, which contains the nucleus. • The axon carries the impulse from the cell body toward the synaptic knobs where it will be transferred to other neurons. ...
Brain
... that is phonetically and grammatically correct but has lost its meaning—word salad. ► Damage in these and other areas can lead to both expressive and receptive language deficits as well as body image problems. ...
... that is phonetically and grammatically correct but has lost its meaning—word salad. ► Damage in these and other areas can lead to both expressive and receptive language deficits as well as body image problems. ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 1-2: Diagram of a motor neuron with myelinated axon. The traditional view of a neuron includes a perikaryon, multiple dendrites and an axon. The perikaryon contains the machinery for transcription and translation of proteins as well as their processing. These proteins must be targeted to som ...
... FIGURE 1-2: Diagram of a motor neuron with myelinated axon. The traditional view of a neuron includes a perikaryon, multiple dendrites and an axon. The perikaryon contains the machinery for transcription and translation of proteins as well as their processing. These proteins must be targeted to som ...
Expression and Functional Interaction of Hepatocyte Growth Factor
... During the development, HGF-SF signals were first detected in El2 mouse brain. At that time and throughout further development, HGF-SF mRNA was prominently expressed in the neuroepithelial layer of the telencephalic vesicle. Furthermore, expression was seen in the developing cortical plate, most pro ...
... During the development, HGF-SF signals were first detected in El2 mouse brain. At that time and throughout further development, HGF-SF mRNA was prominently expressed in the neuroepithelial layer of the telencephalic vesicle. Furthermore, expression was seen in the developing cortical plate, most pro ...
Afferent Synaptic Signaling
... I also recorded synaptic currents in Type II fibers as seen in the two top traces which are from the same cell. The frequency of currents is enhanced by applying extracellular solution with elevated potassium to the tissue, which dopolarizes the outer hair cells and increases their rate of neurotra ...
... I also recorded synaptic currents in Type II fibers as seen in the two top traces which are from the same cell. The frequency of currents is enhanced by applying extracellular solution with elevated potassium to the tissue, which dopolarizes the outer hair cells and increases their rate of neurotra ...
The Auditory Pathway: Transmission between Hair Cells and Eighth
... Stimulus Coding by Primary Afferent Neurons Neuronal signaling in the auditory pathway begins with the spiral ganglion neurons that receive transmitter released from hair cells and send their central axons to the cochlear nucleus of the brainstem. Many decades of single fiber recordings have catalog ...
... Stimulus Coding by Primary Afferent Neurons Neuronal signaling in the auditory pathway begins with the spiral ganglion neurons that receive transmitter released from hair cells and send their central axons to the cochlear nucleus of the brainstem. Many decades of single fiber recordings have catalog ...
Introduction
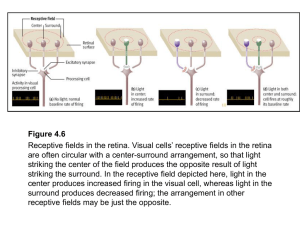
... hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve fibers from each eye meet at the optic chiasm, where fibers from the inside half of each retina cross over to the oppos ...
... hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve fibers from each eye meet at the optic chiasm, where fibers from the inside half of each retina cross over to the oppos ...
ILGA_overview_11-16-09
... receives input from V3a, whose neurons are sensitive to binocular disparity and have small, retinotopic receptive fields (Sakata H et al., 2005), and projects primarily to the anterior intraparietal sulcus (AIP) (Nakamura H et al., 2001). two classes of neurons: surface orientation selective (SO ...
... receives input from V3a, whose neurons are sensitive to binocular disparity and have small, retinotopic receptive fields (Sakata H et al., 2005), and projects primarily to the anterior intraparietal sulcus (AIP) (Nakamura H et al., 2001). two classes of neurons: surface orientation selective (SO ...
chapter 48
... Astrocytes: are found within the CNS and provide structural and metabolic support as well as forming of tight junctions to help form the blood-brain barrier. They also communicate with one another via chemical signals. ...
... Astrocytes: are found within the CNS and provide structural and metabolic support as well as forming of tight junctions to help form the blood-brain barrier. They also communicate with one another via chemical signals. ...
Respiratory System
... In the body, respiration occurs at two levels. Cellular respiration, which takes place in the mitochondria, is the release if energy from the breakdown of food molecules in the presence of oxygen. Organismal respiration is the process of gas exchange. The basic function performed by the respiratory ...
... In the body, respiration occurs at two levels. Cellular respiration, which takes place in the mitochondria, is the release if energy from the breakdown of food molecules in the presence of oxygen. Organismal respiration is the process of gas exchange. The basic function performed by the respiratory ...
Nervous System - Uplift Education
... Action potential calcium ions release neurotransmitter release Post-synaptic neuron Neutrotransmitter uptake sodium gates open action potential Note: information travels as electrical signal within neurons and as chemical signal between them Watch me! ...
... Action potential calcium ions release neurotransmitter release Post-synaptic neuron Neutrotransmitter uptake sodium gates open action potential Note: information travels as electrical signal within neurons and as chemical signal between them Watch me! ...
Neurotransmitters
... Excitatory NTs • Cause an EPSP on the post-synaptic neuron • Glutamate is the most common CNS NT • Aspartic acid is also a NT ...
... Excitatory NTs • Cause an EPSP on the post-synaptic neuron • Glutamate is the most common CNS NT • Aspartic acid is also a NT ...
Anatomy with Elements of Topographic Anatomy
... Identification of all anatomical structures and their topography in relation to body regions. ...
... Identification of all anatomical structures and their topography in relation to body regions. ...
P312Ch04C_BeyondV1
... If complex objects result in the responses of neurons in many different modules, each processing a different aspect of the complex object – one its location, one its movement, one the colors of various parts of it, one the shapes of various parts of it – if it is analyzed into a whole jumble of feat ...
... If complex objects result in the responses of neurons in many different modules, each processing a different aspect of the complex object – one its location, one its movement, one the colors of various parts of it, one the shapes of various parts of it – if it is analyzed into a whole jumble of feat ...
Writing a summary
... Although neurons come in many different shapes and sizes, they are all specialized to receive and transmit information. [adv. clause] Despite their different shapes and sizes, neurons are all specialized to receive and transmit information. [adv. phrase] The different shaped and sized neurons are al ...
... Although neurons come in many different shapes and sizes, they are all specialized to receive and transmit information. [adv. clause] Despite their different shapes and sizes, neurons are all specialized to receive and transmit information. [adv. phrase] The different shaped and sized neurons are al ...
Gustavus/Howard Hughes Medical Institute Outreach Program 2011
... brainstem – the major route by which the forebrain sends information to and receives information from the spinal cord and peripheral nerves; controls respiration and regulation of heart rhythms caudal or posterior – towards the tail cerebellum – a structure located above or dorsal to the bra ...
... brainstem – the major route by which the forebrain sends information to and receives information from the spinal cord and peripheral nerves; controls respiration and regulation of heart rhythms caudal or posterior – towards the tail cerebellum – a structure located above or dorsal to the bra ...
Proposal - people.vcu.edu
... You first start off with a mutant-PTK-7 zebrafish. This mutation will cause this zebrafish to not have a function ptk-7 protein in the membrane to regulate the PCP pathway to help copa neuronal migration. These mutants are able to survive with this mutations, but not without defects; these defects i ...
... You first start off with a mutant-PTK-7 zebrafish. This mutation will cause this zebrafish to not have a function ptk-7 protein in the membrane to regulate the PCP pathway to help copa neuronal migration. These mutants are able to survive with this mutations, but not without defects; these defects i ...
Five Essential Components to the Reflex Arc
... neurons, the muscle contracts, and you take your hand off the stove before your brain even knows it. This is an example of a withdrawal reflex. • Simple reflex behavior involves three neurons, and no brain involvement. Reflexes are automatic events. They involve both motor and sensory neurons, they ...
... neurons, the muscle contracts, and you take your hand off the stove before your brain even knows it. This is an example of a withdrawal reflex. • Simple reflex behavior involves three neurons, and no brain involvement. Reflexes are automatic events. They involve both motor and sensory neurons, they ...
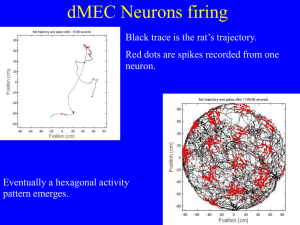
How grid cells neurons encode rat position
... The combined information from the different phases ...
... The combined information from the different phases ...
Glossary of Neuroanatomical Terms and Eponyms
... part of the floor of the fourth ventricle that is shaped somewhat like a penpoint. Calcar. L. spur, used to denote any spur-shaped structure. Calcar avis, an elevation on the medial aspects of the lateral ventricles at the junction of occipital and temporal horns. Also calcarine sulcus of occipital ...
... part of the floor of the fourth ventricle that is shaped somewhat like a penpoint. Calcar. L. spur, used to denote any spur-shaped structure. Calcar avis, an elevation on the medial aspects of the lateral ventricles at the junction of occipital and temporal horns. Also calcarine sulcus of occipital ...
Packet 6- The neuron
... The nervous system, in partnership with the endocrine system, coordinates the body’s actions. The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron, although they make up only 10% of all nervous system cells. 90% of all cells in the NS are NOT neurons…they are glial cells. Neuron support crew (Dis ...
... The nervous system, in partnership with the endocrine system, coordinates the body’s actions. The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron, although they make up only 10% of all nervous system cells. 90% of all cells in the NS are NOT neurons…they are glial cells. Neuron support crew (Dis ...
The Basics: from Neuron to Neuron to the Brain
... Gustavus/Howard Hughes Medical Institute Outreach Program 2011 – 12 Curriculum Materials ...
... Gustavus/Howard Hughes Medical Institute Outreach Program 2011 – 12 Curriculum Materials ...
Peripheral Nervous System Structure of a Nerve Cranial Nerves
... The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the motor subdivision of the PNS that controls body activities automatically. It is composed of a special group of neurons that regulate cardiac muscle (the heart), smooth muscles (found in the walls of the visceral organs and blood vessels), and glands. Althoug ...
... The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the motor subdivision of the PNS that controls body activities automatically. It is composed of a special group of neurons that regulate cardiac muscle (the heart), smooth muscles (found in the walls of the visceral organs and blood vessels), and glands. Althoug ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.