Lecture 5 - Brain I - Linn
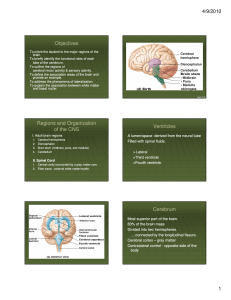
... between cerebral cortex and lower CNS centers. Composed of myelinated fibers bundled into large tracts. Commissures: fibers connecting gray areas of Commissures: the 2 hemisphere. > Corpus callosum (largest) ...
... between cerebral cortex and lower CNS centers. Composed of myelinated fibers bundled into large tracts. Commissures: fibers connecting gray areas of Commissures: the 2 hemisphere. > Corpus callosum (largest) ...
Glossary OF terms in Spinal Cord Injury Research
... controversial. Some investigators consider the period to be relatively short, i.e. several hours during which treatments can be given to prevent progressive or secondary tissue damage. Other investigators may consider the acute period to extend several weeks, during which there may be Wallerian dege ...
... controversial. Some investigators consider the period to be relatively short, i.e. several hours during which treatments can be given to prevent progressive or secondary tissue damage. Other investigators may consider the acute period to extend several weeks, during which there may be Wallerian dege ...
Anatomy of vertebrates` eyeball
... The complexity of the retina becomes simplified by appreciation of the fact that the retina is only three neurons deep. The first neuron, the photoreceptors (i.e. rods and cones), accounts for the outer layers, with each rod and cone having a sensory end organ (layer 9) lying outermost against pigme ...
... The complexity of the retina becomes simplified by appreciation of the fact that the retina is only three neurons deep. The first neuron, the photoreceptors (i.e. rods and cones), accounts for the outer layers, with each rod and cone having a sensory end organ (layer 9) lying outermost against pigme ...
... I can state the function of the medulla, including breathing, heart rate, arousal and sleep I can state the function of the cerebellum, including controlling balance, posture and movement I can describe the role of the limbic system in processing information for memories and influencing emotional an ...
CONSCIOUSNESS FROM NEURONS 1 Abstract. Consciousness
... with an intravenous catheter while they sleep; or the case, with better documentation of the true depth of sleep, where human subjects can continue pressing a switch upon a given signal even though fast asleep ...
... with an intravenous catheter while they sleep; or the case, with better documentation of the true depth of sleep, where human subjects can continue pressing a switch upon a given signal even though fast asleep ...
Central Nervous System - Amudala Assistance Area
... The action of the spinal cord Sensory neurons pick up signals from the skin and transfer that information to connector neurons in the spinal cord and/or brain. This information is relayed on to the motor neurons in the spinal cord to illicit a response. ...
... The action of the spinal cord Sensory neurons pick up signals from the skin and transfer that information to connector neurons in the spinal cord and/or brain. This information is relayed on to the motor neurons in the spinal cord to illicit a response. ...
PEP 3250 Anatomical Kinesiology
... Abduction = moving away from midline of the body (abducting someone means to ...
... Abduction = moving away from midline of the body (abducting someone means to ...
Chapter 15
... and NE function – sympathetic fibers also secrete enkephalin, substance P, neuropeptide Y, somatostatin, neurotensin, or gonadotropin-releasing hormone – parasympathetic fibers stimulate endothelial cells to release the gas, nitric oxide – causes vasodilation by inhibiting smooth muscle tone • funct ...
... and NE function – sympathetic fibers also secrete enkephalin, substance P, neuropeptide Y, somatostatin, neurotensin, or gonadotropin-releasing hormone – parasympathetic fibers stimulate endothelial cells to release the gas, nitric oxide – causes vasodilation by inhibiting smooth muscle tone • funct ...
Central Nervous System
... The action of the spinal cord Sensory neurons pick up signals from the skin and transfer that information to connector neurons in the spinal cord and/or brain. This information is relayed on to the motor neurons in the spinal cord to illicit a response. ...
... The action of the spinal cord Sensory neurons pick up signals from the skin and transfer that information to connector neurons in the spinal cord and/or brain. This information is relayed on to the motor neurons in the spinal cord to illicit a response. ...
The Endocrine System
... Located in a bony cavity just below the base of the brain Body’s master gland Secretes several hormones that regulate the function of other endocrine glands Regulates the body’s growth Stimulates milk production in women who are breast feeding Also secretes endorphins which are chemicals that act on ...
... Located in a bony cavity just below the base of the brain Body’s master gland Secretes several hormones that regulate the function of other endocrine glands Regulates the body’s growth Stimulates milk production in women who are breast feeding Also secretes endorphins which are chemicals that act on ...
PHS 398 (Rev. 9/04), Biographical Sketch Format Page
... This project is to study human embryonic stem cells, differentiated toward a dopamine neuronal phenotype, and injected into monkeys with chemically-induced dopamine depletion for their potential functional benefits on this model of Parkinson's disease. COMPLETED UO1-NS046028 NINDS (P.I.: E.D. Redmon ...
... This project is to study human embryonic stem cells, differentiated toward a dopamine neuronal phenotype, and injected into monkeys with chemically-induced dopamine depletion for their potential functional benefits on this model of Parkinson's disease. COMPLETED UO1-NS046028 NINDS (P.I.: E.D. Redmon ...
MS Word Version
... • The rapid signaling of directly-acting neurotransmitters is important for sensory-motor coordination, communication, and many other higher functions. • Rapid synaptic signaling is essential for coordinating sensory input with motor output, especially during athletic performances. ...
... • The rapid signaling of directly-acting neurotransmitters is important for sensory-motor coordination, communication, and many other higher functions. • Rapid synaptic signaling is essential for coordinating sensory input with motor output, especially during athletic performances. ...
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
... from the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord Relatively short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers Preganglionic neurosomas in lateral horns and nearby regions of spinal cord gray matter – Fibers exit spinal cord by way of spinal nerves T1 to L2 – Lead to nearby sympathetic chain ...
... from the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord Relatively short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers Preganglionic neurosomas in lateral horns and nearby regions of spinal cord gray matter – Fibers exit spinal cord by way of spinal nerves T1 to L2 – Lead to nearby sympathetic chain ...
Abstract
... best seen in the caudal and medial portions where the eye movements as described by Hikosaka and Wurtz SNpc is most developed. The localization of several cells (1981). Whereas only a very small percentage of LDR cells (n = 8) situated at the junction between the SNpc and located within the SNpc sho ...
... best seen in the caudal and medial portions where the eye movements as described by Hikosaka and Wurtz SNpc is most developed. The localization of several cells (1981). Whereas only a very small percentage of LDR cells (n = 8) situated at the junction between the SNpc and located within the SNpc sho ...
Neuronal fiber tracts connecting the brain and ventral nerve cord of
... These global studies gave little information regarding dendritic arborization in specific brain compartments, or axonal projections to distinct neuropile domains of the ventral nerve cord. More detailed information exists for a few selected DNs that were visualized (and often concomitantly physiologi ...
... These global studies gave little information regarding dendritic arborization in specific brain compartments, or axonal projections to distinct neuropile domains of the ventral nerve cord. More detailed information exists for a few selected DNs that were visualized (and often concomitantly physiologi ...
Famous Russian brains: historical attempts to understand intelligence
... scholars of Russian neurology and psychiatry, A.Ya. Kozhevnikov (1836^1902) and S. S. Korsakov (1854^1900), have been studied is largely unknown. A report of the results of this study was published by A. A. Kaputsin in 1925 providing a detailed neuroanatomical assessment of the brains. A considerabl ...
... scholars of Russian neurology and psychiatry, A.Ya. Kozhevnikov (1836^1902) and S. S. Korsakov (1854^1900), have been studied is largely unknown. A report of the results of this study was published by A. A. Kaputsin in 1925 providing a detailed neuroanatomical assessment of the brains. A considerabl ...
Chapter 8
... Control of Movement by the Brain Imitating and Comprehending Movements: Role of the Mirror Neuron System • Investigators found that neurons in an area of the rostral part of the ventral premotor cortex in the monkey brain (area F5) became active when monkeys saw people or other monkeys perform vari ...
... Control of Movement by the Brain Imitating and Comprehending Movements: Role of the Mirror Neuron System • Investigators found that neurons in an area of the rostral part of the ventral premotor cortex in the monkey brain (area F5) became active when monkeys saw people or other monkeys perform vari ...
Neuroscience - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... axonal process (5). Culturing cells for longer periods leads to a more dense network of dendritic processes and continued growth of axons. The cover photograph shows the characteristic features of neuronal cells grown in Neurobasal/B27 for 5 days. Dendritic processes have tapering arbors and frequen ...
... axonal process (5). Culturing cells for longer periods leads to a more dense network of dendritic processes and continued growth of axons. The cover photograph shows the characteristic features of neuronal cells grown in Neurobasal/B27 for 5 days. Dendritic processes have tapering arbors and frequen ...
Cautionary Observations on Preparing and Interpreting Brain
... In situ RNA Hybridization. The in situ RNA hybridization (ISH) technique visualizes cells that possess a particular messenger RNA. It is, thus, a powerful tool for directly detecting gene expression. Until recently, probes for hybridization were generated only after particular genes were cloned. The ...
... In situ RNA Hybridization. The in situ RNA hybridization (ISH) technique visualizes cells that possess a particular messenger RNA. It is, thus, a powerful tool for directly detecting gene expression. Until recently, probes for hybridization were generated only after particular genes were cloned. The ...
44 Nociceptive sensation. Somatic sensory analyzer
... level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
document
... sent along the afferent nerves to the CNS where they synapse with motor neurons of the same muscle. ...
... sent along the afferent nerves to the CNS where they synapse with motor neurons of the same muscle. ...
autonomic nervous system
... from the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord Relatively short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers Preganglionic neurosomas in lateral horns and nearby regions of spinal cord gray matter – Fibers exit spinal cord by way of spinal nerves T1 to L2 – Lead to nearby sympathetic chain ...
... from the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord Relatively short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers Preganglionic neurosomas in lateral horns and nearby regions of spinal cord gray matter – Fibers exit spinal cord by way of spinal nerves T1 to L2 – Lead to nearby sympathetic chain ...
Chapter 10 Somatic and Special Senses
... Outer Layer: The outer (fibrous) layer is the transparent ________________ at the front of the eye, and the white ___________on the exterior of the eye. Middle Layer: The _____________ coat is highly vascular and darkly pigmented and performs two functions: to nourish other tissues of the eye and to ...
... Outer Layer: The outer (fibrous) layer is the transparent ________________ at the front of the eye, and the white ___________on the exterior of the eye. Middle Layer: The _____________ coat is highly vascular and darkly pigmented and performs two functions: to nourish other tissues of the eye and to ...
MARMORATAl - Journal of Neuroscience
... antigens are first expressed and the order in which they are expressed by different cells or tissues. Three of the mAbs produced by Zipser and McKay (Zipser, B., and R. McKay (1981) Nature 289: 549-554) were screened: Lan3-1, Lan3-5, and Lan3-6. Each mAb shows a different pattern of labeling in the ...
... antigens are first expressed and the order in which they are expressed by different cells or tissues. Three of the mAbs produced by Zipser and McKay (Zipser, B., and R. McKay (1981) Nature 289: 549-554) were screened: Lan3-1, Lan3-5, and Lan3-6. Each mAb shows a different pattern of labeling in the ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.