NEURAL CONNECTIONS: Some You Use, Some You Lose
... as Patricia Goldman-Rakic, another neuroscientist who has conducted extensive research on primate brain development, puts it, The synaptic architecture of the cerebral cortex defines the limits of intellectual capacity, and the formation of appropriate synapses is the ultimate step in establishing t ...
... as Patricia Goldman-Rakic, another neuroscientist who has conducted extensive research on primate brain development, puts it, The synaptic architecture of the cerebral cortex defines the limits of intellectual capacity, and the formation of appropriate synapses is the ultimate step in establishing t ...
Brain Imaging Technologies and Their Applications in Neuroscience
... release gamma rays oriented in opposite directions along exactly the same line. ...
... release gamma rays oriented in opposite directions along exactly the same line. ...
1) Which is NOT a characteristic of living organisms
... A) The ossicles are found in your inner ear. B) The ossicles are tiny bones that amplify movement caused by sound waves. C) The ossicles (little calcium crystals on a gelatinous mound) help with proprioception. D) If a high frequency pitch is heard the wide floppy portion of the basilar membrane mov ...
... A) The ossicles are found in your inner ear. B) The ossicles are tiny bones that amplify movement caused by sound waves. C) The ossicles (little calcium crystals on a gelatinous mound) help with proprioception. D) If a high frequency pitch is heard the wide floppy portion of the basilar membrane mov ...
Pathophysiology of Epilepsy
... Pathophysiology of Epilepsy Neurons transition from normal firing pattern to interictal bursts to an ictal stage Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy the most prevalent focal epilepsy ...
... Pathophysiology of Epilepsy Neurons transition from normal firing pattern to interictal bursts to an ictal stage Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy the most prevalent focal epilepsy ...
Neural Coding - Computing Science and Mathematics
... • Neurons that receive inputs from this neuron have 200 msecs to “decode” the signal from the neuron – Information coded in spikes fired by neuron in a 200 msec time window ...
... • Neurons that receive inputs from this neuron have 200 msecs to “decode” the signal from the neuron – Information coded in spikes fired by neuron in a 200 msec time window ...
Chapter 18: Control and Coordination
... types of neurons work together. The illustration on this page shows how the sound of a breaking window might startle you and cause you to drop a glass of water. SENSORY NEURONS When you hear a loud noise, receptors in your ears—the specialized endings of sensory neurons—are stimulated. These sensory ...
... types of neurons work together. The illustration on this page shows how the sound of a breaking window might startle you and cause you to drop a glass of water. SENSORY NEURONS When you hear a loud noise, receptors in your ears—the specialized endings of sensory neurons—are stimulated. These sensory ...
The Muscular/Skeletal System
... • The myelin sheath surrounding the nerves contains cerebrospinal fluid (CFS), which surrounds and baths the nerve. The CFS is most abundant in the brain and spine, where nerves are most numerous. It is a purified product of the blood, strained out in the ventricles, or cavities of the brain, and p ...
... • The myelin sheath surrounding the nerves contains cerebrospinal fluid (CFS), which surrounds and baths the nerve. The CFS is most abundant in the brain and spine, where nerves are most numerous. It is a purified product of the blood, strained out in the ventricles, or cavities of the brain, and p ...
Spinal Cord
... Physiological response produced by activation of specific types of nerve fibers Aδand C fibres that carry noxious sensory information bradykinin, serotonin, prostaglandins, cytokines, ...
... Physiological response produced by activation of specific types of nerve fibers Aδand C fibres that carry noxious sensory information bradykinin, serotonin, prostaglandins, cytokines, ...
Engineering new synaptic connections in the C. elegans connectome
... development of super-resolution methods for obtaining detailed maps of synaptic connectivity has paved the way for uncovering the connectomes of entire brains or brain regions. We describe a third and complementary new strategy for investigating and manipulating neural circuits: the artificial inser ...
... development of super-resolution methods for obtaining detailed maps of synaptic connectivity has paved the way for uncovering the connectomes of entire brains or brain regions. We describe a third and complementary new strategy for investigating and manipulating neural circuits: the artificial inser ...
Nervous System - Warren County Schools
... but growth and maturation continues for several years (new evidence!) The brain reaches maximum weight as a young adult However, we can always grow dendrites! Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... but growth and maturation continues for several years (new evidence!) The brain reaches maximum weight as a young adult However, we can always grow dendrites! Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Impaired intracellular trafficking defines early Parkinson`s disease
... bodies and Lewy neurites. a-Synuclein is encoded by the gene SNCA. Dopamine (DA): a neurotransmitter derived from the amino acid tyrosine. It is released by DA neurons of the midbrain onto medium spiny neurons in the striatum to help regulate movement. Glucocerebrosidase (GBA): an enzyme that cleave ...
... bodies and Lewy neurites. a-Synuclein is encoded by the gene SNCA. Dopamine (DA): a neurotransmitter derived from the amino acid tyrosine. It is released by DA neurons of the midbrain onto medium spiny neurons in the striatum to help regulate movement. Glucocerebrosidase (GBA): an enzyme that cleave ...
Not all vosial categorization tasks require attention
... object, while the original HMAX version of the model (Riesenhuber & Poggio, 1999) predicted recovery from suppression for “sufficiently dissimilar” clutter objects, (i.e. prediction of a U-shaped relationship between clutter tolerance and shape similarity of the clutter objects to the preferred obje ...
... object, while the original HMAX version of the model (Riesenhuber & Poggio, 1999) predicted recovery from suppression for “sufficiently dissimilar” clutter objects, (i.e. prediction of a U-shaped relationship between clutter tolerance and shape similarity of the clutter objects to the preferred obje ...
Peripheral Nervous System, Autonomic Nervous System and reflexes
... the ventral ramus white ramus communicans paravertrebral ganglion in the sympathetic chain. • Preganglion axon may: – Synapse with a same level sympathetic ganglion chain neuron. – Travel up or downward through the sympathetic chain in the paravertebral region to another ganglion. • (Postgangli ...
... the ventral ramus white ramus communicans paravertrebral ganglion in the sympathetic chain. • Preganglion axon may: – Synapse with a same level sympathetic ganglion chain neuron. – Travel up or downward through the sympathetic chain in the paravertebral region to another ganglion. • (Postgangli ...
Orbitofrontal Cortex and Its Contribution to Decision
... When the value of the two drinks is the same, the neuronal firing rate is also equivalent. ...
... When the value of the two drinks is the same, the neuronal firing rate is also equivalent. ...
Notes and comments - Paradigm Shift Now
... Quasicrystals are physical structures which may need QM to be described. According to Roger Penrose, the quasicrystal assemble cannot be obtained by a local adding of atoms one at a time. Rather, a non-local quantum mechanical process must be involved; something like an evolving quantum superpositio ...
... Quasicrystals are physical structures which may need QM to be described. According to Roger Penrose, the quasicrystal assemble cannot be obtained by a local adding of atoms one at a time. Rather, a non-local quantum mechanical process must be involved; something like an evolving quantum superpositio ...
network - Ohio University
... Excitations can be: mainly in one direction signal transformation; in both directions supplementing missing information agreeing upon hypotheses and strengthening weak signals. most excitatory neurons are bi-directional. Inhibition: controls mutual excitations, necessary to avoid extra f ...
... Excitations can be: mainly in one direction signal transformation; in both directions supplementing missing information agreeing upon hypotheses and strengthening weak signals. most excitatory neurons are bi-directional. Inhibition: controls mutual excitations, necessary to avoid extra f ...
EN Sokolov`s Neural Model of Stimuli as Neuro
... The reflex arc activity can be represented as follows: receptors are specific sensory devices that can perceive and react to certain physical impacts of stimuli as signals. Receptors are in turn associated with selective detectors – neurons selectively responding to certain stimuli – and this connec ...
... The reflex arc activity can be represented as follows: receptors are specific sensory devices that can perceive and react to certain physical impacts of stimuli as signals. Receptors are in turn associated with selective detectors – neurons selectively responding to certain stimuli – and this connec ...
Slide ()
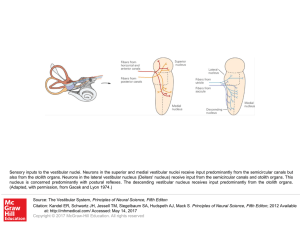
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
Autonomic Nervous System I and II
... An axon may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or Sympathetic chains or An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postganglionic neurons there or An axon may pass through the sy ...
... An axon may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or Sympathetic chains or An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postganglionic neurons there or An axon may pass through the sy ...
File - Wk 1-2
... The submucosal and myenteric plexus’ of the gastrointestinal tract are composed of ganglia The myenteric ganglia form a continuous network from the upper oesophagus to the internal anal sphincter. These act to regulate GIS motility (the movement along the tract) The submucosal ganglia are conc ...
... The submucosal and myenteric plexus’ of the gastrointestinal tract are composed of ganglia The myenteric ganglia form a continuous network from the upper oesophagus to the internal anal sphincter. These act to regulate GIS motility (the movement along the tract) The submucosal ganglia are conc ...
Comparison of nerve cord development
... by the antagonistic activity of homologous secreted molecules decapentaplegic/BMP-4 and short gastrulation/chordin (see De Robertis and Sasai, 1996; Arendt and Nübler-Jung, 1997; and references therein), and the resulting neurogenic territory forms on both sides of a specialized population of midlin ...
... by the antagonistic activity of homologous secreted molecules decapentaplegic/BMP-4 and short gastrulation/chordin (see De Robertis and Sasai, 1996; Arendt and Nübler-Jung, 1997; and references therein), and the resulting neurogenic territory forms on both sides of a specialized population of midlin ...
Introduction to the Human Body
... Try to answer the questions even if you are not sure. What is the difference between anatomy and physiology? What is a cell? What is an organ? ...
... Try to answer the questions even if you are not sure. What is the difference between anatomy and physiology? What is a cell? What is an organ? ...
Text S1.
... All excitatory synaptic weights were initially set to 0.05 and could vary between zero and 0.1 due to STDP. At the maximal weight, each spike would have a 50% probability of evoking a spike in the postsynaptic neuron, due to its summation with intrinsic noise (Figure S1-7). The synaptic weights for ...
... All excitatory synaptic weights were initially set to 0.05 and could vary between zero and 0.1 due to STDP. At the maximal weight, each spike would have a 50% probability of evoking a spike in the postsynaptic neuron, due to its summation with intrinsic noise (Figure S1-7). The synaptic weights for ...
Chapter 15: Chemical Control of the Brain and Behavior
... Copyright © 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... Copyright © 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.