PPT2
... The processes for computing the region and the boundary are tightly coupled The regional properties diffuse within each region and tend to become constant The interruption of the spreading of regional information by boundaries results in sharp discontinuities in the responses across two different re ...
... The processes for computing the region and the boundary are tightly coupled The regional properties diffuse within each region and tend to become constant The interruption of the spreading of regional information by boundaries results in sharp discontinuities in the responses across two different re ...
Ectodermal Derivtives
... the future cervical region and then extends both in cranial and caudal direction ...
... the future cervical region and then extends both in cranial and caudal direction ...
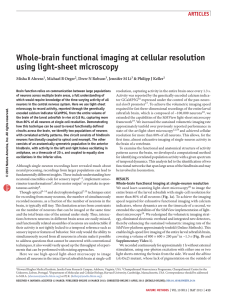
Whole-brain functional imaging at cellular resolution using light
... Brain function relies on communication between large populations of neurons across multiple brain areas, a full understanding of which would require knowledge of the time-varying activity of all neurons in the central nervous system. Here we use light-sheet microscopy to record activity, reported th ...
... Brain function relies on communication between large populations of neurons across multiple brain areas, a full understanding of which would require knowledge of the time-varying activity of all neurons in the central nervous system. Here we use light-sheet microscopy to record activity, reported th ...
Anatomy_Physiology_One_Course Outlines and Scope and
... Explain the anatomical and functional classification of the nervous system. Identify the functions of neurons and neuroglia. Draw a neuron, label its parts, and give the functions of each. Classify three types of neurons in terms of their function. List the events that lead to the generation of a ne ...
... Explain the anatomical and functional classification of the nervous system. Identify the functions of neurons and neuroglia. Draw a neuron, label its parts, and give the functions of each. Classify three types of neurons in terms of their function. List the events that lead to the generation of a ne ...
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular
... vestibular ganglion, which looks like a nodule (enlargement) on the vestibular nerve - axons from vestibular neurons get together with axons of the spiral ganglion (auditory) and give rise to vestibulocochlear nerve = VIII cranial nerve - vestibular axons synapse within vestibular nuclei in medulla, ...
... vestibular ganglion, which looks like a nodule (enlargement) on the vestibular nerve - axons from vestibular neurons get together with axons of the spiral ganglion (auditory) and give rise to vestibulocochlear nerve = VIII cranial nerve - vestibular axons synapse within vestibular nuclei in medulla, ...
Topography of Modular Subunits in the Mushroom Bodies of the
... each slab, thus interacting with the axons of only less than half of Kenyon cells that constitute each slab (Fig. 6B). Different extrinsic neurons with segmented dendrites appear to interact with different sets of dark or light slabs: dendrites of some neurons cover up to 13–14 slabs, whereas those ...
... each slab, thus interacting with the axons of only less than half of Kenyon cells that constitute each slab (Fig. 6B). Different extrinsic neurons with segmented dendrites appear to interact with different sets of dark or light slabs: dendrites of some neurons cover up to 13–14 slabs, whereas those ...
Motor Cortex
... Corticospinal tract Also called Pyramidal tract Motor cortex ---> spinal cord uninterrupted axon 2/3 of axons from motor cortex 1/3 from somatosensory cortex Decussates at medullary pyramids Contralateral control movement ~ ...
... Corticospinal tract Also called Pyramidal tract Motor cortex ---> spinal cord uninterrupted axon 2/3 of axons from motor cortex 1/3 from somatosensory cortex Decussates at medullary pyramids Contralateral control movement ~ ...
Sensa1on and Percep1on
... • Sensa&on in the olfactory system begins when chemicals called odourants enter the nose • Chemical odourants are transduced into neural signals when they come into contact with the cilia of olfactory sensory receptor neurons located in the nasal mucosa • When odourants enter the nose they bind ...
... • Sensa&on in the olfactory system begins when chemicals called odourants enter the nose • Chemical odourants are transduced into neural signals when they come into contact with the cilia of olfactory sensory receptor neurons located in the nasal mucosa • When odourants enter the nose they bind ...
Slide 1 - TeacherWeb
... • If asked to select these objects with their left hand, they succeeded • The right side of the brain doesn’t control speech ...
... • If asked to select these objects with their left hand, they succeeded • The right side of the brain doesn’t control speech ...
Lecture 9B
... • Isochronicity in at least some neuronal networks seems to be achieved via differential myelination and myelination may be experience-dependent. • Considering the many variables affecting conduction delays in an adult brain, genetic instruction alone would seem inadequate to specify the optimal con ...
... • Isochronicity in at least some neuronal networks seems to be achieved via differential myelination and myelination may be experience-dependent. • Considering the many variables affecting conduction delays in an adult brain, genetic instruction alone would seem inadequate to specify the optimal con ...
Central Nervous System (CNS) The Brain Embryonic Development
... • Pineal gland – extends from the posterior border and secretes melatonin • Melatonin – a hormone involved with sleep regulation, sleep-wake cycles, and mood ...
... • Pineal gland – extends from the posterior border and secretes melatonin • Melatonin – a hormone involved with sleep regulation, sleep-wake cycles, and mood ...
Chemical Effects of Ecstasy on the Human Brain
... user to become overcome with euphoria. Though this may seem like a positive effect, over time the brain can no longer identify the natural serotonin and therefore needs Ecstasy in order to balance a person’s mood. Ecstasy causes serotonin neurons to release high amounts of serotonin, which are store ...
... user to become overcome with euphoria. Though this may seem like a positive effect, over time the brain can no longer identify the natural serotonin and therefore needs Ecstasy in order to balance a person’s mood. Ecstasy causes serotonin neurons to release high amounts of serotonin, which are store ...
PowerPoint 11: Nemertea
... Most important in which habitats? Absent in deep-sea, pelagic forms Role in excretion? ...
... Most important in which habitats? Absent in deep-sea, pelagic forms Role in excretion? ...
Unit – M Neuron, Impulse Generation, and Reflex Arc Structures and
... Each axon branches off and ends with a swelled tip or terminal knob that lies close to but not touching the dendrite of another neuron. (or an organ). The entire region is called a synapse. ...
... Each axon branches off and ends with a swelled tip or terminal knob that lies close to but not touching the dendrite of another neuron. (or an organ). The entire region is called a synapse. ...
Population vectors and motor cortex: neural coding or
... that show correlations with neural activity. A common finding has been that many parameters show some correlation, but that the correlations are greatest for movement direction and smallest for acceleration6. Because acceleration is tightly linked to force (according to Newtonian mechanics), this fi ...
... that show correlations with neural activity. A common finding has been that many parameters show some correlation, but that the correlations are greatest for movement direction and smallest for acceleration6. Because acceleration is tightly linked to force (according to Newtonian mechanics), this fi ...
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
... hands at the sides, palms facing forward, feet together. Anatomical directions refer to the patient’s left or right. Each direction is paired with an opposite; caudal is the opposite of cranial, anterior is the opposite of posterior. A lateral view is from the side. An anterior view is from the fron ...
... hands at the sides, palms facing forward, feet together. Anatomical directions refer to the patient’s left or right. Each direction is paired with an opposite; caudal is the opposite of cranial, anterior is the opposite of posterior. A lateral view is from the side. An anterior view is from the fron ...
Grounded cognition Mirror neurons Mirror neurons Mirror neurons in
... => observer-centered (egocentric) spatial framework may be used ...
... => observer-centered (egocentric) spatial framework may be used ...
AandPChp7Brain
... 1. CSF is produced by the choroid plexus of each ventricle. 2. CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. 3. CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4. CSF is absorbed into the ...
... 1. CSF is produced by the choroid plexus of each ventricle. 2. CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. 3. CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4. CSF is absorbed into the ...
Lab Ex. 24 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves
... • The Spinal cord shows enlargements in those areas that will deal with the limbs – Cervical enlargement (scapular region) – Lumbar enlargement (pelvic region) ...
... • The Spinal cord shows enlargements in those areas that will deal with the limbs – Cervical enlargement (scapular region) – Lumbar enlargement (pelvic region) ...
Purinergic signaling in acupuncture
... Purinergic signaling and electroacupuncture Electroacupuncture is a form of acupuncture where a small electric current is passed between pairs of acupuncture needles. This is thought to augment traditional acupuncture and is believed to be particularly helpful in treating pain. The supraspinal antin ...
... Purinergic signaling and electroacupuncture Electroacupuncture is a form of acupuncture where a small electric current is passed between pairs of acupuncture needles. This is thought to augment traditional acupuncture and is believed to be particularly helpful in treating pain. The supraspinal antin ...
Adult spinal cord
... • Posterior gray horn contains somatic and visceral sensory nuclei • Somatic Nervous System (SNS)- The efferent division of the nervous system that innervates skeletal muscle. • Visceral- Pertaining to viscera or their outer coverings. • Viscera- Organs in the ventral body cavity. ...
... • Posterior gray horn contains somatic and visceral sensory nuclei • Somatic Nervous System (SNS)- The efferent division of the nervous system that innervates skeletal muscle. • Visceral- Pertaining to viscera or their outer coverings. • Viscera- Organs in the ventral body cavity. ...
Attention and Consciousness
... Brain basis of conscious experience Results that conscious context activate larger regions in brain were confirmed by observing responses of individual neurons, through electrodes placed in different brain areas. Another example is conscious and unconscious pain in which unconscious pain barely ...
... Brain basis of conscious experience Results that conscious context activate larger regions in brain were confirmed by observing responses of individual neurons, through electrodes placed in different brain areas. Another example is conscious and unconscious pain in which unconscious pain barely ...
What Musicians can Learn about Practicing from Current Brain
... ways to make our practicing more efficient and effective, as well as what to do when we have too much music and not enough time to learn it. After first explaining what happens when you learn something new and how our brains are different from a non-musician’s brain, surprising discoveries about the ...
... ways to make our practicing more efficient and effective, as well as what to do when we have too much music and not enough time to learn it. After first explaining what happens when you learn something new and how our brains are different from a non-musician’s brain, surprising discoveries about the ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.