Lecoq J, Savall J, Vucinic D, Grewe BF, Kim H, Li
... and LM) that were adjacent and separated by only ~1.2 mm (Fig. 2b). On the day of imaging we brought the two GRIN microendoscopes to the two neocortical areas of the anesthetized mouse. After optical alignment of each imaging arm to its microendoscope, we visualized layer 2/3 parvalbumin neurons in ...
... and LM) that were adjacent and separated by only ~1.2 mm (Fig. 2b). On the day of imaging we brought the two GRIN microendoscopes to the two neocortical areas of the anesthetized mouse. After optical alignment of each imaging arm to its microendoscope, we visualized layer 2/3 parvalbumin neurons in ...
the human body: an orientation
... sally acceptable set of reference terms that allows body structures to be located and identified with a high degree of clarity. Initially, students might have diffi culties with the language used to describe anatomy and physiology, but without such a special vocabulary, confusion is bound to occur. ...
... sally acceptable set of reference terms that allows body structures to be located and identified with a high degree of clarity. Initially, students might have diffi culties with the language used to describe anatomy and physiology, but without such a special vocabulary, confusion is bound to occur. ...
The Brain - HallquistCPHS.com
... 4. A technique that produces clearer images of the brain by using magnetic fields and radio waves is known as _ 5. By taking pictures less than a second apart, the ...
... 4. A technique that produces clearer images of the brain by using magnetic fields and radio waves is known as _ 5. By taking pictures less than a second apart, the ...
2006 Newsletter
... with methotrexate to reduce signs and symptoms in adult patients with moderately-toseverely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapies. ...
... with methotrexate to reduce signs and symptoms in adult patients with moderately-toseverely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapies. ...
Sensory input: Sensory structures, classification by function
... 3. analgesia prevents the perception of pain a. intrinsic analgesic system blocks transmission from the sensory neuron to interneurons b. extrinsic analgesia can be applied at the level of the receptor (aspirin), the afferent pathway (benzocaine blocks the transmission of action potentials in the af ...
... 3. analgesia prevents the perception of pain a. intrinsic analgesic system blocks transmission from the sensory neuron to interneurons b. extrinsic analgesia can be applied at the level of the receptor (aspirin), the afferent pathway (benzocaine blocks the transmission of action potentials in the af ...
Generic Visual Perception Processor
... shadows of nostrils. The results are calculated to the end of the image frame being analyzed, and the microprocessor analyzes the resulting histograms to determine characteristics indicative of nostrils, such as the spacing and shaping and shape of the nostrils. Then, the microprocessor directs the ...
... shadows of nostrils. The results are calculated to the end of the image frame being analyzed, and the microprocessor analyzes the resulting histograms to determine characteristics indicative of nostrils, such as the spacing and shaping and shape of the nostrils. Then, the microprocessor directs the ...
Neuronal Differentiation in The Cerebral Cortex of
... the 17th prenatal day, dispersed to the deeper regions during the following days of gestation. The neurons showing impregnations formed cell groups during the 19th prenatal day. These cells were arranged on an axis; whose perikaryons were touching each other. At the beginning of the postnatal period ...
... the 17th prenatal day, dispersed to the deeper regions during the following days of gestation. The neurons showing impregnations formed cell groups during the 19th prenatal day. These cells were arranged on an axis; whose perikaryons were touching each other. At the beginning of the postnatal period ...
Ion Channels and Neuronal Dysfunction in Multiple Sclerosis
... changes are responsible for cerebellar ataxia in these mutants.15 To determine whether different subtypes of sodium channels are expressed in Purkinje cells in demyelinating disorders, Black et al6 first studied the taiep rat, a mutant in which myelin is formed normally but subsequently degenerates ...
... changes are responsible for cerebellar ataxia in these mutants.15 To determine whether different subtypes of sodium channels are expressed in Purkinje cells in demyelinating disorders, Black et al6 first studied the taiep rat, a mutant in which myelin is formed normally but subsequently degenerates ...
Connexionism and Computationalism
... As explained in class, biological neural networks, following the work of Golgi and Cajal have been found to comprise a network of neurons. Each neuron has a clear structure with input “dendrites”, a processing “soma” and an output “axon”. Each neuron is connected on average to around 1000 other neur ...
... As explained in class, biological neural networks, following the work of Golgi and Cajal have been found to comprise a network of neurons. Each neuron has a clear structure with input “dendrites”, a processing “soma” and an output “axon”. Each neuron is connected on average to around 1000 other neur ...
Student Presentation - UNM Computer Science
... “Our artificial automata are much smaller than natural automata in what they do and in the number of components they have, and they’re phenomenally more expensive in terms of space and energy. Why is this so?” Von Neumann also says that producing the answer to this is hopeless, but that there are a ...
... “Our artificial automata are much smaller than natural automata in what they do and in the number of components they have, and they’re phenomenally more expensive in terms of space and energy. Why is this so?” Von Neumann also says that producing the answer to this is hopeless, but that there are a ...
(30 MCQ answers). - Blackwell Publishing
... satiety centre in the ventromedial hypothalamus. But problems arose with this dualcentre hypothesis. Lesions of the ventromedial hypothalamus were found to act indirectly by increasing the secretion of insulin by the pancreas, which in turn reduces plasma glucose concentration, resulting in feeding. ...
... satiety centre in the ventromedial hypothalamus. But problems arose with this dualcentre hypothesis. Lesions of the ventromedial hypothalamus were found to act indirectly by increasing the secretion of insulin by the pancreas, which in turn reduces plasma glucose concentration, resulting in feeding. ...
2016 Poster Abstracts - Molecular Psychiatry Association
... Deletions in the 16.5kb mitochondrial genome have been implicated in a number of mitochondrial disorders, many of which are phenotypically complex but often display overlapping symptoms associated with muscle and/or neurological dysfunction due to the high energy demands of these tissues. While ther ...
... Deletions in the 16.5kb mitochondrial genome have been implicated in a number of mitochondrial disorders, many of which are phenotypically complex but often display overlapping symptoms associated with muscle and/or neurological dysfunction due to the high energy demands of these tissues. While ther ...
Phase IIB / PHGY 825 Organization of the Brain Stem Organization
... important for coordinating a variety of stereotyped behaviors related to the visceral functions of the vagus nerve: • Gastrointestinal responses ...
... important for coordinating a variety of stereotyped behaviors related to the visceral functions of the vagus nerve: • Gastrointestinal responses ...
Design Features in Vertebrate Sensory Systems
... issues many second order branches. These nuclear complex (Brugge and Geisler, collaterals result in information from a sin- 1978; Warr, 1982). This is a precisely orgagle ganglion cell being distributed to sev- nized array of many different types of neueral structures in the central nervous sys- ron ...
... issues many second order branches. These nuclear complex (Brugge and Geisler, collaterals result in information from a sin- 1978; Warr, 1982). This is a precisely orgagle ganglion cell being distributed to sev- nized array of many different types of neueral structures in the central nervous sys- ron ...
SPHS 4050, Neurological Bases, PP 08b
... Whole bundles of axons course together in pathways, like those you see in the illustration above. ...
... Whole bundles of axons course together in pathways, like those you see in the illustration above. ...
Mathematical neuroscience: from neurons to circuits to systems
... conductance cannot be explained by passive properties alone. Moreover, as seen in Fig. 1a, conductance is often observed to not only depend on voltage but also to change over time. In order to explain the anomalous rectification observed in many neuronal currents, Hodgkin and Huxley [11] proposed the ...
... conductance cannot be explained by passive properties alone. Moreover, as seen in Fig. 1a, conductance is often observed to not only depend on voltage but also to change over time. In order to explain the anomalous rectification observed in many neuronal currents, Hodgkin and Huxley [11] proposed the ...
Review Energy limitation as a selective pressure on the evolution of
... are equally applicable throughout the nervous system. Examples are taken from a wide range of sensory modalities in both vertebrates and invertebrates. We aim to place the studies we review into an evolutionary framework. We combine experimentally determined measures of energy consumption from whole ...
... are equally applicable throughout the nervous system. Examples are taken from a wide range of sensory modalities in both vertebrates and invertebrates. We aim to place the studies we review into an evolutionary framework. We combine experimentally determined measures of energy consumption from whole ...
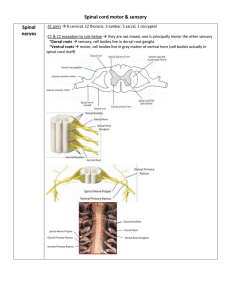
Changes in spinal cord
... *branches or interneurons at terminal level *mainly function to control “automatic functions” such as walking or posture -tectospinal *from superior colliculus to ventral horn of cervical region *decussates at level of colliculus *only functions in upper limb/neck *tectum is associated with visual m ...
... *branches or interneurons at terminal level *mainly function to control “automatic functions” such as walking or posture -tectospinal *from superior colliculus to ventral horn of cervical region *decussates at level of colliculus *only functions in upper limb/neck *tectum is associated with visual m ...
vocabulary - anatomy and physiology one
... Discuss the three major function of the cranial nerves. Distinguish between sensory, motor and mixed nerves. Name the cranial nerves that function only as sensory nerves and name the sense associated with each. Name the cranial nerves that are somatic motor and proprioception only. Name the muscles ...
... Discuss the three major function of the cranial nerves. Distinguish between sensory, motor and mixed nerves. Name the cranial nerves that function only as sensory nerves and name the sense associated with each. Name the cranial nerves that are somatic motor and proprioception only. Name the muscles ...
Nervous System (Complete)
... • Anterior and posterior roots unite to form the trunk of a spinal nerve at the level of their respective intervertebral foramina. The trunk is short. Here the motor and sensory fibers become mixed together, so that a spinal nerve is made up of a mixture of motor and sensory fibers. ...
... • Anterior and posterior roots unite to form the trunk of a spinal nerve at the level of their respective intervertebral foramina. The trunk is short. Here the motor and sensory fibers become mixed together, so that a spinal nerve is made up of a mixture of motor and sensory fibers. ...
Functional Integration of Dopaminergic Neurons Directly Converted
... fibroblasts were cultured with Shh and FGF8 and the efficiency of iDA neuron generation was determined. Cultures treated with Shh and FGF8 generated about 5% Pitx3-eGFP+ cells, which is 2-fold more than in cultures treated with bFGF alone (Figure S1H). These data suggest that neurotrophic factors ar ...
... fibroblasts were cultured with Shh and FGF8 and the efficiency of iDA neuron generation was determined. Cultures treated with Shh and FGF8 generated about 5% Pitx3-eGFP+ cells, which is 2-fold more than in cultures treated with bFGF alone (Figure S1H). These data suggest that neurotrophic factors ar ...
The Brain`s Response to Drugs Teacher`s Guide
... to the axon. The axons then transmit the messages, which are in the form of electrical impulses, to other neurons or body tissues. The axons of many neurons are covered in a fatty substance known as myelin. Myelin has several functions. One of its most important is to increase the rate at which nerv ...
... to the axon. The axons then transmit the messages, which are in the form of electrical impulses, to other neurons or body tissues. The axons of many neurons are covered in a fatty substance known as myelin. Myelin has several functions. One of its most important is to increase the rate at which nerv ...
Cnidarians and the evolutionary origin of the nervous system Review
... physiological complexity observed in the regionalized nervous system and eye-bearing sensory complex (Rhopalia) of cnidarians, an increasing number of examples indicating the evolutionary convergence in both nervous and sensory systems (Nishikawa 2002) make it difficult to simply compare cnidarian a ...
... physiological complexity observed in the regionalized nervous system and eye-bearing sensory complex (Rhopalia) of cnidarians, an increasing number of examples indicating the evolutionary convergence in both nervous and sensory systems (Nishikawa 2002) make it difficult to simply compare cnidarian a ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.