Slide 1
... symbolic rules do not reflect reasoning processes performed by humans. • Biological neural systems can capture highly parallel computations based on representations that are distributed over many neurons. • They learn and generalize from training data; no need for programming it all... • They are ve ...
... symbolic rules do not reflect reasoning processes performed by humans. • Biological neural systems can capture highly parallel computations based on representations that are distributed over many neurons. • They learn and generalize from training data; no need for programming it all... • They are ve ...
kbook or W NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
... tools to ask the question “What does it mean to be human?” ...
... tools to ask the question “What does it mean to be human?” ...
ANS: c, p. 46, F, LO=2.1, (1) - test bank and solution manual for your
... a) acting as insulation and providing structure to surrounding neurons Correct. This answer defines two roles of glial cells. b) shaping cells and moving new neurons into place Incorrect. Glial cells provide structure and insulation to neurons. c) regulating metabolic activity and serving as pain de ...
... a) acting as insulation and providing structure to surrounding neurons Correct. This answer defines two roles of glial cells. b) shaping cells and moving new neurons into place Incorrect. Glial cells provide structure and insulation to neurons. c) regulating metabolic activity and serving as pain de ...
Citron-Kinase, a Protein Essential to Cytokinesis in Neuronal
... follows: kinase domain: GAGTCGGTAGCGGAGAGATGTT and CCCGACACAACAGAC TCAGATC; C itron-nonkinase (N) domain: GTGTGC TAGAGAAGTGAC TGCG and CC TCATCGAGTTGTTTGGACAG, TCGCAACAGC TGTAC TGTCATC and CATC TGC TTTGGC TGTATTTGC, TATC TATTCATGGTGCCGTTG and AGGAGGAGTTC TTCAGGC TGAG. PCR products were cloned into T ...
... follows: kinase domain: GAGTCGGTAGCGGAGAGATGTT and CCCGACACAACAGAC TCAGATC; C itron-nonkinase (N) domain: GTGTGC TAGAGAAGTGAC TGCG and CC TCATCGAGTTGTTTGGACAG, TCGCAACAGC TGTAC TGTCATC and CATC TGC TTTGGC TGTATTTGC, TATC TATTCATGGTGCCGTTG and AGGAGGAGTTC TTCAGGC TGAG. PCR products were cloned into T ...
14. Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... II. Protection and Support of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is protected by three layers of tissue, called spinal meninges, that surround the cord (Fig. 14.3): A. The dura mater is the outermost layer, and it forms a tough protective coating. Between the dura mater and the surrounding bone of the ...
... II. Protection and Support of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is protected by three layers of tissue, called spinal meninges, that surround the cord (Fig. 14.3): A. The dura mater is the outermost layer, and it forms a tough protective coating. Between the dura mater and the surrounding bone of the ...
Projections From the Ventral Cochlear Nucleus to the Dorsal
... type of retrogradely-labeled neuron observed in the granule cell domain (Fig. 1D). This cell type was also less commonly labeled by DCN injections than granule cells but more frequently encountered than unipolar brush cells. The most striking light microscopic feature of the chestnut cell is its unu ...
... type of retrogradely-labeled neuron observed in the granule cell domain (Fig. 1D). This cell type was also less commonly labeled by DCN injections than granule cells but more frequently encountered than unipolar brush cells. The most striking light microscopic feature of the chestnut cell is its unu ...
Evolution of the Size and Functional Areas of the Human Brain
... Behavioral implications of anatomical differences are reviewed in the subsequent sections. Our knowledge of anatomical differences is further advanced than our knowledge of what these differences might mean behaviorally. In general, however, it is generally assumed, implicitly or explicitly, that mo ...
... Behavioral implications of anatomical differences are reviewed in the subsequent sections. Our knowledge of anatomical differences is further advanced than our knowledge of what these differences might mean behaviorally. In general, however, it is generally assumed, implicitly or explicitly, that mo ...
Differentiation in vitro of sympathetic cells from chick
... somitic mesenchyme in this developmental pathway which could not be replaced by either heart or limb-bud mesenchyme in these conditions was also demonstrated. Ventral neural tube also appeared to favour this line of differentiation. However, neural tube and crest in an organ culture system (Bjerre, ...
... somitic mesenchyme in this developmental pathway which could not be replaced by either heart or limb-bud mesenchyme in these conditions was also demonstrated. Ventral neural tube also appeared to favour this line of differentiation. However, neural tube and crest in an organ culture system (Bjerre, ...
CHAPTER TWO - Test Bank 1
... a) acting as insulation and providing structure to surrounding neurons Correct. This answer defines two roles of glial cells. b) shaping cells and moving new neurons into place Incorrect. Glial cells provide structure and insulation to neurons. c) regulating metabolic activity and serving as pain de ...
... a) acting as insulation and providing structure to surrounding neurons Correct. This answer defines two roles of glial cells. b) shaping cells and moving new neurons into place Incorrect. Glial cells provide structure and insulation to neurons. c) regulating metabolic activity and serving as pain de ...
Subcircuit-specific neuromodulation in the prefrontal cortex
... et al., 2011). Recently, it has become evident that L5 PT and IT neurons within rodent PFC possess distinct intrinsic properties, local connectivity, and long-range inputs. Although most of these differences have been characterized in rodents, different categories of PFC pyramidal neurons are also p ...
... et al., 2011). Recently, it has become evident that L5 PT and IT neurons within rodent PFC possess distinct intrinsic properties, local connectivity, and long-range inputs. Although most of these differences have been characterized in rodents, different categories of PFC pyramidal neurons are also p ...
Full Text
... geometric-optical illusions in nineteenth century. However, originated in some of the previous theories, a very important era for the theoretical formulation of illusions began around 1960s leading to the development of very interesting theories later during the past and present centuries. Some of s ...
... geometric-optical illusions in nineteenth century. However, originated in some of the previous theories, a very important era for the theoretical formulation of illusions began around 1960s leading to the development of very interesting theories later during the past and present centuries. Some of s ...
A neurobiological mapping of theory of mind
... symptom schizophrenia, and in particular those with paranoid and delusional schizophrenia. It has been hypothesized that the ToM failure of these patients [26,37,91] is a consequence not so much from a deficit in the representation of mental states, as reported for example by Sarfati et al. [92], bu ...
... symptom schizophrenia, and in particular those with paranoid and delusional schizophrenia. It has been hypothesized that the ToM failure of these patients [26,37,91] is a consequence not so much from a deficit in the representation of mental states, as reported for example by Sarfati et al. [92], bu ...
universidade federal do rio grande do norte instituto do
... Subsequent to the cell discovery, many questions arise on how cells, such microscopical tiny things, organize themselves to develop into an entire and complex organism. These questions opened a new field in biology: development. Until the 1880´s, observation and histology were the only available tec ...
... Subsequent to the cell discovery, many questions arise on how cells, such microscopical tiny things, organize themselves to develop into an entire and complex organism. These questions opened a new field in biology: development. Until the 1880´s, observation and histology were the only available tec ...
Emerging roles of Axin in cerebral cortical development
... connection with other brain regions. Remarkably, the characteristic distribution and connectivity of cortical neurons originate from a single layer of progenitor cells called the neuroepithelium. During cortical development, neural progenitor cells located in the ventricular zone undergo symmetric c ...
... connection with other brain regions. Remarkably, the characteristic distribution and connectivity of cortical neurons originate from a single layer of progenitor cells called the neuroepithelium. During cortical development, neural progenitor cells located in the ventricular zone undergo symmetric c ...
Object Shape Differences Reflected by Somatosensory Cortical
... the volunteers did many trials to assess discrimination limits and achieve a probability of correct response close to 0.75. This was done to control the difficulty of the tests. The subjects received identical instructions before the two conditions. Each ellipsoid was rotated seven times at regular ...
... the volunteers did many trials to assess discrimination limits and achieve a probability of correct response close to 0.75. This was done to control the difficulty of the tests. The subjects received identical instructions before the two conditions. Each ellipsoid was rotated seven times at regular ...
The Foramen of Magendie - Loyola eCommons
... frequent association of these cells with the area indicates that in disappearing the area membranacea is probably replaced first by these cells, wgich in turn disappear, so that the who,le roof is finally composed of the typical, densely staining ependyma. -------"The ependymal lining of the caudal ...
... frequent association of these cells with the area indicates that in disappearing the area membranacea is probably replaced first by these cells, wgich in turn disappear, so that the who,le roof is finally composed of the typical, densely staining ependyma. -------"The ependymal lining of the caudal ...
Crocodilian Forebrain: Evolution and Development
... exception of the dorsal geniculate nucleus, the following dorsal thalamic nuclei were unlabeled: dorsolateralis anterior, dorsomedialis anterior, reuniens pars centralis, reuniens pars diffusa, rotundus, diagonalis, posterocentralis, and medialis complex posterior (Pritz and Stritzel 1988; 1994a). L ...
... exception of the dorsal geniculate nucleus, the following dorsal thalamic nuclei were unlabeled: dorsolateralis anterior, dorsomedialis anterior, reuniens pars centralis, reuniens pars diffusa, rotundus, diagonalis, posterocentralis, and medialis complex posterior (Pritz and Stritzel 1988; 1994a). L ...
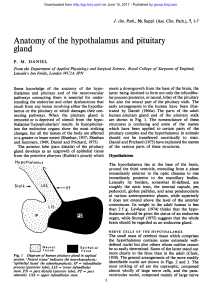
Anatomy of the hypothalamus and pituitary
... few of the neural pathways in the human hypothalamus are known in detail, and much of our Pituitary Gland knowledge of hypothalamic connections has had to be gained from animal experimental work (Raisman, The general arrangements of the pituitary gland are 1966). Much remains to be learned from care ...
... few of the neural pathways in the human hypothalamus are known in detail, and much of our Pituitary Gland knowledge of hypothalamic connections has had to be gained from animal experimental work (Raisman, The general arrangements of the pituitary gland are 1966). Much remains to be learned from care ...
Growth and Functional Efficacy of Intrastriatal Nigral Transplants
... extent of TH-positive cell loss in the host SN (Fig. 2C), the grafts in the severely lesioned rats showed significantly higher numbers of surviving TH-positive neurons compared with the grafts in animals with moderate lesions (5527 ⫾ 896 and 9190 ⫾ 1394, respectively) (Fig. 6 B). This corresponds to ...
... extent of TH-positive cell loss in the host SN (Fig. 2C), the grafts in the severely lesioned rats showed significantly higher numbers of surviving TH-positive neurons compared with the grafts in animals with moderate lesions (5527 ⫾ 896 and 9190 ⫾ 1394, respectively) (Fig. 6 B). This corresponds to ...
A flexible genetic toolkit for arthropod neurogenesis
... with patterning cells with neurogenic potential (module A) and further early steps include the patterning (module B), proliferation (module C) and movement (module D) of neural progenitors. Variants of these modules can be detected across the animal kingdom and allow conclusions to be drawn on the m ...
... with patterning cells with neurogenic potential (module A) and further early steps include the patterning (module B), proliferation (module C) and movement (module D) of neural progenitors. Variants of these modules can be detected across the animal kingdom and allow conclusions to be drawn on the m ...
The Role of Selective Transport in Neuronal Protein
... vesicles containing TfR was almost exclusively directed into dendrites, and this selective transport alone is sufficient to account for the polarization of TfR on the dendritic surface. Downstream selectivity mechanisms may also exist, but these would be redundant. Our results also show that selecti ...
... vesicles containing TfR was almost exclusively directed into dendrites, and this selective transport alone is sufficient to account for the polarization of TfR on the dendritic surface. Downstream selectivity mechanisms may also exist, but these would be redundant. Our results also show that selecti ...
Control of movement direction - Cognitive Science Research Group
... directionally tuned neurons occurs clustered around the onset of movement (e.g., a time window of 400 ms) and may encode information distinct from that provided by firing rate modulations alone. The mechanism, which causes motor neurons to synchronize their activities, may depend on common input wit ...
... directionally tuned neurons occurs clustered around the onset of movement (e.g., a time window of 400 ms) and may encode information distinct from that provided by firing rate modulations alone. The mechanism, which causes motor neurons to synchronize their activities, may depend on common input wit ...
Cranial Nerves
... muscle of the eye, which also controls the movement of the eye. These axons convey nerve impulses for proprioception. Cranial Nerve V is the trigeminal nerve, and likes its name has 3 branches, ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. This cranial nerve conveys impulses for touch, pain, and temperatur ...
... muscle of the eye, which also controls the movement of the eye. These axons convey nerve impulses for proprioception. Cranial Nerve V is the trigeminal nerve, and likes its name has 3 branches, ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. This cranial nerve conveys impulses for touch, pain, and temperatur ...
The Somatosensory System: Receptors and Central Pathways
... A second signal, the Aβ wave, appears as more large fibers are recruited. This component corresponds to group II fibers in skin or muscle nerves and becomes larger as the shock intensity is increased. At higher voltages, when axons in the smaller Aδ range are recruited, the stimulus becomes painful, ...
... A second signal, the Aβ wave, appears as more large fibers are recruited. This component corresponds to group II fibers in skin or muscle nerves and becomes larger as the shock intensity is increased. At higher voltages, when axons in the smaller Aδ range are recruited, the stimulus becomes painful, ...
Mirror neurons or emulator neurons?
... consistent with the goal-to-action account of mirror neuron function. Mirror neurons respond only to meaningful actions because only the meaning, or the assumed goal, provides input to the motor loop (Fig. 1b) and enables action predictions. It is worth noting that mirror neurons do not passively re ...
... consistent with the goal-to-action account of mirror neuron function. Mirror neurons respond only to meaningful actions because only the meaning, or the assumed goal, provides input to the motor loop (Fig. 1b) and enables action predictions. It is worth noting that mirror neurons do not passively re ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.