Module Worksheet - Germantown School District
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
PsychSim 5: NEURAL MESSAGES Name: Section: Date: ______
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis
... The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to the receptors in the post synaptic membrane. 5. The receptors are transmitter-gated ion channels which open when the neurotransmitter binds. Sodium and other positively charged ions diffuse into the post-synaptic membrane. 6. Depo ...
... The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to the receptors in the post synaptic membrane. 5. The receptors are transmitter-gated ion channels which open when the neurotransmitter binds. Sodium and other positively charged ions diffuse into the post-synaptic membrane. 6. Depo ...
Identification of chemical probes for ionotropic glutamate receptors
... We have an exciting opportunity for a talented, highly motivated scientist with a strong background in organic chemistry to join our centre to study for a DPhil. Project outline Ligand-gated ion channels are cell surface proteins that play an important role in fast synaptic transmission and in the m ...
... We have an exciting opportunity for a talented, highly motivated scientist with a strong background in organic chemistry to join our centre to study for a DPhil. Project outline Ligand-gated ion channels are cell surface proteins that play an important role in fast synaptic transmission and in the m ...
Jürgen R. Schwarz
... Information processing within the brain involves the generation of action potentials which are responsible for fast communication between nerve cells. Action potentials have a short duration and are generated by a transient influx of Na+ and a delayed outflow of K+ through voltage-gated ion channels ...
... Information processing within the brain involves the generation of action potentials which are responsible for fast communication between nerve cells. Action potentials have a short duration and are generated by a transient influx of Na+ and a delayed outflow of K+ through voltage-gated ion channels ...
reading guide
... f. Let’s see if you really understand this concept. Draw in another line on the graph to show what the change in membrane potential would look like if a stimulus were applied that did not reach the depolarization threshold. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... f. Let’s see if you really understand this concept. Draw in another line on the graph to show what the change in membrane potential would look like if a stimulus were applied that did not reach the depolarization threshold. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Synaptic vesicles: contain neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) and are located in the synaptic cleft ...
... Synaptic vesicles: contain neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) and are located in the synaptic cleft ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another target cell; a neuron, muscle cell or cell of a gland. Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter an ...
... Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another target cell; a neuron, muscle cell or cell of a gland. Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter an ...
Basis of Membrane Potential Action Potential Movie
... • The speed of nerve impulse conduction also depends on diameter of axon -- larger diameters enable faster conduction • Unmyelinated axon responsible for squid escape behavior is whopping 1 mm in diameter ...
... • The speed of nerve impulse conduction also depends on diameter of axon -- larger diameters enable faster conduction • Unmyelinated axon responsible for squid escape behavior is whopping 1 mm in diameter ...
Nervous System
... covered by Schwann cells. Since these cells are made from lipids, they are insulators. This causes the electrical signal to jump over the Schwann cells increase the speed of the signal. This is known as salutatory conduction. ...
... covered by Schwann cells. Since these cells are made from lipids, they are insulators. This causes the electrical signal to jump over the Schwann cells increase the speed of the signal. This is known as salutatory conduction. ...
ADAM Nervous System Ion Channels Use this program only if you
... Use this program only if you need to review the differences between active and passive cell channels and voltage-gated and chemically-gated channels. Membrane Potential 1. What causes the outside surface of the cell membrane to be more positive? 2. The resting membrane potential in a neuron results ...
... Use this program only if you need to review the differences between active and passive cell channels and voltage-gated and chemically-gated channels. Membrane Potential 1. What causes the outside surface of the cell membrane to be more positive? 2. The resting membrane potential in a neuron results ...
Nerve Cells
... nervous system and peripheral nervous system, respectively. Interactions between glia and neurons control the placement and spacing of myelin sheaths, and the assembly of nerve transmission machinery at the nodes of Ranvier. Another type of glial cell, astrocyctes, is important in producing synapses ...
... nervous system and peripheral nervous system, respectively. Interactions between glia and neurons control the placement and spacing of myelin sheaths, and the assembly of nerve transmission machinery at the nodes of Ranvier. Another type of glial cell, astrocyctes, is important in producing synapses ...
Chapter 4
... Neurotransmitter – chemical stored in the synaptic vesicles that when released transmits messages to other neurons, muscles, or blood vessels Synaptic transmission occurs when neurotransmitter molecules pass across the synaptic cleft and depolarize or hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane. Hyperpo ...
... Neurotransmitter – chemical stored in the synaptic vesicles that when released transmits messages to other neurons, muscles, or blood vessels Synaptic transmission occurs when neurotransmitter molecules pass across the synaptic cleft and depolarize or hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane. Hyperpo ...
Neurotransmission
... A model for Ca2+-triggered vesicle fusion. SNARE proteins on the synaptic vesicle and plasma membranes form a complex that brings together the two membranes. Ca2+ then binds to synaptotagmin on the vesicle membrane, causing the cytoplasmic region of this protein to insert into the plasma membrane a ...
... A model for Ca2+-triggered vesicle fusion. SNARE proteins on the synaptic vesicle and plasma membranes form a complex that brings together the two membranes. Ca2+ then binds to synaptotagmin on the vesicle membrane, causing the cytoplasmic region of this protein to insert into the plasma membrane a ...
Brain Neurotransmitters
... arrows for hunting. The curare binds to the receptor cites where Ach binds, so the Ach cannot be received, this results in paralysis and death. ...
... arrows for hunting. The curare binds to the receptor cites where Ach binds, so the Ach cannot be received, this results in paralysis and death. ...
AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 48 Neurons synapses and
... of saltatory conduction and nodes of Ranvier in your response. ...
... of saltatory conduction and nodes of Ranvier in your response. ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
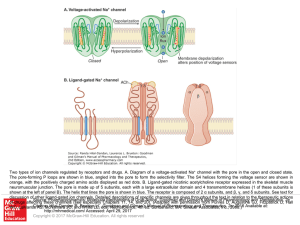
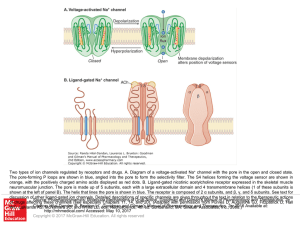
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
Excitatory and inhibitory transmission in the superior olivary complex
... Maintenance of high transmission rates is a major physiological problem since it causes severe depletion of the pool of readily releasable synaptic vesicles. Consequently, there is considerable depression in the number of vesicles released following each sequential action potential of the train. Th ...
... Maintenance of high transmission rates is a major physiological problem since it causes severe depletion of the pool of readily releasable synaptic vesicles. Consequently, there is considerable depression in the number of vesicles released following each sequential action potential of the train. Th ...
Intro-The neuron
... • What functions are supported by frontal lobes? • Do the left and right hemispheres support different abilities? • How does temporal lobe damage affect human function? ...
... • What functions are supported by frontal lobes? • Do the left and right hemispheres support different abilities? • How does temporal lobe damage affect human function? ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.