Neurons - Jordan High School
... Action Potential (Nerve Impulse) All-or-none principle Action potential begins between -60 & -55 mV (threshold) Stimulus triggers action potential, or not at all if doesn’t meet threshold ...
... Action Potential (Nerve Impulse) All-or-none principle Action potential begins between -60 & -55 mV (threshold) Stimulus triggers action potential, or not at all if doesn’t meet threshold ...
Document
... exciting the neuron to fire more action potentials causing an increase in dopamine release. •Nicotine also affects neurons by increasing the number of synaptic vesicles released. ...
... exciting the neuron to fire more action potentials causing an increase in dopamine release. •Nicotine also affects neurons by increasing the number of synaptic vesicles released. ...
Neural-Ville
... 3. It may bind to the first cell's autoreceptors, which tell that cell not to release any more of the neurotransmitter molecules, then leave the autoreceptor and continue trying to bind again somewhere until its activity is ended by step 4, 5 or 6. ...
... 3. It may bind to the first cell's autoreceptors, which tell that cell not to release any more of the neurotransmitter molecules, then leave the autoreceptor and continue trying to bind again somewhere until its activity is ended by step 4, 5 or 6. ...
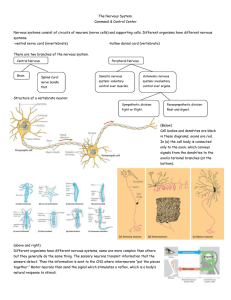
Nervous System - APBio
... (like dominoes) • Because of the refectory period, the impulse can only move in one direction ...
... (like dominoes) • Because of the refectory period, the impulse can only move in one direction ...
CNS II
... inhibit the postsynaptic neuron • Excites with excitatory receptors at the membrane or inhibits with inhibitory receptors – Action potentials cause transmitter release from the presynaptic terminals: role of calcium ions • Presynaptic membrane contains voltage-gated calcium channels • When an action ...
... inhibit the postsynaptic neuron • Excites with excitatory receptors at the membrane or inhibits with inhibitory receptors – Action potentials cause transmitter release from the presynaptic terminals: role of calcium ions • Presynaptic membrane contains voltage-gated calcium channels • When an action ...
Toxicology of the Nervous System
... • Organic mercury from fish is the most significant source of human exposure • Brain and nervous system toxicity ...
... • Organic mercury from fish is the most significant source of human exposure • Brain and nervous system toxicity ...
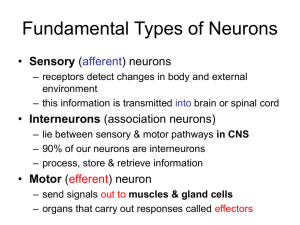
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
here - STAO
... Stimulants increase the activity of the nervous system, while depressants have the opposite effect. Cocaine and amphetamines are similar in structure to norepinephrine, and therefore have similar effects. Caffeine is also a stimulant, but its actions are a little different from the previous two exam ...
... Stimulants increase the activity of the nervous system, while depressants have the opposite effect. Cocaine and amphetamines are similar in structure to norepinephrine, and therefore have similar effects. Caffeine is also a stimulant, but its actions are a little different from the previous two exam ...
Nervous System Neurons And Synapses
... the oligodendrocytes and myelin sheath covering the nerves of CNS. The attacks form hardened scars or plaques (scleroses) along the axons and interfere with nerve conduction. Since the CNS provides commands for skeletal muscles, destruction of the CNS axons will cause a lose of control of the skelet ...
... the oligodendrocytes and myelin sheath covering the nerves of CNS. The attacks form hardened scars or plaques (scleroses) along the axons and interfere with nerve conduction. Since the CNS provides commands for skeletal muscles, destruction of the CNS axons will cause a lose of control of the skelet ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
Action Potentials
... – as long as K+ gates are open – __________________________ __________________________ ...
... – as long as K+ gates are open – __________________________ __________________________ ...
Lectures220Week7Note..
... How the generation of an action potential represents an example of positive feedback. How voltage gated channels generate and keep brief the action potential. The flows of major ions during resting, depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization. How myelination leads to rapid propagation vel ...
... How the generation of an action potential represents an example of positive feedback. How voltage gated channels generate and keep brief the action potential. The flows of major ions during resting, depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization. How myelination leads to rapid propagation vel ...
Nervous
... Action Potential: is the sudden change on stimulation. Na+ ions move in through Na+ gated channels. Gated Ion Channels are open or close in response to membrane stretch, the binding of a specific ligand, or a change in the membrane potential. Direct Synaptic Transmission The neurotransmitter binds t ...
... Action Potential: is the sudden change on stimulation. Na+ ions move in through Na+ gated channels. Gated Ion Channels are open or close in response to membrane stretch, the binding of a specific ligand, or a change in the membrane potential. Direct Synaptic Transmission The neurotransmitter binds t ...
Neurophysiology Worksheet
... ’propagate along the demyelinated axon; therefore, the muscle is not stimulated, leading to paralysis. Eventually, the muscles atrophy because of a lack of adequate activity involving contraction. ...
... ’propagate along the demyelinated axon; therefore, the muscle is not stimulated, leading to paralysis. Eventually, the muscles atrophy because of a lack of adequate activity involving contraction. ...
document
... The inside of a neuron is negatively charged relative to the outside Due to concentrations of positively and negatively charged ions in the brain ...
... The inside of a neuron is negatively charged relative to the outside Due to concentrations of positively and negatively charged ions in the brain ...
Doktryna neuronu
... RD Traub, JG Jefferys and MA Whittington. Enhanced NMDA conductance can account for epileptiform activity induced by low Mg2+ in the rat hippocampal slice, The Journal of Physiology, 1994, 478 (3) 379-393. ...
... RD Traub, JG Jefferys and MA Whittington. Enhanced NMDA conductance can account for epileptiform activity induced by low Mg2+ in the rat hippocampal slice, The Journal of Physiology, 1994, 478 (3) 379-393. ...
Sending Signals Notes
... taken up again by the axon terminal and recycled, or they may simply diffuse away. • NERVE GAS prevents enzymes from breaking down neurotransmitters, as a result muscles in the respiratory and nervous system becomes paralyzed. ...
... taken up again by the axon terminal and recycled, or they may simply diffuse away. • NERVE GAS prevents enzymes from breaking down neurotransmitters, as a result muscles in the respiratory and nervous system becomes paralyzed. ...
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
... 3. Synaptic vesicles fuse with the knob membrane 4. Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane causing the channels to open and allow sodium to leak in-thus setting up the action potential. ...
... 3. Synaptic vesicles fuse with the knob membrane 4. Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane causing the channels to open and allow sodium to leak in-thus setting up the action potential. ...
Synapses
... Chemical Synapse: metabotropic Requires neurotransmitter for transmission Requires G-protein coupled receptor on post-synaptic membrane G-protein activates an enzyme on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane May involve degradative enzymes May involve reuptake transporters on pre-synaptic membrane Ex ...
... Chemical Synapse: metabotropic Requires neurotransmitter for transmission Requires G-protein coupled receptor on post-synaptic membrane G-protein activates an enzyme on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane May involve degradative enzymes May involve reuptake transporters on pre-synaptic membrane Ex ...
E.4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses
... it is reabsorbed by the neuron that released it. This reabsorption happens with the help of a protein called the dopamine transporter. Crack interrupts this cycle. It attaches to the dopamine transporter, preventing the normal reabsorption process. As dopamine builds up in the synapse, it continues ...
... it is reabsorbed by the neuron that released it. This reabsorption happens with the help of a protein called the dopamine transporter. Crack interrupts this cycle. It attaches to the dopamine transporter, preventing the normal reabsorption process. As dopamine builds up in the synapse, it continues ...
Unit 3-2 Nervous System Pt 2 Notes File
... •Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons •Prevents nerve impulses from directly passing from one neuron to the next •Transmission across the synaptic cleft: Is a chemical event (as opposed to an electrical one) Ensures unidirectional communication between neurons ...
... •Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons •Prevents nerve impulses from directly passing from one neuron to the next •Transmission across the synaptic cleft: Is a chemical event (as opposed to an electrical one) Ensures unidirectional communication between neurons ...
Neurotransmisson Practice
... 11. Naturally occurring opiate-like neurotransmitters that are present in the brain are called ________________. When the brain is flooded with drugs such as _____________ or _____________________, it may stop producing these neurotransmitters. 12. Drugs that produce their effects by mimicking neuro ...
... 11. Naturally occurring opiate-like neurotransmitters that are present in the brain are called ________________. When the brain is flooded with drugs such as _____________ or _____________________, it may stop producing these neurotransmitters. 12. Drugs that produce their effects by mimicking neuro ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.