Chapter 9
... The ______________, located between the _______________________ and ___________, contains bundles of myelinated nerve fibers that _______________________ to and from _________________________ of the brain, and masses of gray matter that serve as __________________________. ...
... The ______________, located between the _______________________ and ___________, contains bundles of myelinated nerve fibers that _______________________ to and from _________________________ of the brain, and masses of gray matter that serve as __________________________. ...
Exercise Enhances Brain Health
... CA1 neurons of the hippocampus while stimulation is applied to the Schaffer collaterals of CA3 neurons. The amplitudes of the EPSPs in the CA1 neurons are shown in B. For a single stimulus, the amplitude of the EPSPs is plotted at 100%. When a train of stimuli is applied instead, the amplitude of th ...
... CA1 neurons of the hippocampus while stimulation is applied to the Schaffer collaterals of CA3 neurons. The amplitudes of the EPSPs in the CA1 neurons are shown in B. For a single stimulus, the amplitude of the EPSPs is plotted at 100%. When a train of stimuli is applied instead, the amplitude of th ...
ch 48 nervous system
... • The summed effect of EPSPs and IPSPs determines whether an axon hillock will reach threshold and generate an action potential ...
... • The summed effect of EPSPs and IPSPs determines whether an axon hillock will reach threshold and generate an action potential ...
The Autonomic Nervous System The Sympathetic Division
... • Both preganglionic and postganglionic fibers release acetylcholine – Causes localized and short-term effects ...
... • Both preganglionic and postganglionic fibers release acetylcholine – Causes localized and short-term effects ...
- Philsci
... that this could happen in a way that does not amount to the expenditure of energy at the synaptic terminal, thus avoiding a conflict with the law of energy conservation.5 On a theory of mental causation such as Eccles’, however, the brain is not the control center of the human body. It is merely an ...
... that this could happen in a way that does not amount to the expenditure of energy at the synaptic terminal, thus avoiding a conflict with the law of energy conservation.5 On a theory of mental causation such as Eccles’, however, the brain is not the control center of the human body. It is merely an ...
NEURAL REGULATION OF RESPIRATION LEARNING
... – How brain stem regulates respiration – The other stimuli that modify the respiratory rhythm and the pathways that these signals take to the brain stem. – Voluntary control (cerebral cortex) ...
... – How brain stem regulates respiration – The other stimuli that modify the respiratory rhythm and the pathways that these signals take to the brain stem. – Voluntary control (cerebral cortex) ...
Lecture 17: Sensation
... 1. General sensation relies on sensory receptors that are widely distributed throughout the body. A. Usually. general sensory receptors are the dendrites of a sensory neuron. B. There are a diverse set of different kinds of general receptors, including free dendrites (pain, hair movement, light t ...
... 1. General sensation relies on sensory receptors that are widely distributed throughout the body. A. Usually. general sensory receptors are the dendrites of a sensory neuron. B. There are a diverse set of different kinds of general receptors, including free dendrites (pain, hair movement, light t ...
Introduction and review of Matlab
... the axon of the second neuron. 6. To prevent continuous stimulation or inhibition of the postsynaptic membrane, neurotransmitters are broken down by enzymes or are reabsorbed through the presynaptic membrane by transporters. ...
... the axon of the second neuron. 6. To prevent continuous stimulation or inhibition of the postsynaptic membrane, neurotransmitters are broken down by enzymes or are reabsorbed through the presynaptic membrane by transporters. ...
chapter summary
... simple reflex arcs to centralized brains with distributed, hierarchical regulation. Reflex arcs (found in most animals) consist of sensors, neurons and effectors that quickly detect common disturbances and activate corrective responses. Higher levels of control include anticipation activation of ref ...
... simple reflex arcs to centralized brains with distributed, hierarchical regulation. Reflex arcs (found in most animals) consist of sensors, neurons and effectors that quickly detect common disturbances and activate corrective responses. Higher levels of control include anticipation activation of ref ...
lecture 20
... arises cytoplasm = axoplasm plasma membrane = axolemma axon and collaterals end in fine processes called axon terminals swollen tips called synaptic end bulbs contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters NTs are released when the action potential enters the end bulb ...
... arises cytoplasm = axoplasm plasma membrane = axolemma axon and collaterals end in fine processes called axon terminals swollen tips called synaptic end bulbs contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters NTs are released when the action potential enters the end bulb ...
Transmembrane Transport of Ions and Small Molecules
... concentration gradients. • The combined action of P-class ATP-powered pumps generates the usual ionic milieu of animal cells. • ABC superfamily proteins transport a wide array of substrates, including toxins, drugs, phospholipids, peptides, and proteins, into or out of the cell. ...
... concentration gradients. • The combined action of P-class ATP-powered pumps generates the usual ionic milieu of animal cells. • ABC superfamily proteins transport a wide array of substrates, including toxins, drugs, phospholipids, peptides, and proteins, into or out of the cell. ...
PDF
... channel opening decreases the input membrane resistance inducing “shunting inhibition” (see Andersen et al., 1980; Staley and Mody, 1992; Tang et al., 2011; Wright et al., 2011) that lowers the neuron’s firing probability. Therefore, a weakly depolarizing GABA may exert an inhibitory effect. In contr ...
... channel opening decreases the input membrane resistance inducing “shunting inhibition” (see Andersen et al., 1980; Staley and Mody, 1992; Tang et al., 2011; Wright et al., 2011) that lowers the neuron’s firing probability. Therefore, a weakly depolarizing GABA may exert an inhibitory effect. In contr ...
endocrine system
... Oversupply linked to schizophrenia; undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson’s disease and ADHD ...
... Oversupply linked to schizophrenia; undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson’s disease and ADHD ...
Neuron death - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... Following neuron death, some of the synapses formed in earlier stages of development are eliminated (through retraction of axons) and new synapses are ...
... Following neuron death, some of the synapses formed in earlier stages of development are eliminated (through retraction of axons) and new synapses are ...
Chapter 4 – Sensation
... Rods – Photoreceptors in the retina that respond to lower light intensities and give rise to achromatic (colorless) sensations Cones – Visual receptors that respond to greater light intensities and give rise to chromatic sensations Fovea – The area roughly at the retina’s center where cones ar ...
... Rods – Photoreceptors in the retina that respond to lower light intensities and give rise to achromatic (colorless) sensations Cones – Visual receptors that respond to greater light intensities and give rise to chromatic sensations Fovea – The area roughly at the retina’s center where cones ar ...
Topic Option A Neurobio
... formed by infolding of ectoderm followed by embryonic neural tube can cause spina bifida. elongation of the tube. 12. Application: Events such as strokes may 3. Neurons are initially produced by differentiation promote reorganization of brain function. in the neural tube. 13. Skill: Annotation of a ...
... formed by infolding of ectoderm followed by embryonic neural tube can cause spina bifida. elongation of the tube. 12. Application: Events such as strokes may 3. Neurons are initially produced by differentiation promote reorganization of brain function. in the neural tube. 13. Skill: Annotation of a ...
Special Senses
... senses, in which a specialized receptor cell interprets the stimulus, then sends that information to a separate sensory neuron which will bring the information to the CNS). 2. They extend from the olfactory bulbs and innervate the olfactory epithelium via the olfactory nerve (I) 3. The dendrites are ...
... senses, in which a specialized receptor cell interprets the stimulus, then sends that information to a separate sensory neuron which will bring the information to the CNS). 2. They extend from the olfactory bulbs and innervate the olfactory epithelium via the olfactory nerve (I) 3. The dendrites are ...
History of the Nervous System Cells of the Nervous System
... This is where membrane potentials are summated before entering the axon ...
... This is where membrane potentials are summated before entering the axon ...
Slide 1
... There are two important bifurcations associated with bursting : – Bifurcation of a quiescent state that leads to repetitive spiking . – Bifurcation of a spiking attractor that leads to quiescence . These bifurcations determine the type of burster and hence its neuro-computational ...
... There are two important bifurcations associated with bursting : – Bifurcation of a quiescent state that leads to repetitive spiking . – Bifurcation of a spiking attractor that leads to quiescence . These bifurcations determine the type of burster and hence its neuro-computational ...
SinirBilimin Kısa Tarihi
... 2000[Neural Communication] The communication of discrete neurons (brain cells) using electrical and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) is well established and accepted (Neuron Doctrine). [Localist/Holist Debate] Extreme localism and holism have both been replaced by "connectionism." This view cont ...
... 2000[Neural Communication] The communication of discrete neurons (brain cells) using electrical and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) is well established and accepted (Neuron Doctrine). [Localist/Holist Debate] Extreme localism and holism have both been replaced by "connectionism." This view cont ...
Tutorial 4: Shapes and Roles of Glial Cells Figure 4: Shapes and
... 3. calcium signaling (the use of slowly changing gradients of calcium as a means of cross-glial communication). Receptor sites for neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA have been identified on both astrocytes and Schwann cells. The functional significance of these receptors remains a mystery, ...
... 3. calcium signaling (the use of slowly changing gradients of calcium as a means of cross-glial communication). Receptor sites for neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA have been identified on both astrocytes and Schwann cells. The functional significance of these receptors remains a mystery, ...
No Slide Title
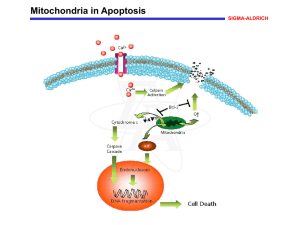
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.