Diapositiva 1
... that are transmitted from dendrites to the axon. The connection established between neurons is called synapse. Synapses are points of control of the transmission of nerve currents. They allow the nerve impulses to pass from one neuron to the other through certain areas. There is a narrow space betwe ...
... that are transmitted from dendrites to the axon. The connection established between neurons is called synapse. Synapses are points of control of the transmission of nerve currents. They allow the nerve impulses to pass from one neuron to the other through certain areas. There is a narrow space betwe ...
Dopamine Modulates the Function of Group II and Group III
... and E). This effect of haloperidol was mimicked by the selective D1 receptor antagonist SCH23390 (20 –50 M) (30.4 ⫾ 2.8% inhibition of EPSCs; n ⫽ 7; p ⬍ 0.01; Fig. 2, C and E), but not by the D2-selective antagonist sulpiride (50 M) (45.7 ⫾ 4.3% inhibition of EPSCs; n ⫽ 6; p ⬎ 0.05; Fig. 2, D and ...
... and E). This effect of haloperidol was mimicked by the selective D1 receptor antagonist SCH23390 (20 –50 M) (30.4 ⫾ 2.8% inhibition of EPSCs; n ⫽ 7; p ⬍ 0.01; Fig. 2, C and E), but not by the D2-selective antagonist sulpiride (50 M) (45.7 ⫾ 4.3% inhibition of EPSCs; n ⫽ 6; p ⬎ 0.05; Fig. 2, D and ...
Lecture 4:
... Motor neurons : Also named efferent neurons: Carry messages away from the CNS (brain and/or spinal cord). ...
... Motor neurons : Also named efferent neurons: Carry messages away from the CNS (brain and/or spinal cord). ...
The Nervous System
... • A neuron has a large cell body that contains the nucleus. • Dendrites - threadlike extensions on the cell body that carry impulses toward the neuron’s cell body. • Axon - carries impulses away from the cell body. ...
... • A neuron has a large cell body that contains the nucleus. • Dendrites - threadlike extensions on the cell body that carry impulses toward the neuron’s cell body. • Axon - carries impulses away from the cell body. ...
Chapter 2: Communication Within the Nervous System
... A good textbook is all about teaching, but there is no teaching if there is no learning. Over the years, my students taught me a great deal about what they needed to help them learn. For one thing, I realized how important it is for students to build on their knowledge throughout the course, so I m ...
... A good textbook is all about teaching, but there is no teaching if there is no learning. Over the years, my students taught me a great deal about what they needed to help them learn. For one thing, I realized how important it is for students to build on their knowledge throughout the course, so I m ...
The Nervous System
... plexuses. It circulates through the brain ventricles and returns to the blood, constantly draining as new CSF forms, keeping the overall volume and pressure relatively constant ...
... plexuses. It circulates through the brain ventricles and returns to the blood, constantly draining as new CSF forms, keeping the overall volume and pressure relatively constant ...
Chapter 2
... y The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenalcortical Axis (HYPAC axis) Integration of endocrine and nervous system function Neuroscience: Functions of Main Types of Neurotransmitters y Functions of Psychoactive Drugs Agonists - increase activity of neurotransmitter by mimicking its effects Antagonists ...
... y The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenalcortical Axis (HYPAC axis) Integration of endocrine and nervous system function Neuroscience: Functions of Main Types of Neurotransmitters y Functions of Psychoactive Drugs Agonists - increase activity of neurotransmitter by mimicking its effects Antagonists ...
Biology 3B Exam 3 Stuff – Here`s a quick list of items for the next
... Stages of cell signaling (reception, transduction and response) Local vs long distance signaling Mobile vs fixed receptor model G-protein, tyrosine kinase and ion channel receptors First & secondary messengers – what are they and how they work Apoptosis? Chapter 41 – animal nutrition H ...
... Stages of cell signaling (reception, transduction and response) Local vs long distance signaling Mobile vs fixed receptor model G-protein, tyrosine kinase and ion channel receptors First & secondary messengers – what are they and how they work Apoptosis? Chapter 41 – animal nutrition H ...
Focus On Vocabulary Chapter 02
... communicating (“chatting”) with neurons and promoting information transmission. In a sense, we do have eyes in the back of our head! The reference here is to the visual cortex (or occipital lobes) that processes visual information and is located at the rear of the brain. So, in a way, seeing is not ...
... communicating (“chatting”) with neurons and promoting information transmission. In a sense, we do have eyes in the back of our head! The reference here is to the visual cortex (or occipital lobes) that processes visual information and is located at the rear of the brain. So, in a way, seeing is not ...
ANATOMY
... The nervous system consists of the brain, the spinal cord and the nerves. The functional, structural unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell called the neuron. ...
... The nervous system consists of the brain, the spinal cord and the nerves. The functional, structural unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell called the neuron. ...
The Anatomy of Language Sydney Lamb Rice University, Houston
... Seven steps of neurotransmitter action ...
... Seven steps of neurotransmitter action ...
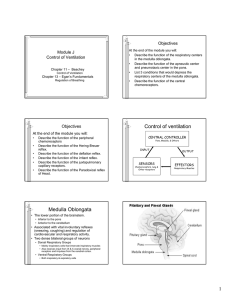
Control of ventilation Medulla Oblongata
... • Located in the medulla of the brain. • Responsive to H+ ions in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). • During hypoventilation, CO2 molecules readily diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 ...
... • Located in the medulla of the brain. • Responsive to H+ ions in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). • During hypoventilation, CO2 molecules readily diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 ...
PowerPoint Presentation - macomb
... • Located in the medulla of the brain. • Responsive to H+ ions in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). • During hypoventilation, CO2 molecules readily diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 ...
... • Located in the medulla of the brain. • Responsive to H+ ions in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). • During hypoventilation, CO2 molecules readily diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 ...
Step back and look at the Science
... and connect to same number of cells Different number of synapses, and shape of axons ...
... and connect to same number of cells Different number of synapses, and shape of axons ...
Brain Jokes (Questions)
... 18. If your dog was a neurologist, what would it do all day? 19. Why do action potentials make good volleyball players? 20. What do you call glia when it is happy? 21. If some of Fred Flintstone's neurotransmitters could talk, what would they say? 22. An action potential takes the train to school. W ...
... 18. If your dog was a neurologist, what would it do all day? 19. Why do action potentials make good volleyball players? 20. What do you call glia when it is happy? 21. If some of Fred Flintstone's neurotransmitters could talk, what would they say? 22. An action potential takes the train to school. W ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... examples of people that you have known in your life that have experienced or struggled with a nervous system disorder. What were the symptoms and struggles? After you finish, get out your notes. ...
... examples of people that you have known in your life that have experienced or struggled with a nervous system disorder. What were the symptoms and struggles? After you finish, get out your notes. ...
Step back and look at the Science
... and connect to same number of cells Different number of synapses, and shape of axons ...
... and connect to same number of cells Different number of synapses, and shape of axons ...
Chapter 15 - FacultyWeb
... 2. The frequency of action potential generation indicates the background level of stimulation. 3. Tonic receptors are active for a short time whenever a change occurs in conditions monitored. 4. When a stimulus increases or decreases, the rate of action potential generation changes. ...
... 2. The frequency of action potential generation indicates the background level of stimulation. 3. Tonic receptors are active for a short time whenever a change occurs in conditions monitored. 4. When a stimulus increases or decreases, the rate of action potential generation changes. ...
REM-off
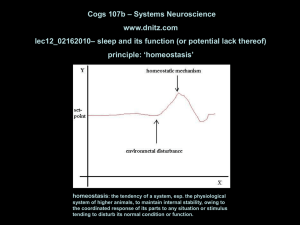
... ‘functional anatomy’ – Even when the strength of a synaptic connection between two neurons is stable (i.e., release of transmitter by the presynaptic neuron opens the same number and type of ionotropic receptors on the postsynaptic neuron), the impact of the presynaptic neuron on the postsynaptic n ...
... ‘functional anatomy’ – Even when the strength of a synaptic connection between two neurons is stable (i.e., release of transmitter by the presynaptic neuron opens the same number and type of ionotropic receptors on the postsynaptic neuron), the impact of the presynaptic neuron on the postsynaptic n ...
Physiologic basis of EMG/NCS or what constitutes a waveform?
... ACH release • Rapid diffusion across cleft in .5 msec timing, bind receptors – Large transmembrane proteins with ACH site and ion channel – Ligand activated vs. voltage activated ...
... ACH release • Rapid diffusion across cleft in .5 msec timing, bind receptors – Large transmembrane proteins with ACH site and ion channel – Ligand activated vs. voltage activated ...
nervous system study guide
... SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM What does each do? Which is involuntary? ...
... SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM What does each do? Which is involuntary? ...
Introduction to Sense Organs
... – sense organ, gasoline engine, light bulb are all transducers • receptor potential – small, local electrical change on a receptor cell brought about by an initial stimulus • results in release of neurotransmitter or a volley of action potentials that generates nerve signals to the CNS ...
... – sense organ, gasoline engine, light bulb are all transducers • receptor potential – small, local electrical change on a receptor cell brought about by an initial stimulus • results in release of neurotransmitter or a volley of action potentials that generates nerve signals to the CNS ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.