Unit 4 Sensation
... Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory: The theory that the retina contains three different types of cones--one most sensitive to red, one to blue, and one to green--which when stimulated in combination can produce any color. RED, GREEN, & BLUE are the PRIMARY COLORS OF LIGHT WAVES. Opponent Process Th ...
... Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory: The theory that the retina contains three different types of cones--one most sensitive to red, one to blue, and one to green--which when stimulated in combination can produce any color. RED, GREEN, & BLUE are the PRIMARY COLORS OF LIGHT WAVES. Opponent Process Th ...
Lec 7 Lab Demo Handout
... release acetylcholine (ACh) that is received by sensory receptors of nicotinic receptors on the alpha motor neurons. Alpha motor neurons send an impulse down their axons via the ventral root of the spinal cord. Subsequently alpha motor neurons release ACh from their axon terminal knobs at the neurom ...
... release acetylcholine (ACh) that is received by sensory receptors of nicotinic receptors on the alpha motor neurons. Alpha motor neurons send an impulse down their axons via the ventral root of the spinal cord. Subsequently alpha motor neurons release ACh from their axon terminal knobs at the neurom ...
Nervous System – Chapter 10
... 1. Facts:-Schwann cells form this insulating cover called a myelin sheath a. composed of lipids and protein b. conducts more rapidly than nerves without a sheath c. believe to contain a source of energy for transmitting the impulse d. only nerves with a myelin sheath are called white matter 2. Locat ...
... 1. Facts:-Schwann cells form this insulating cover called a myelin sheath a. composed of lipids and protein b. conducts more rapidly than nerves without a sheath c. believe to contain a source of energy for transmitting the impulse d. only nerves with a myelin sheath are called white matter 2. Locat ...
Central nervous system
... – In nonmyelinated axons, the action potential travels down an axon one small section at a time – In myelinated fibers, an action potential at one node causes an action potential at the next node • Saltatory (jumping) Conduction ...
... – In nonmyelinated axons, the action potential travels down an axon one small section at a time – In myelinated fibers, an action potential at one node causes an action potential at the next node • Saltatory (jumping) Conduction ...
File
... ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). ● Discuss the effect of the ...
... ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). ● Discuss the effect of the ...
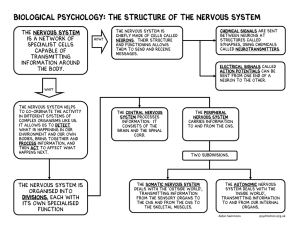
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
Read the perspective by Temel and Jahanshahi here.
... the mouse brain. Four weeks later, magnetic nanoparticles were injected into the same region, where they were detected in the extracellular space (whether they are internalized by any cell in vivo remains to be shown). Mice were then exposed to an external alternating magnetic field that caused the ...
... the mouse brain. Four weeks later, magnetic nanoparticles were injected into the same region, where they were detected in the extracellular space (whether they are internalized by any cell in vivo remains to be shown). Mice were then exposed to an external alternating magnetic field that caused the ...
Slide 1
... – Axon: extends from cell body, carries electrical potential, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons via terminal buttons ...
... – Axon: extends from cell body, carries electrical potential, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons via terminal buttons ...
Joshua Berlin, Ph.D. Department of Pharmacology and Physiology
... pumps. Our second area of investigation is cardiac muscle excitation-contraction coupling, the process by which the cardiac action potential triggers muscle contraction. We are studying how Ca2+ influx controls sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ release and the role of positive feedback mechanisms in ampl ...
... pumps. Our second area of investigation is cardiac muscle excitation-contraction coupling, the process by which the cardiac action potential triggers muscle contraction. We are studying how Ca2+ influx controls sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ release and the role of positive feedback mechanisms in ampl ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... _____________________ nervous systems. •Transmission at these synapses is termed cholinergic: •ACh is NT released by most postganglionic parasympathetic fibers at synapse with effector. ...
... _____________________ nervous systems. •Transmission at these synapses is termed cholinergic: •ACh is NT released by most postganglionic parasympathetic fibers at synapse with effector. ...
Synaptic Transmission 1
... Principles of rapid/focal synaptic transmission via ionotropic receptors • The affinity of transmitter for receptors is usually low (10-100 µM) • Release leads to a high concentration of transmitter (1-10 mM) for a brief period of time in a small volume • Receptor occupancy can be substantial, des ...
... Principles of rapid/focal synaptic transmission via ionotropic receptors • The affinity of transmitter for receptors is usually low (10-100 µM) • Release leads to a high concentration of transmitter (1-10 mM) for a brief period of time in a small volume • Receptor occupancy can be substantial, des ...
Central Nervous system - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... these changes to the central nervous system. 2. Motor neuron A neuron located within the central nervous system that controls the contraction of a muscle or the secretion of a gland. ...
... these changes to the central nervous system. 2. Motor neuron A neuron located within the central nervous system that controls the contraction of a muscle or the secretion of a gland. ...
The Adenosine Story Goes Ionic: CaV2.1
... of a functionally responsive Ca2+ channel with preserved expression levels, but compromised primarily in G-protein-mediated inhibition.22 The hypothesis to be tested by Deboer et al.7 was clear: if CaV2.1 channels mediate some of adenosinergic actions on sleep, then these animals should show attenua ...
... of a functionally responsive Ca2+ channel with preserved expression levels, but compromised primarily in G-protein-mediated inhibition.22 The hypothesis to be tested by Deboer et al.7 was clear: if CaV2.1 channels mediate some of adenosinergic actions on sleep, then these animals should show attenua ...
File Now
... NEUROTRANSMITTERS Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) – inhibitory seizures, bipolar disorder, anxiety, pain Glutamate – excitatory most widely available neurotransmitter, paradoxically both main neurotransmitter for memory and main one responsible for cell death ...
... NEUROTRANSMITTERS Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) – inhibitory seizures, bipolar disorder, anxiety, pain Glutamate – excitatory most widely available neurotransmitter, paradoxically both main neurotransmitter for memory and main one responsible for cell death ...
The Nervous System Lesson Outline LESSON 1 A.
... system of the PNS regulates involuntary actions such as dilating blood vessels and the beating of the heart. It also controls cardiac muscles and ...
... system of the PNS regulates involuntary actions such as dilating blood vessels and the beating of the heart. It also controls cardiac muscles and ...
PAPER #3: EMBARGOED PRESS RELEASE STRICTLY UNDER
... and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons that produce dopamine so that the rats became desensitized to the cocaine. Sin ...
... and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons that produce dopamine so that the rats became desensitized to the cocaine. Sin ...
31.1 Really Neurons
... Homework Name and describe the three types of neurons Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs. Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. Interneurons process the information from sensory neurons and send commands to other interneurons or motor ...
... Homework Name and describe the three types of neurons Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs. Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. Interneurons process the information from sensory neurons and send commands to other interneurons or motor ...
SENSORY AND MOTOR SYSTEMS: REFLEXES
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
B) Nervous System Introduction NtG Spring
... Narrows to form a slender process the rest of the length In some neurons the axon is very short and in others it is very long Ex: axons of toes extend from your spine to your foot (about 3-4 feet) – the longest cells in your body Axons and Axonal Terminals Axons can branch many times but all ...
... Narrows to form a slender process the rest of the length In some neurons the axon is very short and in others it is very long Ex: axons of toes extend from your spine to your foot (about 3-4 feet) – the longest cells in your body Axons and Axonal Terminals Axons can branch many times but all ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) • Mediates control of the internal organs. • The autonomic system is largely involuntary, its control originates in the brainstem and hypothalamus. • Autonomic nervous system innervates the heart, smooth muscles, organs and glands. • The autonomic system makes one gan ...
... Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) • Mediates control of the internal organs. • The autonomic system is largely involuntary, its control originates in the brainstem and hypothalamus. • Autonomic nervous system innervates the heart, smooth muscles, organs and glands. • The autonomic system makes one gan ...
Chapter 7 Part 1 Nervous Tissue
... circulate CSF around the central nervous system. Their apical surfaces are also covered with microvilli, which absorb CSF. Ependymal cells are a type of Glial cell and are also CSF producing cells ...
... circulate CSF around the central nervous system. Their apical surfaces are also covered with microvilli, which absorb CSF. Ependymal cells are a type of Glial cell and are also CSF producing cells ...
Chapter 2
... Define neuroscience and biological psychology, and explain why psychologists study the biological basis of behavior. ...
... Define neuroscience and biological psychology, and explain why psychologists study the biological basis of behavior. ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.