G020297-00 - DCC
... compared to Newton’s theory Mercury's elliptical path around the Sun shifts slightly with each orbit such that its closest point to the Sun (or "perihelion") shifts forward with each pass. ...
... compared to Newton’s theory Mercury's elliptical path around the Sun shifts slightly with each orbit such that its closest point to the Sun (or "perihelion") shifts forward with each pass. ...
Lecture 26
... the main source looked like a point (and thus nearly stellar), hence the term `quasi-stellar object' (QSO), which became quasar. ...
... the main source looked like a point (and thus nearly stellar), hence the term `quasi-stellar object' (QSO), which became quasar. ...
Gravity/An invisible force that pulls a less massive object - Zoe-s-wiki
... galaxy/a system that is made up of billions of stars, star clusters and glowing clouds of dust and gas universe/all of the galaxies and the space around them; everything in space nebula/a cloud of dust and gas within a galaxy Big Bang Theory/the theroy that the universe was created by a huge explosi ...
... galaxy/a system that is made up of billions of stars, star clusters and glowing clouds of dust and gas universe/all of the galaxies and the space around them; everything in space nebula/a cloud of dust and gas within a galaxy Big Bang Theory/the theroy that the universe was created by a huge explosi ...
Example: The gravitational force of attraction between Earth and the
... 15. What is the acceleration due to gravity on the surface on Earth? Use the values in the table above to verify this. 16. a. What would be the acceleration due to gravity experienced by an 1800 kg satellite orbiting Earth 1000 km above Earth’s surface? (7.3 m/s2) b. How high above Earth’s surface w ...
... 15. What is the acceleration due to gravity on the surface on Earth? Use the values in the table above to verify this. 16. a. What would be the acceleration due to gravity experienced by an 1800 kg satellite orbiting Earth 1000 km above Earth’s surface? (7.3 m/s2) b. How high above Earth’s surface w ...
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 13
... 5. The picture below shows two cross sections of the same chunk of the universe, at time intervals separated by 2 billion years. We are on the Milky Way Galaxy, and have measured the distances to a number of other galaxies at both times. Our results (in millions of light years) are shown on the figu ...
... 5. The picture below shows two cross sections of the same chunk of the universe, at time intervals separated by 2 billion years. We are on the Milky Way Galaxy, and have measured the distances to a number of other galaxies at both times. Our results (in millions of light years) are shown on the figu ...
Gravity - Holliday ISD
... force of the object that is falling. F=ma And if you are talking about a falling object the formula would be F=m*9.8m/s2 The force of Earth’s gravity is always downward. When an object is influenced only by the force of gravity, it is said to be in free fall. No matter how large or small an object ...
... force of the object that is falling. F=ma And if you are talking about a falling object the formula would be F=m*9.8m/s2 The force of Earth’s gravity is always downward. When an object is influenced only by the force of gravity, it is said to be in free fall. No matter how large or small an object ...
STUDY GUIDE test Oct 7th
... future of our universe look like? 2. Galaxies-four main shapes, what is our galaxy named and what shape is it? Be able to put space objects in order from biggest to smallest (use the galactic address info) 3. Stars-What is a star? How do they make light and heat? How are stars classified? What are c ...
... future of our universe look like? 2. Galaxies-four main shapes, what is our galaxy named and what shape is it? Be able to put space objects in order from biggest to smallest (use the galactic address info) 3. Stars-What is a star? How do they make light and heat? How are stars classified? What are c ...
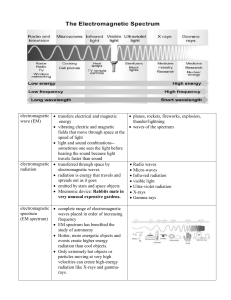
EMS Notes 1617 - Biloxi Public Schools
... to gather and focus light To study the size, composition, and movement of stars and galaxies They make distant objects appear closer and brighter. To find black holes and map galactic centers Some have been used to monitor radio signals given off by earthquakes To map sources and analyze t ...
... to gather and focus light To study the size, composition, and movement of stars and galaxies They make distant objects appear closer and brighter. To find black holes and map galactic centers Some have been used to monitor radio signals given off by earthquakes To map sources and analyze t ...
Hubble`s Law Notes
... are moving away from us, that means the Universe is expanding. If the Universe is expanding, it must have started a single point, like a balloon. http://videos.howstuffworks.com/tlc/29804-understanding-hubbles-law-of-the-expanding-universe-video.htm ...
... are moving away from us, that means the Universe is expanding. If the Universe is expanding, it must have started a single point, like a balloon. http://videos.howstuffworks.com/tlc/29804-understanding-hubbles-law-of-the-expanding-universe-video.htm ...
Wave in the universe - Gallaudet University
... About 3,000 Galaxies in a small patch of the sky. Light travels 5,900,000,000,000 miles in a year… called a Light Year. ...
... About 3,000 Galaxies in a small patch of the sky. Light travels 5,900,000,000,000 miles in a year… called a Light Year. ...
Reflection and Refraction - Gonzaga Physics Department
... use. The focal length is defined as the point at which all parallel rays of light meet after reflecting off of the mirror or passing through the lens. For diverging mirrors/lenses, it is the point from which the diverging rays appear to come. This is shown for lenses in figure 3. f ...
... use. The focal length is defined as the point at which all parallel rays of light meet after reflecting off of the mirror or passing through the lens. For diverging mirrors/lenses, it is the point from which the diverging rays appear to come. This is shown for lenses in figure 3. f ...
Objective Test on Light – Reflection and Refraction
... Any three phenomenon of light are ________, ________ and ________. Propagation of light is ________ in nature. If the reflecting surface is curved inwards for a spherical mirrors it will be called as ________ mirror. A line through pole, P and centre of curvature, O is called ________. Half the dist ...
... Any three phenomenon of light are ________, ________ and ________. Propagation of light is ________ in nature. If the reflecting surface is curved inwards for a spherical mirrors it will be called as ________ mirror. A line through pole, P and centre of curvature, O is called ________. Half the dist ...
The Milky Way - Indiana University Astronomy
... transparent to infrared light, and we can see through the gas and dust to observe the Galactic Center ...
... transparent to infrared light, and we can see through the gas and dust to observe the Galactic Center ...