8.6 Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors
... When light travels into a less optically dense medium, the ray bends away from the ...
... When light travels into a less optically dense medium, the ray bends away from the ...
ch12gravity
... one focus of the ellipse. 2. During equal time intervals, the radius vector from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas. 3. If T is the time that it takes for a planet to make one full revolution around the Sun, and if R is half the major axis of the ellipse (R reduces to the radius of the orbit ...
... one focus of the ellipse. 2. During equal time intervals, the radius vector from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas. 3. If T is the time that it takes for a planet to make one full revolution around the Sun, and if R is half the major axis of the ellipse (R reduces to the radius of the orbit ...
PHSC1053-Review02
... converging lens/mirror diverging lens/mirror binary star radial velocity electromagnetic radiation polarization coherent/incoherent light X-rays gamma rays radio ultraviolet infrared Waves: How fast do waves travel? How do waves propagate? What do they transmit? What different types of waves are the ...
... converging lens/mirror diverging lens/mirror binary star radial velocity electromagnetic radiation polarization coherent/incoherent light X-rays gamma rays radio ultraviolet infrared Waves: How fast do waves travel? How do waves propagate? What do they transmit? What different types of waves are the ...
ASTR_CGT_motionenergygravity_V03
... P.12.6 Qualitatively apply the concept of angular momentum. P.12.7 Recognize that nothing travels faster than the speed of light in a vacuum, which is the same for all observers no matter how they or the light source are moving P.12.3 Interpret and apply Newton’s three laws of motion ...
... P.12.6 Qualitatively apply the concept of angular momentum. P.12.7 Recognize that nothing travels faster than the speed of light in a vacuum, which is the same for all observers no matter how they or the light source are moving P.12.3 Interpret and apply Newton’s three laws of motion ...
The Degenerate Remnants of Massive Stars
... Spacetime interval: between two events (xA,yA,zA,tA) & (xB,yB,zB,tB) in flat spacetime ...
... Spacetime interval: between two events (xA,yA,zA,tA) & (xB,yB,zB,tB) in flat spacetime ...
Announcements
... Disk has young stars with orbits nearly in plane Initially gravity pulled in matter from all directions. Stars formed during this stage have random orbits passing close to center Later, rotation made any remaining gas flatten into disk. Stars forming after this have orbits in disk. ...
... Disk has young stars with orbits nearly in plane Initially gravity pulled in matter from all directions. Stars formed during this stage have random orbits passing close to center Later, rotation made any remaining gas flatten into disk. Stars forming after this have orbits in disk. ...
Astronomy
... Astronomy Galaxies Test Name: Directions: Answer the following questions with the most correct answers. TRUE/FALSE: 1. _____ Hubble classified galaxies 2. _____ There are three main classifications of galaxies 3. _____ Elliptical galaxies have little or no star formation 4. _____ Elliptical galaxies ...
... Astronomy Galaxies Test Name: Directions: Answer the following questions with the most correct answers. TRUE/FALSE: 1. _____ Hubble classified galaxies 2. _____ There are three main classifications of galaxies 3. _____ Elliptical galaxies have little or no star formation 4. _____ Elliptical galaxies ...
Topics on the Sun and the Life
... based on carbonbased compounds, called organic molecules • These organic molecules occur naturally in the interstellar clouds of gas and dust, called nebula, throughout galaxies ...
... based on carbonbased compounds, called organic molecules • These organic molecules occur naturally in the interstellar clouds of gas and dust, called nebula, throughout galaxies ...
The Merger of Two Disk Galaxies
... colored blue, while stars in their central bulges are shown in yellow. Red indicates dark matter that surrounds each galaxy. The total elapsed time for this simulation is one billion years. ...
... colored blue, while stars in their central bulges are shown in yellow. Red indicates dark matter that surrounds each galaxy. The total elapsed time for this simulation is one billion years. ...
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory
... Their measurements showed that the light from these stars was bent as it grazed the Sun, by the exact amount of Einstein's predictions. The light never changes course, but merely follows the curvature of space. Astronomers now refer to this displacement of light as gravitational lensing. LIGO-G9900X ...
... Their measurements showed that the light from these stars was bent as it grazed the Sun, by the exact amount of Einstein's predictions. The light never changes course, but merely follows the curvature of space. Astronomers now refer to this displacement of light as gravitational lensing. LIGO-G9900X ...
Slide 1
... GR via Einstein’s curved space time formulation predicts q=4GMs /bc2 which predicts an effect 8 times larger than a classical approach! Even so the angle with b as the solar radius is at most only 1.74” of arc, a difficult measurement which has been tested (Eddington 1914,1919) but with an error Fac ...
... GR via Einstein’s curved space time formulation predicts q=4GMs /bc2 which predicts an effect 8 times larger than a classical approach! Even so the angle with b as the solar radius is at most only 1.74” of arc, a difficult measurement which has been tested (Eddington 1914,1919) but with an error Fac ...
AST101 Lecture 20 The Ecology of the Galaxy
... • About 1010 years old • 105 - 106 stars • Radius ~ 10 light years • Most massive star: ~ 1 solar mass • ~150 globular clusters known in Milky Way ...
... • About 1010 years old • 105 - 106 stars • Radius ~ 10 light years • Most massive star: ~ 1 solar mass • ~150 globular clusters known in Milky Way ...
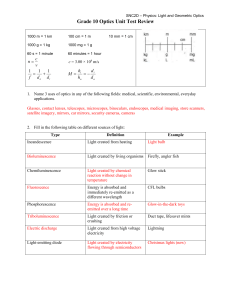
optics_unit_review 2D - East Northumberland Secondary School
... Compare and contrast incandescent, compact fluorescent, and LED (light-emitting diode) light sources. Describe the properties of LASERS. Using a diagram, label the angle of incidence, incident ray, normal, reflected ray, angle of reflection, and plane mirror. What are the laws of reflection? If you ...
... Compare and contrast incandescent, compact fluorescent, and LED (light-emitting diode) light sources. Describe the properties of LASERS. Using a diagram, label the angle of incidence, incident ray, normal, reflected ray, angle of reflection, and plane mirror. What are the laws of reflection? If you ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... ESO 137-001: X-ray Tails from Galaxy Plunging into the Core of the Galaxy Cluster A3627 ...
... ESO 137-001: X-ray Tails from Galaxy Plunging into the Core of the Galaxy Cluster A3627 ...
Day_10
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation g ~ 10 m/s2 “the acceleration of gravity” & g x m is your weight! • Newton’s law of gravitation states: Two bodies attract each other with a force that is directly proportional the product of their masses and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance betwee ...
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation g ~ 10 m/s2 “the acceleration of gravity” & g x m is your weight! • Newton’s law of gravitation states: Two bodies attract each other with a force that is directly proportional the product of their masses and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance betwee ...