chapt10_holes_lecture_animation
... • Carries information to muscles and glands • Divisions of the Motor Division: • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
... • Carries information to muscles and glands • Divisions of the Motor Division: • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
PowerPoint to accompany Hole’s Human Anatomy and
... • Carries information to muscles and glands • Divisions of the Motor Division: • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
... • Carries information to muscles and glands • Divisions of the Motor Division: • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
2015-2016_1Semester_Exam2_140116
... Opening of voltage gated Ca+ ion channels Docking Exocytosis Receptor activation/ligand binding Re-uptake of NTs ...
... Opening of voltage gated Ca+ ion channels Docking Exocytosis Receptor activation/ligand binding Re-uptake of NTs ...
Transport and local translational regulation of mRNAs in neurons
... In the style of "old fashioned" WCBR workshops, where formal presentations are brief and audience participation in the discussion is encouraged, this session will host a wideranging and speculative WCBR workshop on local protein synthesis in dendrites. Greenough will discuss recent research on mecha ...
... In the style of "old fashioned" WCBR workshops, where formal presentations are brief and audience participation in the discussion is encouraged, this session will host a wideranging and speculative WCBR workshop on local protein synthesis in dendrites. Greenough will discuss recent research on mecha ...
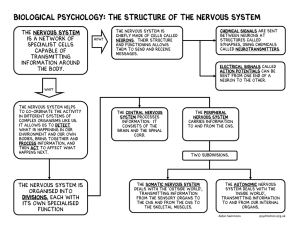
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
chapt12-nervous system
... Transmission of the nerve impulse from one neuron to another takes place at a synapse when a neurotransmitter molecule is released from an axon bulb into a synaptic cleft. The binding of the neurotransmitter to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane causes either excitation or inhibition. Neurotrans ...
... Transmission of the nerve impulse from one neuron to another takes place at a synapse when a neurotransmitter molecule is released from an axon bulb into a synaptic cleft. The binding of the neurotransmitter to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane causes either excitation or inhibition. Neurotrans ...
Chapter_03_4E
... less negative relative to outside and is caused by a change in the membrane’s Na+ permeability (>–70 mV) Hyperpolarization occurs when inside of cell becomes more negative relative to outside (<–70 mV) Graded potentials are localized changes in membrane potential (either depolarization or hyperpolar ...
... less negative relative to outside and is caused by a change in the membrane’s Na+ permeability (>–70 mV) Hyperpolarization occurs when inside of cell becomes more negative relative to outside (<–70 mV) Graded potentials are localized changes in membrane potential (either depolarization or hyperpolar ...
The Nervous System
... received is sufficient to overcome the amount of inhibitory neurotransmitters received, the neuron fires. If not, only local excitation occurs. The total process allows neurons to fine-tune to the environment. ...
... received is sufficient to overcome the amount of inhibitory neurotransmitters received, the neuron fires. If not, only local excitation occurs. The total process allows neurons to fine-tune to the environment. ...
Lange Physiology > Section II
... As noted above, axons conduct impulses in either direction. However, conduction at synapses procedes in only one direction, ie, orthodromic, because the neurotransmitter at the synapse is in the presynaptic and not in the postsynaptic cell. The one-way gate at the synapses is necessary for orderly ...
... As noted above, axons conduct impulses in either direction. However, conduction at synapses procedes in only one direction, ie, orthodromic, because the neurotransmitter at the synapse is in the presynaptic and not in the postsynaptic cell. The one-way gate at the synapses is necessary for orderly ...
Neurons - MrsMcFadin
... • An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. • A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives a stimulus to its dendrites large enough to start a nerve impulse from the cell body • Once it begins, the impulse travels quickly down the axon away fro ...
... • An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. • A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives a stimulus to its dendrites large enough to start a nerve impulse from the cell body • Once it begins, the impulse travels quickly down the axon away fro ...
Resting Membrane Potential
... resting to firing? • The resting membrane potential of a neuron is -70 mV • In order for a neuron to fire a signal, the membrane potential must reach a certain threshold, around -55 mV. • This happens when another neuron stimulates it and allows a few Na+ channels to open and a few Na+ ions enter th ...
... resting to firing? • The resting membrane potential of a neuron is -70 mV • In order for a neuron to fire a signal, the membrane potential must reach a certain threshold, around -55 mV. • This happens when another neuron stimulates it and allows a few Na+ channels to open and a few Na+ ions enter th ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... Figure 2.11 (a) Shapes of some glia cells. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin sheaths that insulate certain vertebrate axons in the central nervous system; Schwann cells have a similar function in the periphery. The oligodendrocyte is shown here forming a segment of myelin sheath for two axons; in fac ...
... Figure 2.11 (a) Shapes of some glia cells. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin sheaths that insulate certain vertebrate axons in the central nervous system; Schwann cells have a similar function in the periphery. The oligodendrocyte is shown here forming a segment of myelin sheath for two axons; in fac ...
Describe how action potentials are generated
... • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long peripheral processes (e.g. again, the great toe) ...
... • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long peripheral processes (e.g. again, the great toe) ...
Describe how action potentials are generated and
... • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long peripheral processes (e.g. again, the great toe) ...
... • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long peripheral processes (e.g. again, the great toe) ...
The Auditory Pathway: Transmission between Hair Cells and Eighth
... acoustic responses of these primary afferents.61 Each spiral ganglion neuron responds selectively to the frequency of sound that is optimal for the inner hair cell to which it is attached. Each inner hair cell is the sole presynaptic partner of a group of type I afferent neurons, numbering from 10 t ...
... acoustic responses of these primary afferents.61 Each spiral ganglion neuron responds selectively to the frequency of sound that is optimal for the inner hair cell to which it is attached. Each inner hair cell is the sole presynaptic partner of a group of type I afferent neurons, numbering from 10 t ...
Biology 12 - Excretion
... A MOTOR neuron has a long axon and short dendrites. In the first part of the nerve impulse, the ion SODIUM moves to the inside of the neuron. The junction between one neuron and another is called a SYNAPSE. Each division of the autonomic nervous system controls the same organs, but they generally ha ...
... A MOTOR neuron has a long axon and short dendrites. In the first part of the nerve impulse, the ion SODIUM moves to the inside of the neuron. The junction between one neuron and another is called a SYNAPSE. Each division of the autonomic nervous system controls the same organs, but they generally ha ...
My Reaction Test Score = Neural Transmission
... axon. This wave of changing electrical charge flows down the axon until it reaches the terminal button. At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These ...
... axon. This wave of changing electrical charge flows down the axon until it reaches the terminal button. At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These ...
Neurons
... Dendrites are treelike extensions at the beginning of a neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body. These tiny protrusions receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma. Dendrites are also covered with synapses. Dendrite Characteristics ...
... Dendrites are treelike extensions at the beginning of a neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body. These tiny protrusions receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma. Dendrites are also covered with synapses. Dendrite Characteristics ...
Neurotransmitter
... channels between two neurons. It allows transmission of nerve impulse directly from one neuron to the other. – Chemical Synapses In chemical synapse, chemicals (neurotransmitters) are released at synapses and attach at other neuron’s receptors to transmit nerve impulse. ...
... channels between two neurons. It allows transmission of nerve impulse directly from one neuron to the other. – Chemical Synapses In chemical synapse, chemicals (neurotransmitters) are released at synapses and attach at other neuron’s receptors to transmit nerve impulse. ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... up a current that spreads out from the site of the action potential. Again, just like the graded potentials, it will decay with distance. However, if the current spreads to another site on the membrane containing voltage-gated Na+ channels and the current still has sufficient voltage to depolarize t ...
... up a current that spreads out from the site of the action potential. Again, just like the graded potentials, it will decay with distance. However, if the current spreads to another site on the membrane containing voltage-gated Na+ channels and the current still has sufficient voltage to depolarize t ...
Neuroplasticity - Bakersfield College
... route, interact with guidance molecules Fasciculation – the tendency of developing axons to grow along the paths established by preceding axons ...
... route, interact with guidance molecules Fasciculation – the tendency of developing axons to grow along the paths established by preceding axons ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.