Chapter 48 PowerPoint 2016 - Spring
... to a change in membrane potential • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell • The movement of Na+ into the cell increases the depolarization and causes even more Na+ channels to open • A strong stimulus results in a massive change in membran ...
... to a change in membrane potential • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell • The movement of Na+ into the cell increases the depolarization and causes even more Na+ channels to open • A strong stimulus results in a massive change in membran ...
Midterm 2 review - UCSD Cognitive Science
... – Glu + Gly opens channel to Ca ++, – Magnesium (Mg++) block removed by membrane depolarization ...
... – Glu + Gly opens channel to Ca ++, – Magnesium (Mg++) block removed by membrane depolarization ...
Sharks are osmoregulators that maintain high internal salt
... Why is the synaptic cleft a very narrow space between synapsing neurons? a) Neurotransmitters are quickly degraded. b) Nerve impulses cannot travel very far. c) The ion channels on the post-synaptic cleft must be in direct contact with the presynaptic membrane. ...
... Why is the synaptic cleft a very narrow space between synapsing neurons? a) Neurotransmitters are quickly degraded. b) Nerve impulses cannot travel very far. c) The ion channels on the post-synaptic cleft must be in direct contact with the presynaptic membrane. ...
The First Open International Symposium
... neuroscience. While previous studies in several species have implicated specific classes of interneurons in the regulation of locomotion, their roles and activity pattern during ongoing behavior remain poorly understood. The Drosophila larval peristalsis is generated by a traveling wave of motor act ...
... neuroscience. While previous studies in several species have implicated specific classes of interneurons in the regulation of locomotion, their roles and activity pattern during ongoing behavior remain poorly understood. The Drosophila larval peristalsis is generated by a traveling wave of motor act ...
Lesson 3 Brain Communication
... point,” or space between two neurons. • It is located between the axon terminal of one neuron and dendritic receptor of another. • The junction point of two or more neurons where cell communication takes place. • The axon terminal sends the nerve impulse and the dendritic receptor receives the nerve ...
... point,” or space between two neurons. • It is located between the axon terminal of one neuron and dendritic receptor of another. • The junction point of two or more neurons where cell communication takes place. • The axon terminal sends the nerve impulse and the dendritic receptor receives the nerve ...
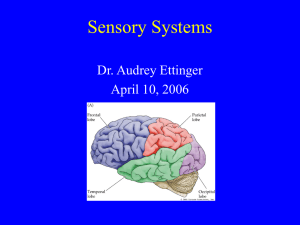
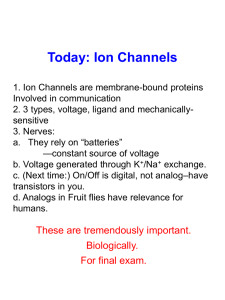
Sensory Systems - Cedar Crest College
... the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
... the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
to Psychology 3
... - the stable voltage is disrupted upon the stimulation by neurotransmitters at dendrites - channels along the axon membrane open to allow cations into the cell easily resulting in an electric current along the axon - after the action potential, another cannot occur until the -70 mV potential is rest ...
... - the stable voltage is disrupted upon the stimulation by neurotransmitters at dendrites - channels along the axon membrane open to allow cations into the cell easily resulting in an electric current along the axon - after the action potential, another cannot occur until the -70 mV potential is rest ...
Neurons and the Nervous System
... • Action potentials travel in only one direction: toward the synaptic terminals ...
... • Action potentials travel in only one direction: toward the synaptic terminals ...
Microscopic Nervous System and Reflexes with answers
... the cell body; begins as a single fiber but may give off side branches; near its end it may have fine extensions that contact the receptive surfaces of other cells, transmitting fibers of the neuron ...
... the cell body; begins as a single fiber but may give off side branches; near its end it may have fine extensions that contact the receptive surfaces of other cells, transmitting fibers of the neuron ...
Невротрансмитери в ЦНС
... GABA receptors: GABAA and GABAB. The benzodiazepines owe their sedative action to facilitation of this inhibitory neurotransmitter, binding to a discrete site on the GABAA receptor. ...
... GABA receptors: GABAA and GABAB. The benzodiazepines owe their sedative action to facilitation of this inhibitory neurotransmitter, binding to a discrete site on the GABAA receptor. ...
SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Composed of somatic parts of CNS
... neuron of the paravertebral ganglion at that level 4. Pass through the sympathetic trunk without synapsing with anything and go through a splanchnic nerve to get to prevertebral ganglia o Splanchnics innervate the abdominopelvic viscera o PRESYNAPTIC SYMPATHETIC FIBERS that innervate head, neck, bod ...
... neuron of the paravertebral ganglion at that level 4. Pass through the sympathetic trunk without synapsing with anything and go through a splanchnic nerve to get to prevertebral ganglia o Splanchnics innervate the abdominopelvic viscera o PRESYNAPTIC SYMPATHETIC FIBERS that innervate head, neck, bod ...
Neuromuscular Transmission - Dr. Logothetis
... The diversity of neurotransmitters is extensive, but their receptors can be grouped into two broad classes: ligand-gated ion channels and G protein-coupled receptors. By far the most-studied receptor is the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, the first ligand-gated ion channel to be purified, c ...
... The diversity of neurotransmitters is extensive, but their receptors can be grouped into two broad classes: ligand-gated ion channels and G protein-coupled receptors. By far the most-studied receptor is the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, the first ligand-gated ion channel to be purified, c ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... o This represents the movement of far fewer ions than would be required to alter the chemical concentration gradient. ...
... o This represents the movement of far fewer ions than would be required to alter the chemical concentration gradient. ...
slides
... • The muscular system makes up nearly half the weight of the human body • Muscles provide the forces that enable the body to move. Muscles stretch across joints to link one bone with another and work in groups to respond to nerve impulses. ...
... • The muscular system makes up nearly half the weight of the human body • Muscles provide the forces that enable the body to move. Muscles stretch across joints to link one bone with another and work in groups to respond to nerve impulses. ...
summary
... stretch across joints to link one bone with another and work in groups to respond to nerve impulses. ...
... stretch across joints to link one bone with another and work in groups to respond to nerve impulses. ...
Development & Neuroplasticity - U
... connections are more likely to die suggests that cell death increases the overall accuracy of synaptic connections ...
... connections are more likely to die suggests that cell death increases the overall accuracy of synaptic connections ...
Bell Work: What occurs during facilitated diffusion? Why is it
... Transport Proteins Span the membrane, change shape when they bind to molecules. Some bind to only one type of molecule, others to more than one type of molecule. Key Feature All use chemical energy to move a substance against the gradient. Most use ATP. Example: Neurons need to have a higher ...
... Transport Proteins Span the membrane, change shape when they bind to molecules. Some bind to only one type of molecule, others to more than one type of molecule. Key Feature All use chemical energy to move a substance against the gradient. Most use ATP. Example: Neurons need to have a higher ...
Lecture Outline
... o This represents the movement of far fewer ions than would be required to alter the chemical concentration gradient. ...
... o This represents the movement of far fewer ions than would be required to alter the chemical concentration gradient. ...
Chapter 17:
... painkillers produced in the CNS, blocking the pain transmitter that usually attaches to the injured organ allowing the perception of pain opiates (heroin, codeine, morphine) block the production of the pain transmitter. Since they act to decrease the production of natural painkillers, the amount o ...
... painkillers produced in the CNS, blocking the pain transmitter that usually attaches to the injured organ allowing the perception of pain opiates (heroin, codeine, morphine) block the production of the pain transmitter. Since they act to decrease the production of natural painkillers, the amount o ...
Bump attractors and the homogeneity assumption
... • The input to the SAM cells are determined by a comparison of the output of the output cells to the output of the input cells ...
... • The input to the SAM cells are determined by a comparison of the output of the output cells to the output of the input cells ...
Methods S1.
... We would like to finally note that such a particular definition of information transfer is meaningful only for short-term plastic synapses and, consequently, for history-dependent PSCs. An ideal synapse that transmits spikes always by identical PSC amplitude, would clearly not allow an observer to r ...
... We would like to finally note that such a particular definition of information transfer is meaningful only for short-term plastic synapses and, consequently, for history-dependent PSCs. An ideal synapse that transmits spikes always by identical PSC amplitude, would clearly not allow an observer to r ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.