Neurons & Transmission of Information
... •Synapse = junction where the axon terminal of the sending neuron communicates with a receiving neuron across the synaptic cleft •Neurotransmitters = chemical that is released into the synaptic cleft from the axon terminal of the sending neuron, crosses the synapse, & binds to appropriate receptor s ...
... •Synapse = junction where the axon terminal of the sending neuron communicates with a receiving neuron across the synaptic cleft •Neurotransmitters = chemical that is released into the synaptic cleft from the axon terminal of the sending neuron, crosses the synapse, & binds to appropriate receptor s ...
Slide ()
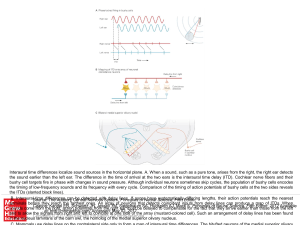
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
Hailee Denson Biology 1090 Mark Radandt Taking Sides Analysis
... deciphering meaning from these codelike brain signals. For years investigators have used several methods to interpret, or decode, the meaning in the stream of spikes coming from the retina. One method counts spikes from each axon separately over some period: the higher the firing rate, the stronger ...
... deciphering meaning from these codelike brain signals. For years investigators have used several methods to interpret, or decode, the meaning in the stream of spikes coming from the retina. One method counts spikes from each axon separately over some period: the higher the firing rate, the stronger ...
Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Like people moving to the same city…it makes doing their job easier (forming complex circuits) If neurons are communicating a similar message they will bundle with other like Neurons to improve the efficiency of the message delivery 9. What role does the Spinal Cord play in Neural Communication? ...
... Like people moving to the same city…it makes doing their job easier (forming complex circuits) If neurons are communicating a similar message they will bundle with other like Neurons to improve the efficiency of the message delivery 9. What role does the Spinal Cord play in Neural Communication? ...
Somatosensory system
... Mechanoreceptors in muscle and joints 1. Muscle spindle receptors – detect the extent and rate of muscle contraction, endings in parallel with muscle fibers 2. Golgi tendon organs – detect tension exerted by the muscle, ending in series with muscle fibers 3. Joint capsule receptors – detect flexion ...
... Mechanoreceptors in muscle and joints 1. Muscle spindle receptors – detect the extent and rate of muscle contraction, endings in parallel with muscle fibers 2. Golgi tendon organs – detect tension exerted by the muscle, ending in series with muscle fibers 3. Joint capsule receptors – detect flexion ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... Chapter 48 – Neurons, Synapses and Signaling – Homework 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contra ...
... Chapter 48 – Neurons, Synapses and Signaling – Homework 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contra ...
Ch. 2 the LGN and Striate Cortex
... • Neurons that fire to specific features of a stimulus • Pathway away from retina shows neurons that fire to more complex stimuli • Cells that are feature detectors: – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
... • Neurons that fire to specific features of a stimulus • Pathway away from retina shows neurons that fire to more complex stimuli • Cells that are feature detectors: – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
Beyond Spikes: Neural Codes and the Chemical Vocabulary of
... research, which we will refer to by the more general term connectionism, does not concern itself too much with biological realism, so the “neuron” states do not have to correspond to anything an actual cell has to deal with. Even in these cases, though, some of the biological language is preserved. ...
... research, which we will refer to by the more general term connectionism, does not concern itself too much with biological realism, so the “neuron” states do not have to correspond to anything an actual cell has to deal with. Even in these cases, though, some of the biological language is preserved. ...
How the Nervous System Works
... The nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps maintain homeostasis. A stimulus is any change or signal in the environment that can make ...
... The nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps maintain homeostasis. A stimulus is any change or signal in the environment that can make ...
Group Redundancy Measures Reveals Redundancy Reduction in the Auditory Pathway
... The current section focuses on the relation between single spikes and short windows of the acoustic stimuli shortly preceding them (which we denote as frames). As the set of possible frames is very large and no frame actually repeats itself, we must rst pre-process the stimuli to reduce frames dime ...
... The current section focuses on the relation between single spikes and short windows of the acoustic stimuli shortly preceding them (which we denote as frames). As the set of possible frames is very large and no frame actually repeats itself, we must rst pre-process the stimuli to reduce frames dime ...
as a PDF - University of Sussex
... However sparse coding is not the only way to reduce energy consumption by neurons using action potentials (APs). Changing the kinetics of the ion channels involved in generating the spike can reduce the energy requirements of the APs. Sengupta et al. [22] show that considerable differences in the re ...
... However sparse coding is not the only way to reduce energy consumption by neurons using action potentials (APs). Changing the kinetics of the ion channels involved in generating the spike can reduce the energy requirements of the APs. Sengupta et al. [22] show that considerable differences in the re ...
deep learning with different types of neurons
... Deep learning networks can be trained for both supervised and also unsupervised learning tasks. Deep learning network architecture is similar to the normal neural network but it has more hidden layers. ...
... Deep learning networks can be trained for both supervised and also unsupervised learning tasks. Deep learning network architecture is similar to the normal neural network but it has more hidden layers. ...
Nervous System = communication conduit b/w brain
... Myelin sheath has gaps (nodes of Ranvier) along axon Na+/K+ cannot diffuse through myelin but they can reach plasma membrane at these nodes This allows action potential to jump from node to node, increasing speed of impulse as it travels length of axon. Some neurons have myelin, some do not ...
... Myelin sheath has gaps (nodes of Ranvier) along axon Na+/K+ cannot diffuse through myelin but they can reach plasma membrane at these nodes This allows action potential to jump from node to node, increasing speed of impulse as it travels length of axon. Some neurons have myelin, some do not ...
ppt
... but does not know the precise post-stimulus time at which the considered responses were emitted, it might set the decoder using the wrong response probabilities (for example, those corresponding to window 2 rather than window 1). The stimulus reconstruction will then be flawed and information will b ...
... but does not know the precise post-stimulus time at which the considered responses were emitted, it might set the decoder using the wrong response probabilities (for example, those corresponding to window 2 rather than window 1). The stimulus reconstruction will then be flawed and information will b ...
Neurons: Our Building Blocks
... Neurons: Our Building Blocks -Neurons are cells specialized to receive, process and transmit information to other cells. -Bundles of neurons are called nerves. ...
... Neurons: Our Building Blocks -Neurons are cells specialized to receive, process and transmit information to other cells. -Bundles of neurons are called nerves. ...
Neurology - wsscience
... Phagocytic activities in the neural tissue Surrounding nerve cell bodies in peripheral ganglia ...
... Phagocytic activities in the neural tissue Surrounding nerve cell bodies in peripheral ganglia ...
Module I. Introduction to biophysical models of individual cells and... plane analysis important to capture phenomenology and sometimes – biophysical mechanisms
... 1. Read about neurons, or about phase-plane methods. We are learning terminology, getting everybody on the same page 2. Simulate a Hodgkin-huxley model in matlab, make it spike. 3. Consider other currents. e.g. IK-Ca, IAHP, IA, Ih, IM, IKLT,IT. Pick 2 of the currents. Explain what happens at differe ...
... 1. Read about neurons, or about phase-plane methods. We are learning terminology, getting everybody on the same page 2. Simulate a Hodgkin-huxley model in matlab, make it spike. 3. Consider other currents. e.g. IK-Ca, IAHP, IA, Ih, IM, IKLT,IT. Pick 2 of the currents. Explain what happens at differe ...
Chapter 2
... 31. Which of the following would contribute to the negative resting membrane potential of a neuron? (p 17) 32. Which of the following states is true regarding the resting membrane potential of a neuron? (45) 33. When the membrane potential becomes positive, this is called __________. (p 46) 34. Wha ...
... 31. Which of the following would contribute to the negative resting membrane potential of a neuron? (p 17) 32. Which of the following states is true regarding the resting membrane potential of a neuron? (45) 33. When the membrane potential becomes positive, this is called __________. (p 46) 34. Wha ...
17-01-05 1 Golgi - stained neurons Neuronal function
... main metabolic centre of neuron main (but not only) site of protein synthesis lots of mitochondria lots of endoplasmic reticulum size in vertebrates: small: 8 µm e.g. granule cells in cerebellum large: 50 µm layer V motor cortical neurons largest: 200 µm Mauthner cell in fish brainstem size in inver ...
... main metabolic centre of neuron main (but not only) site of protein synthesis lots of mitochondria lots of endoplasmic reticulum size in vertebrates: small: 8 µm e.g. granule cells in cerebellum large: 50 µm layer V motor cortical neurons largest: 200 µm Mauthner cell in fish brainstem size in inver ...