Neurophysiology: Sensing and categorizing
... In early sensory areas of the cerebral cortex, stimulus representation appears to depend almost exclusively on elementary physical attributes, such as the orientation of visual edges, the frequency of an auditory tone, or the pressure of a somatosensory stimulus applied to the skin. Neural responses ...
... In early sensory areas of the cerebral cortex, stimulus representation appears to depend almost exclusively on elementary physical attributes, such as the orientation of visual edges, the frequency of an auditory tone, or the pressure of a somatosensory stimulus applied to the skin. Neural responses ...
JARINGAN SYARAF TIRUAN
... They are particularly fault tolerant – this is equivalent to the “graceful degradation” found in biological systems. They are very noise tolerant – so they can cope with situations where normal symbolic systems would have difficulty. In principle, they can do anything a symbolic/logic system can do, ...
... They are particularly fault tolerant – this is equivalent to the “graceful degradation” found in biological systems. They are very noise tolerant – so they can cope with situations where normal symbolic systems would have difficulty. In principle, they can do anything a symbolic/logic system can do, ...
How fast is the speed of thought?
... more sophisticated the information analysis will be. However, even with a reaction time of 400-500 ms for the recognition and discrimination of visual stimuli, there will still be only about 20-30 ms processing time per synapse. How fast can you see? Another way of looking at processing times is to ...
... more sophisticated the information analysis will be. However, even with a reaction time of 400-500 ms for the recognition and discrimination of visual stimuli, there will still be only about 20-30 ms processing time per synapse. How fast can you see? Another way of looking at processing times is to ...
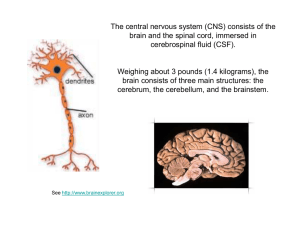
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
pre02
... • Switched Capacitor (SC) is a circuit made of one capacitor and two switches which connect the capacitor with a given frequency alternately to the input an output of the SC. This simulates the behaviors of a resistor, so SCs are used in integrated circuits instead of resistors. The resistance is se ...
... • Switched Capacitor (SC) is a circuit made of one capacitor and two switches which connect the capacitor with a given frequency alternately to the input an output of the SC. This simulates the behaviors of a resistor, so SCs are used in integrated circuits instead of resistors. The resistance is se ...
Paying attention to correlated neural activity
... are remarkably complicated and counterintuitive1–5. However, we have no choice. If we are to understand how neural activity relates to behavioral performance, we need to measure how much information is conveyed by populations of neurons, which depends heavily on the exact pattern of correlated activ ...
... are remarkably complicated and counterintuitive1–5. However, we have no choice. If we are to understand how neural activity relates to behavioral performance, we need to measure how much information is conveyed by populations of neurons, which depends heavily on the exact pattern of correlated activ ...
nervous system
... a.) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm; location of cellular metabolic activity b.) Dendrites: carry impulses from the environment or from other neurons toward the cell body c.) Axon: carries impulses away from the cell body d.) Node: increase the speed at which an impulse can ...
... a.) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm; location of cellular metabolic activity b.) Dendrites: carry impulses from the environment or from other neurons toward the cell body c.) Axon: carries impulses away from the cell body d.) Node: increase the speed at which an impulse can ...
Laminar and Columnar organization of the cerebral cortex
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
Neural Nets: introduction
... and bind to receptor molecules in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron thus changing their shape. – This opens up holes that allow specific ions in or out. • The effectiveness of the synapse can be changed – vary the number of vesicles of transmitter – vary the number of receptor molecules. • Syn ...
... and bind to receptor molecules in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron thus changing their shape. – This opens up holes that allow specific ions in or out. • The effectiveness of the synapse can be changed – vary the number of vesicles of transmitter – vary the number of receptor molecules. • Syn ...
Synaptic Transmission
... potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
... potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
Chapter 33 Nervous System
... iv. Contains all neurons that are not part of central nervous system, including sensory neurons and motor neurons v. Neurons in peripheral nervous system can be classified as part of somatic nervous system or autonomic nervous system vi. Somatic nervous system 1. Voluntary 2. Relays information to a ...
... iv. Contains all neurons that are not part of central nervous system, including sensory neurons and motor neurons v. Neurons in peripheral nervous system can be classified as part of somatic nervous system or autonomic nervous system vi. Somatic nervous system 1. Voluntary 2. Relays information to a ...
CHANGES OF THE CELL BODY OF NEURONS IN CENTRAL
... In morphological investigations we observed structurally modified neurons in the gray matter of the cerebrum, cerebellum and the spinal cord of all experimental groups of mice, but in mice line 129/Sv damaged of neurons more intensive. In laboratory mice of all lines of the oppressed behavioral acti ...
... In morphological investigations we observed structurally modified neurons in the gray matter of the cerebrum, cerebellum and the spinal cord of all experimental groups of mice, but in mice line 129/Sv damaged of neurons more intensive. In laboratory mice of all lines of the oppressed behavioral acti ...
Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which
... fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amount of generalization is normal, over generalizing to the CS+ has been implicated as a marker ...
... fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amount of generalization is normal, over generalizing to the CS+ has been implicated as a marker ...
AP Psychology - Ms. Hofmann`s Website
... Google: Neurons the messengers and click on the following site: http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/morris2/chapter2/medialib/summary/1.html ...
... Google: Neurons the messengers and click on the following site: http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/morris2/chapter2/medialib/summary/1.html ...
Nociceptive sensation. Somatic sensory analyzer
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
PsychSim 5: PSYCHOLOGY`S TIMELINE
... This activity describes what researchers have learned about the special abilities of the left and right sides of the brain. You will learn how information is transmitted to these two hemispheres and about the unique function of each. Hemispheric Connections What is the name of the band of fibers c ...
... This activity describes what researchers have learned about the special abilities of the left and right sides of the brain. You will learn how information is transmitted to these two hemispheres and about the unique function of each. Hemispheric Connections What is the name of the band of fibers c ...
Your Nervous System
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex cognitive processes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Located outside of the skull and spine Serves to bring sensory information into the CNS and carry motor signals out of the CNS ...
... Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex cognitive processes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Located outside of the skull and spine Serves to bring sensory information into the CNS and carry motor signals out of the CNS ...
Request pdf
... T o be regarded as specialized types of nerve cells are the receptor cells that are found at the first stage of any sensory system. T h e receptor can be defined as a neuron in which the generator potential is produced not by synaptic action but by particular environmental stimuli such as pressure, ...
... T o be regarded as specialized types of nerve cells are the receptor cells that are found at the first stage of any sensory system. T h e receptor can be defined as a neuron in which the generator potential is produced not by synaptic action but by particular environmental stimuli such as pressure, ...