THE NEURON (Slides 4 to 14) • Based on the PowerPoint attached
... The firing is caused by an influx of sodium. It takes a few milliseconds to ‘fire’ sending an electrical impulse to the synapse, the threshold of excitation must be exceeded for the neuron to fire. The connections of the neurons to other neurons determine whether the neuron is likely to fire or not ...
... The firing is caused by an influx of sodium. It takes a few milliseconds to ‘fire’ sending an electrical impulse to the synapse, the threshold of excitation must be exceeded for the neuron to fire. The connections of the neurons to other neurons determine whether the neuron is likely to fire or not ...
A natural example of different circuit architectures for analogous
... Akira Sakurai and Paul S. Katz Neuroscience Institute, Georgia State University ...
... Akira Sakurai and Paul S. Katz Neuroscience Institute, Georgia State University ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
3-1-neuron _1
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
PDF
... another is in how these very similar neurons connect with each other. For humans, these maps would have special significance because an Atlas of Connections (ie, the human connectome) would represent a blueprint of ourselves, including imprints of all those things that are not in our genome, such as ...
... another is in how these very similar neurons connect with each other. For humans, these maps would have special significance because an Atlas of Connections (ie, the human connectome) would represent a blueprint of ourselves, including imprints of all those things that are not in our genome, such as ...
The Nervous System - Canton Local Schools
... Neuron: a nerve cell. The basic building block of the nervous system Dendrite: The bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward cell body Axon: the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers. Used to pass messages to other neurons or musc ...
... Neuron: a nerve cell. The basic building block of the nervous system Dendrite: The bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward cell body Axon: the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers. Used to pass messages to other neurons or musc ...
IN SEARCH OF PRINCIPLES IN INTEGRATIVE BIOLOGY
... priori that only the number and the spacing of impulses are available for coding (Fig. 4). But somewhat more sophisticated questions are being investigated today. For example, what level of statistical confidence does the postsynaptic cell require to distinguish a single significant change in freque ...
... priori that only the number and the spacing of impulses are available for coding (Fig. 4). But somewhat more sophisticated questions are being investigated today. For example, what level of statistical confidence does the postsynaptic cell require to distinguish a single significant change in freque ...
bioii ch10 ppt
... •This is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It is also the major excitatory transmitter in the brain, and major mediator of excitatory signals in the mammalian central nervous system, involved in most aspects of normal brain functions including cognition, ...
... •This is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It is also the major excitatory transmitter in the brain, and major mediator of excitatory signals in the mammalian central nervous system, involved in most aspects of normal brain functions including cognition, ...
Nociceptive system
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
The neural basis for combinatorial coding in a cortical population response
... Constructing a model population. We consider first a model population in which each cell responds independently to its sensory inputs. Mathematically, this means that the probability of responses from the population can be decomposed as a product of probabilities for each individual cell, as in Equa ...
... Constructing a model population. We consider first a model population in which each cell responds independently to its sensory inputs. Mathematically, this means that the probability of responses from the population can be decomposed as a product of probabilities for each individual cell, as in Equa ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
Neurons_and_Neurotranmission
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
Ch 4 V Cortexb - Texas A&M University
... • Neurons that fire to specific features of a stimulus • Pathway away from retina shows neurons that fire to more complex stimuli • Cells that are feature detectors: – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
... • Neurons that fire to specific features of a stimulus • Pathway away from retina shows neurons that fire to more complex stimuli • Cells that are feature detectors: – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
Slide ()
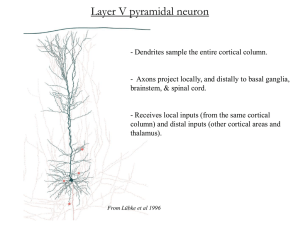
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Myelin Sheath: a layer of fatty cells encasing the fibers of many axons which allows faster transmission speeds in neurons. ...
... Myelin Sheath: a layer of fatty cells encasing the fibers of many axons which allows faster transmission speeds in neurons. ...
Print this Page Presentation Abstract Program#/Poster#: 532.07/GG10
... suppression circuitry consisting of both SOM+ and PV+ inhibitory neurons in which the differences in experimental observations are accounted for by differences in the inhibitory neuron subclasses in terms of their network ...
... suppression circuitry consisting of both SOM+ and PV+ inhibitory neurons in which the differences in experimental observations are accounted for by differences in the inhibitory neuron subclasses in terms of their network ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
1 Introduction to Neurobiology Rudolf Cardinal NST 1B
... in exchange for potassium (K+) in the ratio 3:2; this results in a potential difference across the membrane known as the membrane potential. In neurons at rest, this is approximately –65 mV (with respect to the outside); this is termed the resting potential. If the membrane potential is raised (depo ...
... in exchange for potassium (K+) in the ratio 3:2; this results in a potential difference across the membrane known as the membrane potential. In neurons at rest, this is approximately –65 mV (with respect to the outside); this is termed the resting potential. If the membrane potential is raised (depo ...
Page 1
... correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line before the number as you watch the video. The Nervous System _________1. What are things in our environment that cause an organism to react called? A. responses B. senses C. stimuli D ...
... correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line before the number as you watch the video. The Nervous System _________1. What are things in our environment that cause an organism to react called? A. responses B. senses C. stimuli D ...
Neuron Structure
... this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC bi ...
... this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC bi ...