doc psych 100 review summary
... Double-consciousness (patients re-live past streams while being aware of the present) They occur in an all or none pattern (don’t go backward, are not mixed with other experiences and stop as suddenly as they started upon removal of the stimulation) The same experience can be elicited by re-stimulat ...
... Double-consciousness (patients re-live past streams while being aware of the present) They occur in an all or none pattern (don’t go backward, are not mixed with other experiences and stop as suddenly as they started upon removal of the stimulation) The same experience can be elicited by re-stimulat ...
The fertile brain - Health Research Council
... Professor Allan Herbison from the Department of Physiology, Associate Professor Dave Grattan and Dr Greg Anderson from the Department of Anatomy and Structural Biology are pooling their expertise to find answers to key questions. A recent Fertility New Zealand study found nearly 25 per cent of New Z ...
... Professor Allan Herbison from the Department of Physiology, Associate Professor Dave Grattan and Dr Greg Anderson from the Department of Anatomy and Structural Biology are pooling their expertise to find answers to key questions. A recent Fertility New Zealand study found nearly 25 per cent of New Z ...
PRINCIPLES OF SENSORY TRANSDUCTION
... FIGURE 4 Center/surround organization of receptive fields is common in sensory systems. In this organization, a stimulus in the center of the receptive field produces one effect, usually excitation, whereas a stimulus in the surround area has the opposite effect, usually inhibition. (A) In the soma ...
... FIGURE 4 Center/surround organization of receptive fields is common in sensory systems. In this organization, a stimulus in the center of the receptive field produces one effect, usually excitation, whereas a stimulus in the surround area has the opposite effect, usually inhibition. (A) In the soma ...
Somatic nervous system
... The somatic nervous system processes sensory information and controls all voluntary muscular systems within the body, with the exception of reflex arcs. The basic route of nerve signals within the efferent somatic nervous system involves a sequence that begins in the upper cell bodies of motor neuro ...
... The somatic nervous system processes sensory information and controls all voluntary muscular systems within the body, with the exception of reflex arcs. The basic route of nerve signals within the efferent somatic nervous system involves a sequence that begins in the upper cell bodies of motor neuro ...
The Nervous System
... Neurotransmitters diffuse from the end of one neuron to receptors on the next neuron. When they land on the specific receptor they allow gates to open that allow sodium to enter - this ignites the electro-chemical impulse to begin in the the next neuron. ...
... Neurotransmitters diffuse from the end of one neuron to receptors on the next neuron. When they land on the specific receptor they allow gates to open that allow sodium to enter - this ignites the electro-chemical impulse to begin in the the next neuron. ...
Efficient Coding Hypothesis and an Introduction to
... relating to the Efficient Coding Hypothesis that were published in the last several years. We present some misconceptions about the theory behind Efficient Coding Hypothesis, and criticisms of some experimental results [Simoncelli 2003]. The purpose of Vision The efficient coding of visual informati ...
... relating to the Efficient Coding Hypothesis that were published in the last several years. We present some misconceptions about the theory behind Efficient Coding Hypothesis, and criticisms of some experimental results [Simoncelli 2003]. The purpose of Vision The efficient coding of visual informati ...
12-nervoussystemintro - Alexmac
... • Injured neurons in the central nervous system don’t regenerate easily. • Some neurons in peripheral nervous system can regrow and repair a small gap. ...
... • Injured neurons in the central nervous system don’t regenerate easily. • Some neurons in peripheral nervous system can regrow and repair a small gap. ...
nervous system
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes (axons/dendrite ...
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes (axons/dendrite ...
Power Point
... During an action potential, depolarization can change the membrane potential from –70 mV to about +30 mV. During repolarization the membrane potential returns to –70 mV. The nerve fiber cannot be stimulated again until repolarization is complete. This period is called the refractory period. If the s ...
... During an action potential, depolarization can change the membrane potential from –70 mV to about +30 mV. During repolarization the membrane potential returns to –70 mV. The nerve fiber cannot be stimulated again until repolarization is complete. This period is called the refractory period. If the s ...
Week7
... • Components of a neuron: cell body, dendrites, axon, synaptic terminals. • The electrical potential across the cell membrane exhibits spikes called action potentials. • Originating in the cell body, this spike travels down the axon and causes chemical neurotransmitters to be released at synaptic te ...
... • Components of a neuron: cell body, dendrites, axon, synaptic terminals. • The electrical potential across the cell membrane exhibits spikes called action potentials. • Originating in the cell body, this spike travels down the axon and causes chemical neurotransmitters to be released at synaptic te ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... The three essential functions of the nervous system are: 1. sense changes 2. integrate and interpret 3. respond How do the various components of the nervous system cooperate in performing these functions? ...
... The three essential functions of the nervous system are: 1. sense changes 2. integrate and interpret 3. respond How do the various components of the nervous system cooperate in performing these functions? ...
Central nervous system
... 3 kinds of synapses with different modes of action • Excitatory cholinergic synapse • Inhibitory GABA-ergic synapse • Excitatory adrenergic synapse ...
... 3 kinds of synapses with different modes of action • Excitatory cholinergic synapse • Inhibitory GABA-ergic synapse • Excitatory adrenergic synapse ...
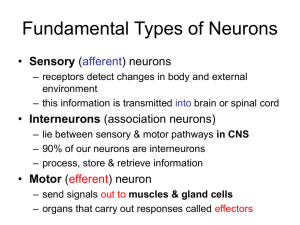
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
Artificial Intelligence Connectionist Models Inspired by the brain
... Connectionist Models In contrast to symbolic models ● Based on the brain paradigm or brain metaphor ● Have enjoyed much success in recent years ● Synonyms ...
... Connectionist Models In contrast to symbolic models ● Based on the brain paradigm or brain metaphor ● Have enjoyed much success in recent years ● Synonyms ...
NeuralCell-Neurons.stud
... by Axon Length 1. Golgi type I Neurons • Long axons (longest from the cortex to the tip of spinal cord, 50-70 cm) 2. Golgi type II Neurons • Short axons (shortest axons terminate only a few micron from cell body, interneurons) 3. Amacrine Neurons • An unusual cell type, lack axons ...
... by Axon Length 1. Golgi type I Neurons • Long axons (longest from the cortex to the tip of spinal cord, 50-70 cm) 2. Golgi type II Neurons • Short axons (shortest axons terminate only a few micron from cell body, interneurons) 3. Amacrine Neurons • An unusual cell type, lack axons ...
Nervous System - s3.amazonaws.com
... secrete cerebrospinal fluid into the fluid-filled spaces of the brain (ventricles) and spinal cord (central canal). • These capillaries are quite selective in allowing nutrients to pass into the brain, but not waste products. • This selective mechanism is called the blood-brain barrier and helps mai ...
... secrete cerebrospinal fluid into the fluid-filled spaces of the brain (ventricles) and spinal cord (central canal). • These capillaries are quite selective in allowing nutrients to pass into the brain, but not waste products. • This selective mechanism is called the blood-brain barrier and helps mai ...
Slide ()
... Different neural mechanisms underlie long-term potentiation at each of the three synapses in the trisynaptic pathway in the hippocampus. Long-term potentiation (LTP) is present at synapses throughout the hippocampus but depends to differing degrees on activation of NMDA-type glutamate receptors. A. ...
... Different neural mechanisms underlie long-term potentiation at each of the three synapses in the trisynaptic pathway in the hippocampus. Long-term potentiation (LTP) is present at synapses throughout the hippocampus but depends to differing degrees on activation of NMDA-type glutamate receptors. A. ...
The Nervous System
... on to motor neurons. • Motor Neurons: carry impulses away from the brain and spinal cord. ...
... on to motor neurons. • Motor Neurons: carry impulses away from the brain and spinal cord. ...
Spinal Cord
... 1st order neurons Soma in ganglion of dorsal root or cranial nerve Synapse with 2nd order neuron 2nd order neurons Soma in dorsal horn or ...
... 1st order neurons Soma in ganglion of dorsal root or cranial nerve Synapse with 2nd order neuron 2nd order neurons Soma in dorsal horn or ...
Motor
... neurons innervating axial musculature are located medially, whereas those innervating the distal musculature are located more laterally. ...
... neurons innervating axial musculature are located medially, whereas those innervating the distal musculature are located more laterally. ...
Factual - Cengage
... Hz to 5000 Hz), pitch perception depends on a combination of place and frequency coding; for high-frequency sounds (over 5000 Hz), pitch perception depends on place coding only. ...
... Hz to 5000 Hz), pitch perception depends on a combination of place and frequency coding; for high-frequency sounds (over 5000 Hz), pitch perception depends on place coding only. ...
Nervous System Ch 10 Notes - Reading Community Schools
... Refractory Period • Absolute – Time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential • Relative – Time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential • Under normal conditions each fiber may conduct 10-500 impulses per second • Larger neurons conduct up to 2500 p ...
... Refractory Period • Absolute – Time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential • Relative – Time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential • Under normal conditions each fiber may conduct 10-500 impulses per second • Larger neurons conduct up to 2500 p ...