Slide ()
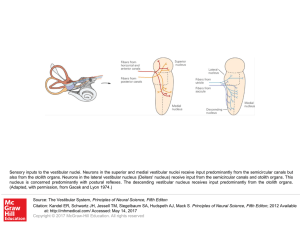
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
October 25
... Initial processing at the glomeruli separate smells into broad categories. Information passes from the bulbs into olfactory tracts (bundles of axons) projecting to primitive regions of cortex, then to the thalamus, and finally to the cortex. Parallel pathways process smell in many areas of the corte ...
... Initial processing at the glomeruli separate smells into broad categories. Information passes from the bulbs into olfactory tracts (bundles of axons) projecting to primitive regions of cortex, then to the thalamus, and finally to the cortex. Parallel pathways process smell in many areas of the corte ...
Neuroanatomy Handout #1: The Motor Neuron
... sodium channels open and closing potassium channels • Local anesthetic drugs block sodium channels and therefore prevent action potentials from occurring. – Example: Novocain • General anesthetics open potassium channels wider than usual ...
... sodium channels open and closing potassium channels • Local anesthetic drugs block sodium channels and therefore prevent action potentials from occurring. – Example: Novocain • General anesthetics open potassium channels wider than usual ...
22 reflexes 1 - The reflex arc
... This is what you call a MONOSYNAPTIC arc If there are any interneurons in the way between the afferent and the efferent neurons, this is called a POLYSYNAPTIC arc. There can be anywhere up to 200 synapses in a polysynaptic arc In the childish diagram above, some important elements have been omitted: ...
... This is what you call a MONOSYNAPTIC arc If there are any interneurons in the way between the afferent and the efferent neurons, this is called a POLYSYNAPTIC arc. There can be anywhere up to 200 synapses in a polysynaptic arc In the childish diagram above, some important elements have been omitted: ...
APP Ch_3 Outline
... Action Potential – A very brief shift in a Neuron’s electrical charge that travels along an axon. Absolute Refractory Period – Minimum length of time after an action potential during which another action potential cannot begin. Only about 1 or 2 Milliseconds. All-Or-None Law – Neural Impulses ...
... Action Potential – A very brief shift in a Neuron’s electrical charge that travels along an axon. Absolute Refractory Period – Minimum length of time after an action potential during which another action potential cannot begin. Only about 1 or 2 Milliseconds. All-Or-None Law – Neural Impulses ...
Introduction slides - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... The current best strategy for solving this problem: - figure out an algorithm for translating latent variables into actions - map it onto the brain - do experiments to see if the mapping is correct ...
... The current best strategy for solving this problem: - figure out an algorithm for translating latent variables into actions - map it onto the brain - do experiments to see if the mapping is correct ...
53 XIX BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O`Brien)
... environment to sensory neurons. b. Sensory neurons connect to neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). c. The central nervous system integrates information and activates motor neurons. d. Motor neurons transmit information to effectors in glands or muscles. e. Reflexes are rapid responses that c ...
... environment to sensory neurons. b. Sensory neurons connect to neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). c. The central nervous system integrates information and activates motor neurons. d. Motor neurons transmit information to effectors in glands or muscles. e. Reflexes are rapid responses that c ...
Properties of reflex action
... to interneurons then to efferent i.e. one way direction • At synapse, conduction only in one direction from the presynaptic neuron to the post-synaptic neuron, because the transmitter releasing vesicles present only in the pre-synaptic membrane ...
... to interneurons then to efferent i.e. one way direction • At synapse, conduction only in one direction from the presynaptic neuron to the post-synaptic neuron, because the transmitter releasing vesicles present only in the pre-synaptic membrane ...
Slide 1
... 1. Neurons are electrically active; They have a resting voltage, and can undergo electrical changes ...
... 1. Neurons are electrically active; They have a resting voltage, and can undergo electrical changes ...
Neuron Stations
... halves sticking out. Take the 2 halves and twist them together into a single extension. Axons send information received from the neuron to the next neuron in its path. Axons can be as long as 3 meters and information can travel as fast as 100 meters/second (224 miles/hour). Q3: What else can travel ...
... halves sticking out. Take the 2 halves and twist them together into a single extension. Axons send information received from the neuron to the next neuron in its path. Axons can be as long as 3 meters and information can travel as fast as 100 meters/second (224 miles/hour). Q3: What else can travel ...
structure and function of the neurologic system
... – Neurotransmitter binds the receptor on the postsynaptic neuron • Signals opening of nearby Na+ channels • Membrane potential changes in the postsynaptic neuron • Generation of action potential • Action potential travels through postsynaptic neuron’s dendrite, cell body and axon to axon ending ...
... – Neurotransmitter binds the receptor on the postsynaptic neuron • Signals opening of nearby Na+ channels • Membrane potential changes in the postsynaptic neuron • Generation of action potential • Action potential travels through postsynaptic neuron’s dendrite, cell body and axon to axon ending ...
Sonia Gasparini, PhD Degrees Assistant Professor of Cell Biology & Anatomy and
... these neurons. By elucidating the mechanisms of dendritic integration in the entorhinal cortex, these studies will increase our knowledge of memory processing. Relating pathological effects to electrophysiological properties of neuronal compartments that have not been fully explored, such as dendrit ...
... these neurons. By elucidating the mechanisms of dendritic integration in the entorhinal cortex, these studies will increase our knowledge of memory processing. Relating pathological effects to electrophysiological properties of neuronal compartments that have not been fully explored, such as dendrit ...
DM-Lecture-10 - WordPress.com
... axon via the cell body •Axon connects to dendrites via synapses – Synapses vary in strength – Synapses may be excitatory or inhibitory ...
... axon via the cell body •Axon connects to dendrites via synapses – Synapses vary in strength – Synapses may be excitatory or inhibitory ...
1 Neurons 2 Electrical activity of neurons at rest.
... filament that arises from the cell body and travels for a distance, as far as 1 meter in humans or even more in other species. There are axons, for example that run from your spine to your toes. As a general rule, dendrites receive inputs to the neuron and the axon is used to transmit the output. Th ...
... filament that arises from the cell body and travels for a distance, as far as 1 meter in humans or even more in other species. There are axons, for example that run from your spine to your toes. As a general rule, dendrites receive inputs to the neuron and the axon is used to transmit the output. Th ...
Language within our grasp:
... Mirroring as communication • These are very general ‘semantic’ encoders – They fire with presentation of the action from many perspective, near and far – They are sensitive to the apparent purpose of the action • In this way, they represent the actions and (thereby) represent a common thread of und ...
... Mirroring as communication • These are very general ‘semantic’ encoders – They fire with presentation of the action from many perspective, near and far – They are sensitive to the apparent purpose of the action • In this way, they represent the actions and (thereby) represent a common thread of und ...
PDF
... Stay tuned for more information and the launch announcement. Announcing the CereStage 96 channel Headstage This is exciting news for all Plexon OmniPlex® or MAP Data Acquisition System customers using the Utah Array in their research. We have just launched the CereStage 96 channel unity, gain headst ...
... Stay tuned for more information and the launch announcement. Announcing the CereStage 96 channel Headstage This is exciting news for all Plexon OmniPlex® or MAP Data Acquisition System customers using the Utah Array in their research. We have just launched the CereStage 96 channel unity, gain headst ...
CHAPTER NINE: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... neurotransmitters ii. Composed of two parts 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons ii. Prevents nerve impulses from ___________ passing from one neuron ...
... neurotransmitters ii. Composed of two parts 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons ii. Prevents nerve impulses from ___________ passing from one neuron ...
Control of Motor Movement
... Motor neuron – carries response away form CNS to effector Effector – muscle or gland ...
... Motor neuron – carries response away form CNS to effector Effector – muscle or gland ...
Document
... One afternoon’s worth of results: 1. Action Potential “all or nothing” character of electrical excitation. ...
... One afternoon’s worth of results: 1. Action Potential “all or nothing” character of electrical excitation. ...
11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... A. A synapse is a junction that mediates information transfer between neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell (p. 406; Fig. 11.16). B. Neurons conducting impulses toward the synapse are presynaptic cells, and neurons carrying impulses away from the synapse are postsynaptic cells (p. 406). C ...
... A. A synapse is a junction that mediates information transfer between neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell (p. 406; Fig. 11.16). B. Neurons conducting impulses toward the synapse are presynaptic cells, and neurons carrying impulses away from the synapse are postsynaptic cells (p. 406). C ...























