AP Ch. 2 vocab
... the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron also called synaptic gap or cleft chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons ...
... the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron also called synaptic gap or cleft chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons ...
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Sensory neurons: (Afferent) Carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) toward the central nervous system. Motor neurons: (motoneurons) (Efferent) Carry signals away from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body. Receptors: Sense the environm ...
... Sensory neurons: (Afferent) Carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) toward the central nervous system. Motor neurons: (motoneurons) (Efferent) Carry signals away from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body. Receptors: Sense the environm ...
Neural Development
... They collect together to form each of the various brain structures and acquire specific ways of transmitting nerve messages. Their processes, or axons, grow long distances to find and connect with appropriate partners, forming elaborate and specific circuits. Finally, sculpting action eliminates red ...
... They collect together to form each of the various brain structures and acquire specific ways of transmitting nerve messages. Their processes, or axons, grow long distances to find and connect with appropriate partners, forming elaborate and specific circuits. Finally, sculpting action eliminates red ...
cns structure - Department of Physiology
... center of receptive field, due to increased receptor density. However, this is not a precise mechanism because an increase in the number of action potentials could also mean a more intense stimulus was applied. Two stimulus points ...
... center of receptive field, due to increased receptor density. However, this is not a precise mechanism because an increase in the number of action potentials could also mean a more intense stimulus was applied. Two stimulus points ...
31.1 The Neuron
... Functions of the Nervous System • The nervous system records sensory data from the body’s external and internal conditions, sends that information to the Central Nervous System for processing and then responds to the stimuli. ...
... Functions of the Nervous System • The nervous system records sensory data from the body’s external and internal conditions, sends that information to the Central Nervous System for processing and then responds to the stimuli. ...
Nervous System Notes
... How a Nerve Impulse Travels • Nerve impulses can travels as fast as 120 meters per second! THAT’S FAST! • Messages travel from the Cell Body, down the axon, and to the axon tips! ...
... How a Nerve Impulse Travels • Nerve impulses can travels as fast as 120 meters per second! THAT’S FAST! • Messages travel from the Cell Body, down the axon, and to the axon tips! ...
Computational Models of Neural Auditory Processing
... by Ohm and Helmholtz. This crude model makes it difficult for them to relate new models and experimental results to details of reality. The present line of investigation seeks to apply the modern tools of signal processing and discrete simulation of physical systems to provide a new substrate of fro ...
... by Ohm and Helmholtz. This crude model makes it difficult for them to relate new models and experimental results to details of reality. The present line of investigation seeks to apply the modern tools of signal processing and discrete simulation of physical systems to provide a new substrate of fro ...
Neural Networks
... Planning in building a Neural Network Decisions must be taken on the following: - The number of units to use. - The type of units required. - Connection between the units. ...
... Planning in building a Neural Network Decisions must be taken on the following: - The number of units to use. - The type of units required. - Connection between the units. ...
Slide ()
... Neurogenic and myopathic diseases have different effects on the motor unit. A. A motor unit potential is recorded by inserting a needle electrode into the muscle. The muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron are not usually adjacent to one another, yet the highly effective transmission at t ...
... Neurogenic and myopathic diseases have different effects on the motor unit. A. A motor unit potential is recorded by inserting a needle electrode into the muscle. The muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron are not usually adjacent to one another, yet the highly effective transmission at t ...
Chapter 13 - Los Angeles City College
... 1. Sensory Input: Conduction of signals from sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, skin, etc.) to information processing centers (brain and spinal cord). 2. Integration: Interpretation of sensory signals and development of a response. Occurs in brain and spinal cord. 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signa ...
... 1. Sensory Input: Conduction of signals from sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, skin, etc.) to information processing centers (brain and spinal cord). 2. Integration: Interpretation of sensory signals and development of a response. Occurs in brain and spinal cord. 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signa ...
Study questions for this lab.
... ascend upward toward the brain? Where is this tract located? Where are third order neuronal cell bodies located in the pain and temperature pathway? Of what use is this knowledge about the routes by which the various sensory modalities pass from the spinal cord to the brain? What is an electromyogra ...
... ascend upward toward the brain? Where is this tract located? Where are third order neuronal cell bodies located in the pain and temperature pathway? Of what use is this knowledge about the routes by which the various sensory modalities pass from the spinal cord to the brain? What is an electromyogra ...
Slide ()
... The pattern of motor neuron activity can change the biochemical and functional properties of skeletal muscle cells. A. Muscle fibers have characteristic metabolic, molecular, and electrical properties that identify them as "slow" (tonic) or "fast" (phasic) types. The micrograph on the right shows a ...
... The pattern of motor neuron activity can change the biochemical and functional properties of skeletal muscle cells. A. Muscle fibers have characteristic metabolic, molecular, and electrical properties that identify them as "slow" (tonic) or "fast" (phasic) types. The micrograph on the right shows a ...
Document
... LIP (lateral intraparietal) – contains a map of neurons representing the saliency of spatial locations VIP (ventral intraparietal) – receives input from the senses. Represented space in head-centered reference frame MT (also known as V5, or middle temporal) is part of the visual cortex. The mi ...
... LIP (lateral intraparietal) – contains a map of neurons representing the saliency of spatial locations VIP (ventral intraparietal) – receives input from the senses. Represented space in head-centered reference frame MT (also known as V5, or middle temporal) is part of the visual cortex. The mi ...
Biological Processes Neurons
... Before the accident Gage was: “wellbalanced, a shrewd businessman, controlled, considerate, and soft spoken..” After the accident he was: “fitful, irreverent, profane, irritable, demanding, and unable to plan for the future” According to his doctor “the equilibrium or balance…between his intellectua ...
... Before the accident Gage was: “wellbalanced, a shrewd businessman, controlled, considerate, and soft spoken..” After the accident he was: “fitful, irreverent, profane, irritable, demanding, and unable to plan for the future” According to his doctor “the equilibrium or balance…between his intellectua ...
Unit 3A Nervous System - Teacher Version
... • Neurotransmitters – the chemical messengers that carry information across the synapse between one neuron and then next are released from terminal buttons on the sending neuron Can be: – Excitatiatory Neurotransmitters – make the neuron receiving neuron more likely to generate an action potential • ...
... • Neurotransmitters – the chemical messengers that carry information across the synapse between one neuron and then next are released from terminal buttons on the sending neuron Can be: – Excitatiatory Neurotransmitters – make the neuron receiving neuron more likely to generate an action potential • ...
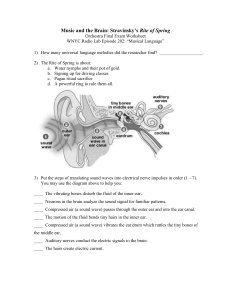
Music and the Brain: Stravinsky`s Rite of Spring
... b. irregular, jagged nerve impulse patterns c. loud impulse patterns d. euphoria 6) When auditory neurons struggle to make sense of a sound they release: a. the dogs b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. ...
... b. irregular, jagged nerve impulse patterns c. loud impulse patterns d. euphoria 6) When auditory neurons struggle to make sense of a sound they release: a. the dogs b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. ...
Outline10 Action Potl
... b. Efferent Division - output motor signals from CNS to effector organs Functional types of neurons 1. sensory (afferent) neurons - input to CNS from sensory receptors; dendrites located at receptors, axons in nerves, cell bodies in ganglia outside the CNS 2. motor (efferent) neurons - output from C ...
... b. Efferent Division - output motor signals from CNS to effector organs Functional types of neurons 1. sensory (afferent) neurons - input to CNS from sensory receptors; dendrites located at receptors, axons in nerves, cell bodies in ganglia outside the CNS 2. motor (efferent) neurons - output from C ...
excitatory neurotransmitter
... the next neuron in the neural pathway. GABA has an opposing effect on the body to Glutamate. One of the main roles of GABA is to assist in the ‘switching off’ of the Sympathetic Nervous System. The Sympathetic Nervous System activates a person’s fight-or-flight response when a threat or stressor is ...
... the next neuron in the neural pathway. GABA has an opposing effect on the body to Glutamate. One of the main roles of GABA is to assist in the ‘switching off’ of the Sympathetic Nervous System. The Sympathetic Nervous System activates a person’s fight-or-flight response when a threat or stressor is ...
chapter the nervous system and the effects of drugs
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...