Americans Lead the World in Hours Worked
... But increasingly efficient Europeans and Japanese workers are chipping away at the United States lead in productivity -- the amount of goods and services produced for each hour worked -- according to the 600-page study by the International Labor Organization. Americans put in an average 1,966 hours ...
... But increasingly efficient Europeans and Japanese workers are chipping away at the United States lead in productivity -- the amount of goods and services produced for each hour worked -- according to the 600-page study by the International Labor Organization. Americans put in an average 1,966 hours ...
World Trade Organization (WTO)
... Saudi Arabia and China. 15 are elected Objectives of the IMF include: 1. stabilization of foreign exchange rates 2. establish convertible currencies to facilitate international trade 3. lend money to members in financial ...
... Saudi Arabia and China. 15 are elected Objectives of the IMF include: 1. stabilization of foreign exchange rates 2. establish convertible currencies to facilitate international trade 3. lend money to members in financial ...
Introduction to Economics – 4 weeks (Chapters 1,2,3
... 3.3 Who Decides What in Different Economic Systems? In answering the three economic questions, every society develops an economic system. A traditional economy relies on custom and tradition to dictate production and consumption. The goals are economic security and stability. In a command econ ...
... 3.3 Who Decides What in Different Economic Systems? In answering the three economic questions, every society develops an economic system. A traditional economy relies on custom and tradition to dictate production and consumption. The goals are economic security and stability. In a command econ ...
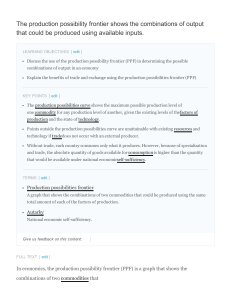
The production possibility frontier shows the
... existing resources and technology if trade does not occur with an outside producer. The PPF will shift outwards if more inputs (such as capital orlabor) become available or if technological progress makes it possible to produce more output with the same level of inputs. An outward shift means that m ...
... existing resources and technology if trade does not occur with an outside producer. The PPF will shift outwards if more inputs (such as capital orlabor) become available or if technological progress makes it possible to produce more output with the same level of inputs. An outward shift means that m ...
Assigment 1 Microeconomics
... 2. How does the PPC illustrate the concepts of opportunity cost, scarcity, tradeoffs, and the necessity for allocating scarce goods and resources? In your answer describe each of the economic terms. This may be more easily explained by first defining each term. Opportunity cost is the opportunity wi ...
... 2. How does the PPC illustrate the concepts of opportunity cost, scarcity, tradeoffs, and the necessity for allocating scarce goods and resources? In your answer describe each of the economic terms. This may be more easily explained by first defining each term. Opportunity cost is the opportunity wi ...
Problem Set 1
... equipment and the like) as well as the foregone wages that you would have received if you had worked instead. If your alternative activity was studying in the library, then the cost is the direct cost as well as the lost benefits of studying (for example, a higher grade on a test, less studying in t ...
... equipment and the like) as well as the foregone wages that you would have received if you had worked instead. If your alternative activity was studying in the library, then the cost is the direct cost as well as the lost benefits of studying (for example, a higher grade on a test, less studying in t ...
37 KB IB Exam questions
... 12. Perfect price discrimination. Explain what it is and provide some examples of perfect or imperfect price discrimination. 13. CPI as the measure of inflation. Explain the definition and provide some examples of situations where official CPI overstates the true cost of living. 14. Long-run factors ...
... 12. Perfect price discrimination. Explain what it is and provide some examples of perfect or imperfect price discrimination. 13. CPI as the measure of inflation. Explain the definition and provide some examples of situations where official CPI overstates the true cost of living. 14. Long-run factors ...
Document
... The fall in the marginal cost of production causes a favorable shift in supply and a lower price accompanied by greater output. ...
... The fall in the marginal cost of production causes a favorable shift in supply and a lower price accompanied by greater output. ...
Exam1 2014 Spring
... c. does not change as more of the good is produced. d. may increase, decrease, or not change as more of the good is produced. Figure 2-3 ...
... c. does not change as more of the good is produced. d. may increase, decrease, or not change as more of the good is produced. Figure 2-3 ...
Economics 441: Arvind Panagariya
... In the absence of trade, Home could gain 3 bananas by foregoing 2 apples, and Foreign could gain one apple by foregoing five bananas. Trade allows each country to trade two bananas for one apple. Home could then gain four bananas by foregoing ...
... In the absence of trade, Home could gain 3 bananas by foregoing 2 apples, and Foreign could gain one apple by foregoing five bananas. Trade allows each country to trade two bananas for one apple. Home could then gain four bananas by foregoing ...
Economics 441: Arvind Panagariya
... In the absence of trade, Home could gain 3 bananas by foregoing 2 apples, and Foreign could gain one apple by foregoing five bananas. Trade allows each country to trade two bananas for one apple. Home could then gain four bananas by foregoing ...
... In the absence of trade, Home could gain 3 bananas by foregoing 2 apples, and Foreign could gain one apple by foregoing five bananas. Trade allows each country to trade two bananas for one apple. Home could then gain four bananas by foregoing ...
Q.1 Why is a production possibilities curve concave - E
... one good increases then less resources will be available for other goods. MRT is the rate at which the units of one good have to be sacrificed to produce one more unit of the other good in a two goods economy. Suppose an economy produces only two goods X and Y. Further suppose that by employing thes ...
... one good increases then less resources will be available for other goods. MRT is the rate at which the units of one good have to be sacrificed to produce one more unit of the other good in a two goods economy. Suppose an economy produces only two goods X and Y. Further suppose that by employing thes ...
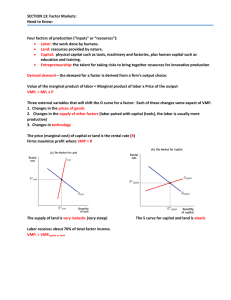
SECTION 13: Factor Markets: Need to Know: Four factors of production (“inputs” or “resources”):
... wage takers ‐ additional cost of hiring the next unit of labor, or marginal factor cost of labor (MFCL) was constant and equal to the wage (supply of labor was a horizontal line at the market wage) Monopsony – a market in which there is only one buyer; in the labor market it must offer higher and ...
... wage takers ‐ additional cost of hiring the next unit of labor, or marginal factor cost of labor (MFCL) was constant and equal to the wage (supply of labor was a horizontal line at the market wage) Monopsony – a market in which there is only one buyer; in the labor market it must offer higher and ...
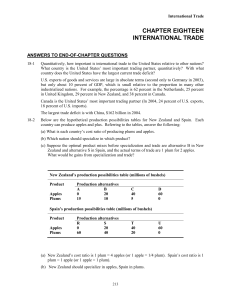
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... Below are the hypothetical production possibilities tables for New Zealand and Spain. Each country can produce apples and plus. Referring to the tables, answer the following: (a) What is each country’s cost ratio of producing plums and apples. (b) Which nation should specialize in which product? (c) ...
... Below are the hypothetical production possibilities tables for New Zealand and Spain. Each country can produce apples and plus. Referring to the tables, answer the following: (a) What is each country’s cost ratio of producing plums and apples. (b) Which nation should specialize in which product? (c) ...
Unit 01: Basic Concepts (Macro/Micro) Scarcity The Economic
... -Average cost curves intersect MC at their maximums ...
... -Average cost curves intersect MC at their maximums ...
Founding Father`s Comments on Free Trade
... Washington also advocated that the nation remain as self-sufficient as possible to ensure its independence. In his first annual message (January, 1790) he stated a "free people ought not only to be armed but disciplined; . . . and their safety and interest require that they should promote such manuf ...
... Washington also advocated that the nation remain as self-sufficient as possible to ensure its independence. In his first annual message (January, 1790) he stated a "free people ought not only to be armed but disciplined; . . . and their safety and interest require that they should promote such manuf ...
Econ Test Review
... The most desirable alternative to a chosen activity. Production possibilities graph Efficiency Underutilization Guns or Butter Decision ...
... The most desirable alternative to a chosen activity. Production possibilities graph Efficiency Underutilization Guns or Butter Decision ...
Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction Supply and Demand
... • Latin for “all things being equal”. • In a graph or example, ceteris paribus means that all other variables are fixed. ...
... • Latin for “all things being equal”. • In a graph or example, ceteris paribus means that all other variables are fixed. ...
Economic Factors Influencing Design
... willing to pay higher prices for those goods, and more workers will work on making them. In time, this will create a shortage of consumer goods, and workers will be drawn back toward making them. Likewise, when there's more demand for land, the land factories gear up and crank out more land -- or, w ...
... willing to pay higher prices for those goods, and more workers will work on making them. In time, this will create a shortage of consumer goods, and workers will be drawn back toward making them. Likewise, when there's more demand for land, the land factories gear up and crank out more land -- or, w ...
Principles of Microeconomics Solutions to Sample Mid-Term Examination
... 9. C - By exploiting the lowest cost production first the opportunity cost of producing additional units of a good increases and, thus, the slope of PPC increases (i.e., it is bowed outward). 10. D 11. B- A change in the price of gasoline never cause a change in the demand for gasoline; only a chang ...
... 9. C - By exploiting the lowest cost production first the opportunity cost of producing additional units of a good increases and, thus, the slope of PPC increases (i.e., it is bowed outward). 10. D 11. B- A change in the price of gasoline never cause a change in the demand for gasoline; only a chang ...
Business Essentials, 7th Edition Ebert/Griffin
... Exchange Rates Impact Global Trade (cont’d) • When an economy’s currency is weak: – Domestic companies find it easier to export products – Foreign companies find it harder to import products – Foreign companies may invest in domestic production facilities ...
... Exchange Rates Impact Global Trade (cont’d) • When an economy’s currency is weak: – Domestic companies find it easier to export products – Foreign companies find it harder to import products – Foreign companies may invest in domestic production facilities ...
Ch.5 Vocabulary Quiz _____ Name period A. Law of supply H
... _____6. A level of production in which the marginal product of labor increases as the number of workers increases. _____7. The change in output from hiring one additional unit of labor. _____8. Tendency of suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price. _____9. A graph of the quantity supplied ...
... _____6. A level of production in which the marginal product of labor increases as the number of workers increases. _____7. The change in output from hiring one additional unit of labor. _____8. Tendency of suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price. _____9. A graph of the quantity supplied ...
Fundamentals of Economics
... of two goods that an economy can produce with given resources and technology. A production possibilities frontier (PPF) represents the boundary or frontier of the economy's production capabilities. As a frontier, it is the maximum production possible given existing (fixed) resources and technology. ...
... of two goods that an economy can produce with given resources and technology. A production possibilities frontier (PPF) represents the boundary or frontier of the economy's production capabilities. As a frontier, it is the maximum production possible given existing (fixed) resources and technology. ...
Powerpoint 4.1 - Marketing Education
... Have limited resources in one or more of the factors of production Different countries can produce specific goods such as: • U.S. and Canada: Agriculture • Saudi Arabia and Russia: Oil • India and Japan: Computer science and Technology ...
... Have limited resources in one or more of the factors of production Different countries can produce specific goods such as: • U.S. and Canada: Agriculture • Saudi Arabia and Russia: Oil • India and Japan: Computer science and Technology ...
Chapter 7 David Ricardo
... – But if the wage rate rises the price of A will have to rise relative to B to maintain equality in profit rates • Similar problems arise if there are two types of labour and wage differentials change, or if different capitals have different durability or rates of turnover • Ricardo assumed that the ...
... – But if the wage rate rises the price of A will have to rise relative to B to maintain equality in profit rates • Similar problems arise if there are two types of labour and wage differentials change, or if different capitals have different durability or rates of turnover • Ricardo assumed that the ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.