Principles-of-Economics-9th-Edition-Case-Solution
... A producer has an absolute advantage over another in the production of a good or service if he or she can produce that product using fewer resources. A producer has a comparative advantage over another in the production of a good or service if he or she can produce that product at a lower opportunit ...
... A producer has an absolute advantage over another in the production of a good or service if he or she can produce that product using fewer resources. A producer has a comparative advantage over another in the production of a good or service if he or she can produce that product at a lower opportunit ...
Intermediate Microeconomics
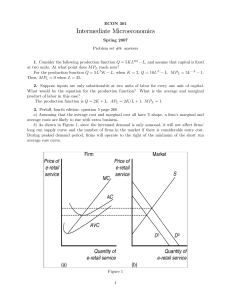
... 2. Suppose inputs are only substitutable at two units of labor for every one unit of capital. What would be the equation for the production function? What is the average and marginal product of labor in this case? The production function is Q = 2K + L. APL = 2K/L + 1. M PL = 1. 3. Perloff, fourth edi ...
... 2. Suppose inputs are only substitutable at two units of labor for every one unit of capital. What would be the equation for the production function? What is the average and marginal product of labor in this case? The production function is Q = 2K + L. APL = 2K/L + 1. M PL = 1. 3. Perloff, fourth edi ...
Answers to First Midterm
... and Allen work separately and both produce some cleaned houses as well as some mowed lawns. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Since Mary can absolutely clean more houses than Allen in the available time, Mary should clean houses and Allen should mow lawns. b. Since Allen can absolutel ...
... and Allen work separately and both produce some cleaned houses as well as some mowed lawns. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Since Mary can absolutely clean more houses than Allen in the available time, Mary should clean houses and Allen should mow lawns. b. Since Allen can absolutel ...
Microeconomics I
... 2. A family of indifference curves depicts a person’s tastes, but surely, these tastes are not determined by genes and fixed forever. People are born with few tastes (a liking for warmth and mother’s milk, a dislike of falling, loud noises, and being wet). Thereafter, tastes are learned (from paren ...
... 2. A family of indifference curves depicts a person’s tastes, but surely, these tastes are not determined by genes and fixed forever. People are born with few tastes (a liking for warmth and mother’s milk, a dislike of falling, loud noises, and being wet). Thereafter, tastes are learned (from paren ...
specific factors model
... instantaneously and costlessly from one industry to another – Changes in an economy’s output mix have differential effects on the demand for different factors of production 湖南大学经济与贸易学院 ...
... instantaneously and costlessly from one industry to another – Changes in an economy’s output mix have differential effects on the demand for different factors of production 湖南大学经济与贸易学院 ...
Document
... b. Change in the consumer surplus = $4.5, deadweight loss = $3 c. Change in the consumer surplus = $4.5, deadweight loss = $1.5 d. Change in the consumer surplus = $3.5, deadweight loss = $1.5 e. Change in the consumer surplus = $3.5, deadweight loss = $3 ...
... b. Change in the consumer surplus = $4.5, deadweight loss = $3 c. Change in the consumer surplus = $4.5, deadweight loss = $1.5 d. Change in the consumer surplus = $3.5, deadweight loss = $1.5 e. Change in the consumer surplus = $3.5, deadweight loss = $3 ...
Two
... 8. If there is a positive externality in the production of a good, too little of that good will be produced. 9. Decreasing marginal product of labor and decreasing returns to scale are exactly the same the thing. 10. If entry into a competitive market does not effect costs the long run supply curve ...
... 8. If there is a positive externality in the production of a good, too little of that good will be produced. 9. Decreasing marginal product of labor and decreasing returns to scale are exactly the same the thing. 10. If entry into a competitive market does not effect costs the long run supply curve ...
Development and Industry review questions
... b. A multinational trade zone in which most tariffs have been eliminated c. A protectionist coalition that denies trade access from other countries ...
... b. A multinational trade zone in which most tariffs have been eliminated c. A protectionist coalition that denies trade access from other countries ...
the full speech - EESC European Economic and Social
... number of jobs depending on trade because of the increased number of trade of intermediate goods and services and in particular the increased proportion of services in the international trade. Global chains are important for the EU economy and here are some facts supporting this assumption: ...
... number of jobs depending on trade because of the increased number of trade of intermediate goods and services and in particular the increased proportion of services in the international trade. Global chains are important for the EU economy and here are some facts supporting this assumption: ...
Name:
... e. APR-Annual Percentage Rate (interest rate on CC or loan) f. Bankruptcy-legal declaration that a judge has to approve . . stating you cannot pay back your debt *Note: student loans MUST ALWAYS be paid back g. FICO Score h. Credit Card Act 2009 i. Liquidity- ability to turn something into cash (eas ...
... e. APR-Annual Percentage Rate (interest rate on CC or loan) f. Bankruptcy-legal declaration that a judge has to approve . . stating you cannot pay back your debt *Note: student loans MUST ALWAYS be paid back g. FICO Score h. Credit Card Act 2009 i. Liquidity- ability to turn something into cash (eas ...
Principles of Microeconomics Sample Mid-Term Examination
... this restaurant increased its price by 20%, its total revenue for the next month increased to $13,440. As a result of this price increase, however, the monthly sales of pop decreased from 3,500 cans to 3,000 cans. Using the arc elasticity method, a) find the price elasticity of demand for this resta ...
... this restaurant increased its price by 20%, its total revenue for the next month increased to $13,440. As a result of this price increase, however, the monthly sales of pop decreased from 3,500 cans to 3,000 cans. Using the arc elasticity method, a) find the price elasticity of demand for this resta ...
Name: ______ Student No.: ______ Quiz #2 Microeconomics
... D. All of the above. 4. In response to an increase in the wage rate, the income effect will usually cause a person to: A. have a horizontal labor supply curve. B. supply the same hours of labor. C. supply more hours of labor. D. supply fewer hours of labor. 5. The marginal rate of technical substitu ...
... D. All of the above. 4. In response to an increase in the wage rate, the income effect will usually cause a person to: A. have a horizontal labor supply curve. B. supply the same hours of labor. C. supply more hours of labor. D. supply fewer hours of labor. 5. The marginal rate of technical substitu ...
Economics 11 Fall 2008 Prof Woolf
... B) it tells us that growth is based on the original level of income or money plus interest or growth on top of the previous year's growth. Correct C) it tells us that putting animals in compounds is better for the health, hence the nation's agricultural economy will grow faster. D) it is part of the ...
... B) it tells us that growth is based on the original level of income or money plus interest or growth on top of the previous year's growth. Correct C) it tells us that putting animals in compounds is better for the health, hence the nation's agricultural economy will grow faster. D) it is part of the ...
Ch9
... grown substantially over time • Most nations produce less than a small fraction of the total supply of any good or service, which allows these nations to benefit from the differences in domestic opportunity costs and global opportunity costs ...
... grown substantially over time • Most nations produce less than a small fraction of the total supply of any good or service, which allows these nations to benefit from the differences in domestic opportunity costs and global opportunity costs ...
instructional objectives
... now includes Hong Kong), Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. The collapse of communism has led to the emergence of former Soviet republics and Eastern bloc countries as world trade participants. Specialization and Comparative Advantage A. The U.S. is referred to as an “open economy” when it is place ...
... now includes Hong Kong), Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. The collapse of communism has led to the emergence of former Soviet republics and Eastern bloc countries as world trade participants. Specialization and Comparative Advantage A. The U.S. is referred to as an “open economy” when it is place ...
Raul Prebisch
... countries, which could be expected to continue in the absence of major changes.” (Singer), ----(a New International Economic Order as we would now say) ...
... countries, which could be expected to continue in the absence of major changes.” (Singer), ----(a New International Economic Order as we would now say) ...
The livelihood model
... export to Europe. Thus exports of general agricultural goods from the mid-Atlantic states and from New England to the West Indies paid for their imports of goods from Europe. The general principles regarding trade apply here, as always. Each ‘nation’ exports the product in which it has the lowest op ...
... export to Europe. Thus exports of general agricultural goods from the mid-Atlantic states and from New England to the West Indies paid for their imports of goods from Europe. The general principles regarding trade apply here, as always. Each ‘nation’ exports the product in which it has the lowest op ...
Chapter 1
... provide the good at a lower opportunity cost than can the other country. d. supply the good to a wealthier group of buyers than can the other country. Country A can produce 10 tires or 30 pairs of boots with one unit of resources. Country B can produce 15 tires or 30 pairs of boots with one unit of ...
... provide the good at a lower opportunity cost than can the other country. d. supply the good to a wealthier group of buyers than can the other country. Country A can produce 10 tires or 30 pairs of boots with one unit of resources. Country B can produce 15 tires or 30 pairs of boots with one unit of ...
The Economizing Problem
... Points inside the curve (line) indicate unemployment or misallocation of resources Points outside indicate unattainable levels of production Optimal use of resources is indicated by a point on the curve, exact point is determined by that particular society ...
... Points inside the curve (line) indicate unemployment or misallocation of resources Points outside indicate unattainable levels of production Optimal use of resources is indicated by a point on the curve, exact point is determined by that particular society ...
Name: ______ Student No.: ______ Quiz #3 Microeconomics
... 6. If the marginal productivity of labor is constant for all levels of output, then the average productivity of labor: A. is constant. B. equals the marginal productivity of labor. C. Both A and B above. D. Neither A or B. 7. Suppose the cost of producing two goods, x and y, can be represented as C ...
... 6. If the marginal productivity of labor is constant for all levels of output, then the average productivity of labor: A. is constant. B. equals the marginal productivity of labor. C. Both A and B above. D. Neither A or B. 7. Suppose the cost of producing two goods, x and y, can be represented as C ...
Distinguished Ministers, Director General, Excellencies and Delegates
... We have come a long way since our attempt at launching a new Round in Seattle two years ago. We are now facing a different world and have learned from our experience in Seattle. The world trading system is faced with various new challenges and threats. We have seen clear signals of cooling of the in ...
... We have come a long way since our attempt at launching a new Round in Seattle two years ago. We are now facing a different world and have learned from our experience in Seattle. The world trading system is faced with various new challenges and threats. We have seen clear signals of cooling of the in ...
FinalSS-207 - UC Davis economics
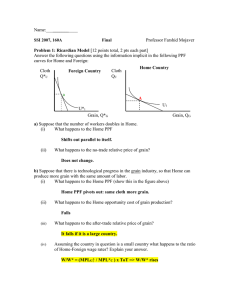
... Consider an outsourcing model where the Home country has a higher relative wage of skilled labor than the Foreign country (like China) and the costs of capital and trade are uniformly higher than Foreign. (a) What kind of good will be outsourced from Home country on the value chain? That is, will th ...
... Consider an outsourcing model where the Home country has a higher relative wage of skilled labor than the Foreign country (like China) and the costs of capital and trade are uniformly higher than Foreign. (a) What kind of good will be outsourced from Home country on the value chain? That is, will th ...
Quiz4
... b) [2 marks] Assume the price of labor is w and the rental rate of capital is r . Assume that K is variable now. Derive the long-run total cost function. Answer: Note that we have a production function in which inputs are perfect substitutes. Thus, given w and r , we can compare marginal product of ...
... b) [2 marks] Assume the price of labor is w and the rental rate of capital is r . Assume that K is variable now. Derive the long-run total cost function. Answer: Note that we have a production function in which inputs are perfect substitutes. Thus, given w and r , we can compare marginal product of ...
Chapter 2
... trade areas, and the established markets in Europe, Japan, and U.S. Companies need to be more efficient, improve productivity, expand global reach, and respond quickly. Greater growth in international sales expected by smaller firms. ...
... trade areas, and the established markets in Europe, Japan, and U.S. Companies need to be more efficient, improve productivity, expand global reach, and respond quickly. Greater growth in international sales expected by smaller firms. ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.