ECON 8010
... (15) 6. Label TRUE, FALSE, or UNCERTAIN each of the following statements of these Marshall-Hicks rules, and rigorously defend your answer. The Marshall-Hicks formula for the own-wage elasticity of demand for labor is ...
... (15) 6. Label TRUE, FALSE, or UNCERTAIN each of the following statements of these Marshall-Hicks rules, and rigorously defend your answer. The Marshall-Hicks formula for the own-wage elasticity of demand for labor is ...
ap microeconomics - Northview High School
... 2. Distinguish between opportunity cost, scarcity, and tradeoffs. 3. Use a production possibilities curve (PPC) to illustrate opportunity cost and growth. 4. Describe the impact of specialization and division of labor on efficiency, productivity, and growth. 5. Contrast positive economics and normat ...
... 2. Distinguish between opportunity cost, scarcity, and tradeoffs. 3. Use a production possibilities curve (PPC) to illustrate opportunity cost and growth. 4. Describe the impact of specialization and division of labor on efficiency, productivity, and growth. 5. Contrast positive economics and normat ...
Assignment 2
... Determine the marginal revenue products for consultants and for the computer services employed by CCS. (Assume constant returns to factors in part A.) ...
... Determine the marginal revenue products for consultants and for the computer services employed by CCS. (Assume constant returns to factors in part A.) ...
Economic Integration Theory
... – Can increase production as long as price you can sell at is equal or above mc. • Market supply is aggregated over all firms. – Horizontal sum. ...
... – Can increase production as long as price you can sell at is equal or above mc. • Market supply is aggregated over all firms. – Horizontal sum. ...
What was Nixon`s name for his supporters?
... Because consumers see an increasing price as a greater loss (according to Prospect theory) ...
... Because consumers see an increasing price as a greater loss (according to Prospect theory) ...
INTERNATIONAL TRADE REGULATION
... • Most Favored Nation-requires member nations to of the WTO to offer all member nations their most favorable tariff rates – Exceptions » Countries can raise barriers to the importation of goods from specific countries that are considered in violation of GATT principles-illegal subsidies and dumping ...
... • Most Favored Nation-requires member nations to of the WTO to offer all member nations their most favorable tariff rates – Exceptions » Countries can raise barriers to the importation of goods from specific countries that are considered in violation of GATT principles-illegal subsidies and dumping ...
ECON 501
... The Efficiency of Perfect Competition Adam Smith put forth the idea that a competitive market would ensure that resources would find their way to where they were most valued (the invisible hand). He provided the framework that has given rise to modern welfare economics. The fundamental Theorem of We ...
... The Efficiency of Perfect Competition Adam Smith put forth the idea that a competitive market would ensure that resources would find their way to where they were most valued (the invisible hand). He provided the framework that has given rise to modern welfare economics. The fundamental Theorem of We ...
Econ 101, sections 2 and 6, S06
... *. increase and the equilibrium quantity will either increase, decrease, or stay the same. b. decrease and the equilibrium quantity will either increase, decrease, or stay the same. c. either increase, decrease, or stay the same, and the equilibrium quantity will increase. d. either increase, decrea ...
... *. increase and the equilibrium quantity will either increase, decrease, or stay the same. b. decrease and the equilibrium quantity will either increase, decrease, or stay the same. c. either increase, decrease, or stay the same, and the equilibrium quantity will increase. d. either increase, decrea ...
Intro Micro Exam 3, Fall 2006
... You may not attach additional paper to this exam. You may use the back page for additional space. If something is unclear, please do not hesitate to ask for clarification. 1. “In the long run, there is no difference between monopolistic competition and perfect competition.” True, false, or ambiguous ...
... You may not attach additional paper to this exam. You may use the back page for additional space. If something is unclear, please do not hesitate to ask for clarification. 1. “In the long run, there is no difference between monopolistic competition and perfect competition.” True, false, or ambiguous ...
Ch. 18 Outline Part 2
... ….an increase in W will increase the Labor you will supply …..think of the “law of supply” ….but an increase in Labor supplied by you = a decrease in leisure time W increase = increase in opportunity cost of leisure ...
... ….an increase in W will increase the Labor you will supply …..think of the “law of supply” ….but an increase in Labor supplied by you = a decrease in leisure time W increase = increase in opportunity cost of leisure ...
ECON 2301 Spring 2003
... for orange juice (OJ) is inelastic, will a rise in the price of OJ increase or decrease the revenue received by orange juice sellers?” (1st edition: 1-10, p. 193); and Problems and Applications: p. 202, 3.3; p. 206, 5.2; p. ...
... for orange juice (OJ) is inelastic, will a rise in the price of OJ increase or decrease the revenue received by orange juice sellers?” (1st edition: 1-10, p. 193); and Problems and Applications: p. 202, 3.3; p. 206, 5.2; p. ...
Answers
... market by some simple process that costs $0.02 per pound. Finland is a small country and takes as given the world price of cornflakes, which is $2.00 per pound. The Finns produce no corn flakes and they are currently (in the presence of the Vitamin D requirement) buying 400,000 pounds of corn flakes ...
... market by some simple process that costs $0.02 per pound. Finland is a small country and takes as given the world price of cornflakes, which is $2.00 per pound. The Finns produce no corn flakes and they are currently (in the presence of the Vitamin D requirement) buying 400,000 pounds of corn flakes ...
Scientific Method, Models, and Gains to Trade
... • Absolute advantage – Rancher than farmer is more efficient and producing both meat and potatoes ...
... • Absolute advantage – Rancher than farmer is more efficient and producing both meat and potatoes ...
Chapter 7
... Democratic Globalization: democratization lowers inequality and promotes economic growth ...
... Democratic Globalization: democratization lowers inequality and promotes economic growth ...
Trade Essay – Final Copy
... To explain how advance economies can affect foreign developing economies through export subsidization, a simple classical model of supply and demand by Krugman and Obstfeld can be constructed to explain the affects to the exporting and importing country. For this model, the exporting home country wi ...
... To explain how advance economies can affect foreign developing economies through export subsidization, a simple classical model of supply and demand by Krugman and Obstfeld can be constructed to explain the affects to the exporting and importing country. For this model, the exporting home country wi ...
Opportunity Cost
... Opportunity Cost: The amount of other products that must be forgone or satisfied to obtain 1 unit of a specific good. The opportunity cost of each additional unit of a good is greater than the opportunity cost of the preceding one. Opportunity cost is measured in real terms (goods v. money) The more ...
... Opportunity Cost: The amount of other products that must be forgone or satisfied to obtain 1 unit of a specific good. The opportunity cost of each additional unit of a good is greater than the opportunity cost of the preceding one. Opportunity cost is measured in real terms (goods v. money) The more ...
Exam 2 Review Problems (Hints and Answers)
... $20/hour). It seems like China could produce virtually everything cheaper than could America, and yet China imports various goods from the U.S., such as office machines. Why do they do this? They do this because they have a comparative advantage in some products, while the U.S. has a comparative adv ...
... $20/hour). It seems like China could produce virtually everything cheaper than could America, and yet China imports various goods from the U.S., such as office machines. Why do they do this? They do this because they have a comparative advantage in some products, while the U.S. has a comparative adv ...
Task 1: Sample multiple choice and data interpretation questions
... a surplus of 800 units would develop. a shortage of 800 units would develop. 1500 units would be sold. more consumers would be able to enjoy the product than at a price of $24. ...
... a surplus of 800 units would develop. a shortage of 800 units would develop. 1500 units would be sold. more consumers would be able to enjoy the product than at a price of $24. ...
Honors Economics Unit 2 Study Guide
... 17. How is time related to the elasticity and inelasticity of supply?(104-106) 18. What are two ways that the government can have an influence on supply?(117-118) 19. What are examples of goods with elastic supply? (104-106) Inelastic supply?(104-106) 20. On what type of goods does the government ge ...
... 17. How is time related to the elasticity and inelasticity of supply?(104-106) 18. What are two ways that the government can have an influence on supply?(117-118) 19. What are examples of goods with elastic supply? (104-106) Inelastic supply?(104-106) 20. On what type of goods does the government ge ...
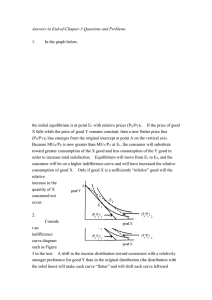
Answers to End-of-Chapter-5 Questions and Problems
... In Figure 8 in the text, consider the lower intersection point (not labeled) of isoquant Q0 with budget line B1. At that point, MPPL/MPPK is less than w/r, since the isoquant is flatter than the isocost line. This indicates that MPPL/w < MPPK/r, or that, at the margin, the output obtained per dollar ...
... In Figure 8 in the text, consider the lower intersection point (not labeled) of isoquant Q0 with budget line B1. At that point, MPPL/MPPK is less than w/r, since the isoquant is flatter than the isocost line. This indicates that MPPL/w < MPPK/r, or that, at the margin, the output obtained per dollar ...
Final Exam I Intermediate Microeconomics Fall 2005 I. True
... 2. A competitive firm has a production function described as follows. "Weekly output is the square root of the minimum of the number of units of capital and the number of units of labor employed per week." Suppose that in the short run this firm must use 16 units of capital but can vary its amount o ...
... 2. A competitive firm has a production function described as follows. "Weekly output is the square root of the minimum of the number of units of capital and the number of units of labor employed per week." Suppose that in the short run this firm must use 16 units of capital but can vary its amount o ...
Econ 101, sections 4 and 5, S09
... a. Positive statements can, in principle, be confirmed or refuted by examining evidence. b. Normative statements involve value judgments. *. Any statement making a claim about the future is necessarily normative. d. Deciding what is good or bad policy is not just a matter of science. 14. Which of th ...
... a. Positive statements can, in principle, be confirmed or refuted by examining evidence. b. Normative statements involve value judgments. *. Any statement making a claim about the future is necessarily normative. d. Deciding what is good or bad policy is not just a matter of science. 14. Which of th ...
Test questions - December, 2002
... (K) a 1 % decrease in Q and a 1.5 % increase in TR (L) a 2/3 % decrease in Q and a 4/3 % increase in TR (M) a 3 % increase in Q and a 4.5 % increase in TR (N) a 2 % increase in Q and a 4 % increase in TR (O) a 1 % increase in Q and a 3 % increase in TR (P) a 2/3 % increase in Q and a 10/3 % increase ...
... (K) a 1 % decrease in Q and a 1.5 % increase in TR (L) a 2/3 % decrease in Q and a 4/3 % increase in TR (M) a 3 % increase in Q and a 4.5 % increase in TR (N) a 2 % increase in Q and a 4 % increase in TR (O) a 1 % increase in Q and a 3 % increase in TR (P) a 2/3 % increase in Q and a 10/3 % increase ...
Reading 9: Changes in Exchange Rates and their effects on Imports
... Upper Left (US imports): At each price in $, British firms get more £ for their goods (before they got £0.25/$, now they get £0.50/$). Thus, they will supply more goods to US: supply of US imports increases (supply curve shifts down since fewer dollars are being spent on US imports). The amount of U ...
... Upper Left (US imports): At each price in $, British firms get more £ for their goods (before they got £0.25/$, now they get £0.50/$). Thus, they will supply more goods to US: supply of US imports increases (supply curve shifts down since fewer dollars are being spent on US imports). The amount of U ...
If two inputs (capital and labor) are gross
... the marginal product of labor is MPL = 15 units of output per day, and the daily wage rate is W = $90 per day. The firm should adjust P, or W, or both in order to equate marginal revenue product to the marginal expense of labor. not alter the employment level, as the firm is already earning a profit ...
... the marginal product of labor is MPL = 15 units of output per day, and the daily wage rate is W = $90 per day. The firm should adjust P, or W, or both in order to equate marginal revenue product to the marginal expense of labor. not alter the employment level, as the firm is already earning a profit ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.