Major Field Test in Economics Sample Questions
... Copyright © 2014 Educational Testing Service Permission to reproduce this document is hereby granted to institutions (colleges and universities) administering the Major Field Tests for internal use only. No commercial or further distribution is permitted. Other persons or agencies wishing to obtain ...
... Copyright © 2014 Educational Testing Service Permission to reproduce this document is hereby granted to institutions (colleges and universities) administering the Major Field Tests for internal use only. No commercial or further distribution is permitted. Other persons or agencies wishing to obtain ...
Graph Definitions
... • Opportunity cost—the value of the most desired goods or services that are forgone in order to obtain something else. • Opportunity cost applies to society as a whole: To produce more of one thing means we must shift resources away from something else. • PPF is simply a graphical illustration of op ...
... • Opportunity cost—the value of the most desired goods or services that are forgone in order to obtain something else. • Opportunity cost applies to society as a whole: To produce more of one thing means we must shift resources away from something else. • PPF is simply a graphical illustration of op ...
FREE Sample Here
... the unit just covers the extra (marginal) cost of producing that unit. To measure producer surplus for a product using real world data, three major pieces of information are needed. First, the market price. Second, the quantity supplied. Third, some information about the slope (or shape) of the supp ...
... the unit just covers the extra (marginal) cost of producing that unit. To measure producer surplus for a product using real world data, three major pieces of information are needed. First, the market price. Second, the quantity supplied. Third, some information about the slope (or shape) of the supp ...
JEOPARDY
... A government payment that partially covers the cost of an economic activity. Example: Government made payments to double the supply of ethanol (gasoline substitute) ...
... A government payment that partially covers the cost of an economic activity. Example: Government made payments to double the supply of ethanol (gasoline substitute) ...
Course Syllabus - California State University, Bakersfield
... Microeconomics is the study of the behavior of individual decision makers in the economic system, particularly households and business firms. It contrasts with macroeconomics, which is the study of the behavior of the economic system as a whole. Successful study of economics requires an ability to e ...
... Microeconomics is the study of the behavior of individual decision makers in the economic system, particularly households and business firms. It contrasts with macroeconomics, which is the study of the behavior of the economic system as a whole. Successful study of economics requires an ability to e ...
sample first exam - Shepherd Webpages
... b. Restricting the immigration of workers from other countries. c. Encouraging women to stay home and raise families rather than entering the work force. d. All of the above will increase long-run growth. ...
... b. Restricting the immigration of workers from other countries. c. Encouraging women to stay home and raise families rather than entering the work force. d. All of the above will increase long-run growth. ...
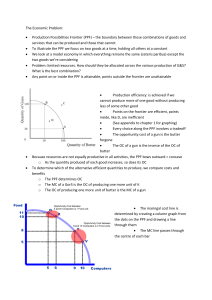
The Economic Problem: • Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF
... services that can be produced and those that cannot To illustrate the PPF we focus on two goods at a time, holding all others at a constant We look at a model economy in which everything remains the same (ceteris paribus) except the two goods we’re considering Problem: limited resources. How should ...
... services that can be produced and those that cannot To illustrate the PPF we focus on two goods at a time, holding all others at a constant We look at a model economy in which everything remains the same (ceteris paribus) except the two goods we’re considering Problem: limited resources. How should ...
Chapter 3 Demand and Supply
... wake of the creation or escalation of a government-mandated minimum wage, because they lose their jobs or fail to find jobs when they enter the labor force. Making it illegal to pay less than a given amount does not make a worker’s productivity worth that amount—and, if it is not, that worker is unl ...
... wake of the creation or escalation of a government-mandated minimum wage, because they lose their jobs or fail to find jobs when they enter the labor force. Making it illegal to pay less than a given amount does not make a worker’s productivity worth that amount—and, if it is not, that worker is unl ...
Introduction - New Perspectives on the World Economy
... Moving from autarky to either importing or exporting involves a net increase in welfare for the country involved ...
... Moving from autarky to either importing or exporting involves a net increase in welfare for the country involved ...
Theory of Production
... The least cost input bundle lies on the isocost line tangent to the Isoquant. In other words the slopes of the two are equal: -MPL/MPK = -w/r. Cross multiplying leads to MPL/w = MPK/r, which is interpreted as that the output per $ spent is equal across all inputs. If this were not the case then the ...
... The least cost input bundle lies on the isocost line tangent to the Isoquant. In other words the slopes of the two are equal: -MPL/MPK = -w/r. Cross multiplying leads to MPL/w = MPK/r, which is interpreted as that the output per $ spent is equal across all inputs. If this were not the case then the ...
AP Micro Concepts
... Unit IV: Imperfect Competition Characteristics of Monopolies Barriers to Entry MR Below Demand (Graphs) Elastic vs. Inelastic Range Profit-Maximizing Price and Quantity ...
... Unit IV: Imperfect Competition Characteristics of Monopolies Barriers to Entry MR Below Demand (Graphs) Elastic vs. Inelastic Range Profit-Maximizing Price and Quantity ...
2012 - Commerce Tutoring
... D) the theory shouldn't be taken seriously. E) that the theory is not useful because consumption involves irrational human behaviour. ...
... D) the theory shouldn't be taken seriously. E) that the theory is not useful because consumption involves irrational human behaviour. ...
Chapter 8 - McGraw
... Some nations have abundant fertile farm land; others do not. Some nations have a labor force with specific skills; others do ...
... Some nations have abundant fertile farm land; others do not. Some nations have a labor force with specific skills; others do ...
Absolute Advantage
... Gains from Trade Moving from autarky to either importing or exporting involves a net increase in welfare for the country involved Known as gains from trade Many popular writings on the world economy suggest trade relationships are a win-lose proposition for the countries involved The gains fr ...
... Gains from Trade Moving from autarky to either importing or exporting involves a net increase in welfare for the country involved Known as gains from trade Many popular writings on the world economy suggest trade relationships are a win-lose proposition for the countries involved The gains fr ...
Ch 2 - Business Competitive Environment
... • In the 1990s the US was the run away leading performer in the industrial world. • The US claimed nine of the ten largest companies in the world by 1998 compared to only two in 1990. • Nine of the fifteen most profitable banks are in the US compared to none in 1990. • The wealthiest man in the worl ...
... • In the 1990s the US was the run away leading performer in the industrial world. • The US claimed nine of the ten largest companies in the world by 1998 compared to only two in 1990. • Nine of the fifteen most profitable banks are in the US compared to none in 1990. • The wealthiest man in the worl ...
1. a. They currently have together 4 fish and 4 pounds
... industry is not known. Those potentially losing their comparative advantage will be screaming while the gainers will be silent. b. The horizontal supply curve implies that any changes in cost will be fully reflected in prices. Hence all gains from lower wages outside the US will be incorporated into ...
... industry is not known. Those potentially losing their comparative advantage will be screaming while the gainers will be silent. b. The horizontal supply curve implies that any changes in cost will be fully reflected in prices. Hence all gains from lower wages outside the US will be incorporated into ...
w04ex1 - Rose
... B. What is the opportunity cost of producing one more wool coat in South Korea? (1 points) C. What is the opportunity cost of producing one more television in South Korea? (1 points) D. What is the opportunity cost of producing one more wool coat in North Korea? (1 points) E. What is the opportunity ...
... B. What is the opportunity cost of producing one more wool coat in South Korea? (1 points) C. What is the opportunity cost of producing one more television in South Korea? (1 points) D. What is the opportunity cost of producing one more wool coat in North Korea? (1 points) E. What is the opportunity ...
View/Open
... Consequently, a decrease in farm milk price as would occur under deregulation could very well result in an increase in Canadian milk supply if farmers were no longer subject to production controls. Highlighting this apparent paradox alone makes the paper a worthy one as the failure to differentiate ...
... Consequently, a decrease in farm milk price as would occur under deregulation could very well result in an increase in Canadian milk supply if farmers were no longer subject to production controls. Highlighting this apparent paradox alone makes the paper a worthy one as the failure to differentiate ...
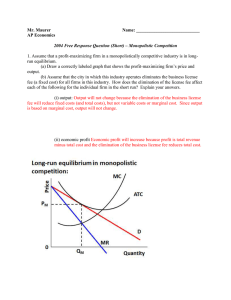
Mr. Maurer Name: AP Economics 2004 Free Response Question
... 1. Assume that the cellular telephone industry is monopolistically competitive. (a) Assume that cellular telephone manufacturers are earning short-run economic profits. Draw a correctly labeled graph for a typical firm in the industry and show each of the following. (i) The profit-maximizing output ...
... 1. Assume that the cellular telephone industry is monopolistically competitive. (a) Assume that cellular telephone manufacturers are earning short-run economic profits. Draw a correctly labeled graph for a typical firm in the industry and show each of the following. (i) The profit-maximizing output ...
Perfect Competition
... production as well as the revenues (TR & MR) generated. We have observed that the MR curve in this case also represents the demand curve for this product. As you recall this demand curve demonstrates a series of prices and quantities at which demand exists. But no-where have we indicated or implied ...
... production as well as the revenues (TR & MR) generated. We have observed that the MR curve in this case also represents the demand curve for this product. As you recall this demand curve demonstrates a series of prices and quantities at which demand exists. But no-where have we indicated or implied ...
International Trade Homework # 4 Solutions
... graph the equilibrium under free trade. What is the world price? What is the volume of trade? When they are allowed to trade, there is no distortion in prices so we have a common world price of P w = P = P ∗ . In order to find equilibrium, we set import demand equal to export supply giving: MD(P ) = ...
... graph the equilibrium under free trade. What is the world price? What is the volume of trade? When they are allowed to trade, there is no distortion in prices so we have a common world price of P w = P = P ∗ . In order to find equilibrium, we set import demand equal to export supply giving: MD(P ) = ...
Higher Order Thinking Questions - a Necessity
... (ii) Payment of income tax by a production unit. (iii)Services rendered by family members to each other. ...
... (ii) Payment of income tax by a production unit. (iii)Services rendered by family members to each other. ...
Econ 310 Practice Questions: Chaps. 1-3 1. Explicit
... both goods x and y are bads. x and y are substitutes. y is a good and x is a bad. x is a good and y is a bad. ...
... both goods x and y are bads. x and y are substitutes. y is a good and x is a bad. x is a good and y is a bad. ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.