Explain. - Boards.ie
... Discuss the economic consequences of a slower rate of economic growth in Ireland? In Ireland at present, would you expect GNP to be greater than, equal to, or less than GDP? Explain. Explain what determines the size of each of the components of national income? What is meant by the term multiplier? ...
... Discuss the economic consequences of a slower rate of economic growth in Ireland? In Ireland at present, would you expect GNP to be greater than, equal to, or less than GDP? Explain. Explain what determines the size of each of the components of national income? What is meant by the term multiplier? ...
Answers to PS 3
... b) Does the d1 curve shift or pivot due to the opening of trade? Explain why or why not? d1 curve becomes flatter (see d2 in Figure 2) due to an increase in the number of varieties available to consumers after trade (which makes them more price sensitive). c) Compare your answer to (b) with the case ...
... b) Does the d1 curve shift or pivot due to the opening of trade? Explain why or why not? d1 curve becomes flatter (see d2 in Figure 2) due to an increase in the number of varieties available to consumers after trade (which makes them more price sensitive). c) Compare your answer to (b) with the case ...
Chapter 09 Key Question Solutions
... competitive long-run equilibrium. Assuming constant costs, employ these diagrams to show how (a) an increase and (b) a decrease in market demand will upset that long-run equilibrium. Trace graphically and describe verbally the adjustment processes by which long-run equilibrium is restored. Now rewor ...
... competitive long-run equilibrium. Assuming constant costs, employ these diagrams to show how (a) an increase and (b) a decrease in market demand will upset that long-run equilibrium. Trace graphically and describe verbally the adjustment processes by which long-run equilibrium is restored. Now rewor ...
9‑3 (Key Question) Use the following demand schedule to determine
... competitive long-run equilibrium. Assuming constant costs, employ these diagrams to show how (a) an increase and (b) a decrease in market demand will upset that long-run equilibrium. Trace graphically and describe verbally the adjustment processes by which long-run equilibrium is restored. Now rewor ...
... competitive long-run equilibrium. Assuming constant costs, employ these diagrams to show how (a) an increase and (b) a decrease in market demand will upset that long-run equilibrium. Trace graphically and describe verbally the adjustment processes by which long-run equilibrium is restored. Now rewor ...
21‑3 (Key Question) Use the following demand schedule to
... competitive long-run equilibrium. Assuming constant costs, employ these diagrams to show how (a) an increase and (b) a decrease in market demand will upset that long-run equilibrium. Trace graphically and describe verbally the adjustment processes by which long-run equilibrium is restored. Now rewor ...
... competitive long-run equilibrium. Assuming constant costs, employ these diagrams to show how (a) an increase and (b) a decrease in market demand will upset that long-run equilibrium. Trace graphically and describe verbally the adjustment processes by which long-run equilibrium is restored. Now rewor ...
ECON460: Answer Key to Problem Set 1
... 2. What would a monopoly’s marginal revenue be if it chose a point on the demand curve where the price elasticity of demand equals -1? Why would it never be optimal to choose such a point, given positive marginal costs? Would the monopoly rather produce less or more? Answer: Using the Lerner index, ...
... 2. What would a monopoly’s marginal revenue be if it chose a point on the demand curve where the price elasticity of demand equals -1? Why would it never be optimal to choose such a point, given positive marginal costs? Would the monopoly rather produce less or more? Answer: Using the Lerner index, ...
Chapter 5 Modern International Trade Theory
... competition is that market conditions included both monopoly and competition factors. Or that is market status between perfect competition and monopoly. Imperfect competitive market structure vary widely, there is not a fixed and unified theoretical framework to describe it. But there are two forms ...
... competition is that market conditions included both monopoly and competition factors. Or that is market status between perfect competition and monopoly. Imperfect competitive market structure vary widely, there is not a fixed and unified theoretical framework to describe it. But there are two forms ...
ECON 3070-100 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory
... 17. The second will be on Thursday, July 7, and will cover only the second part of the course. Each exam will be worth 100 points. In addition to these exams, a quiz will be given on Tuesday, June 14. This quiz, worth 20 points, will cover all material treated through June 13. The idea behind the qu ...
... 17. The second will be on Thursday, July 7, and will cover only the second part of the course. Each exam will be worth 100 points. In addition to these exams, a quiz will be given on Tuesday, June 14. This quiz, worth 20 points, will cover all material treated through June 13. The idea behind the qu ...
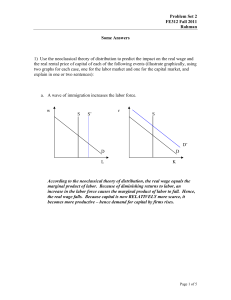
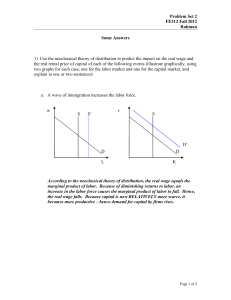
Problem Set 2 FE312 Fall 2011 Rahman Some Answers 1
... parameter A by 10%. What happens to total output (in percentage change)? The real rental price of capital (in percentage change)? The real wage (in percentage change)? Everything goes up by 10%. ...
... parameter A by 10%. What happens to total output (in percentage change)? The real rental price of capital (in percentage change)? The real wage (in percentage change)? Everything goes up by 10%. ...
Partial Answer Key
... parameter A by 10%. What happens to total output (in percentage change)? The real rental price of capital (in percentage change)? The real wage (in percentage change)? Everything goes up by 10%. ...
... parameter A by 10%. What happens to total output (in percentage change)? The real rental price of capital (in percentage change)? The real wage (in percentage change)? Everything goes up by 10%. ...
Word
... Suppose a world of two countries that are trading freely, with the home country importing good X, and exporting good Y to Foreign. Suppose now that Home (only) experiences an improvement in its technology so that the factors employed in its X industry become more productive by, say, 10%. What will t ...
... Suppose a world of two countries that are trading freely, with the home country importing good X, and exporting good Y to Foreign. Suppose now that Home (only) experiences an improvement in its technology so that the factors employed in its X industry become more productive by, say, 10%. What will t ...
Answers to Practice Questions 2
... g) After the quota program, the consumer surplus is $1800 and the producer surplus is $200. Therefore, the total gain from trade with the quota is $2000, which is less than the gains from trade without the quota ($2500). If you compute the net gains from trade with the quota to no foreign trade, you ...
... g) After the quota program, the consumer surplus is $1800 and the producer surplus is $200. Therefore, the total gain from trade with the quota is $2000, which is less than the gains from trade without the quota ($2500). If you compute the net gains from trade with the quota to no foreign trade, you ...
Econ 101, section 3, F06
... Econ 101, section 3, F06 Schroeter Final Exam, Blue Choose the single best answer for each question. 1. A bowed outward shape for a production possibility frontier reflects the fact that a. the opportunity cost of producing a good decreases as more of the good is produced. b. technological change is ...
... Econ 101, section 3, F06 Schroeter Final Exam, Blue Choose the single best answer for each question. 1. A bowed outward shape for a production possibility frontier reflects the fact that a. the opportunity cost of producing a good decreases as more of the good is produced. b. technological change is ...
ECO 154/254
... The central thesis of The Wealth of Nations is that capital is best employed for the production and distribution of wealth under conditions of governmental noninterference, or laissez-faire, and free trade. In Smith's view, the production and exchange of goods can be stimulated, and a consequent ris ...
... The central thesis of The Wealth of Nations is that capital is best employed for the production and distribution of wealth under conditions of governmental noninterference, or laissez-faire, and free trade. In Smith's view, the production and exchange of goods can be stimulated, and a consequent ris ...
global political economy
... Internal measures may cause a recession; but in the process the current and capital accounts may be improved ( reduced imports due to lower domestic income, increased direct investment from abroad due to higher domestic interest rates) Liberals favor short term liquidity and internal measures. The g ...
... Internal measures may cause a recession; but in the process the current and capital accounts may be improved ( reduced imports due to lower domestic income, increased direct investment from abroad due to higher domestic interest rates) Liberals favor short term liquidity and internal measures. The g ...
Microeconomics II Due: June 14, 2013 (16:00) HOMEWORK Mr
... where x1 is the number of pounds of lemons he uses and x2 is the number of hours he spends squeezing them. a. Find his cost function. b. If lemons cost $1 per pound, the wage rate is $1 per hour, and the price of lemonade is p, find Earl’s marginal cost function. c. Find Earl’s supply function. 4. C ...
... where x1 is the number of pounds of lemons he uses and x2 is the number of hours he spends squeezing them. a. Find his cost function. b. If lemons cost $1 per pound, the wage rate is $1 per hour, and the price of lemonade is p, find Earl’s marginal cost function. c. Find Earl’s supply function. 4. C ...
Strategic Competition
... dependent on their husbands. And husbands can make a living without dependence on their fathers for farmland, or for the tools of their craft, and are no longer burdened with total responsibility for providing the family with income. To discern whether patriarchy (in its many different cultural for ...
... dependent on their husbands. And husbands can make a living without dependence on their fathers for farmland, or for the tools of their craft, and are no longer burdened with total responsibility for providing the family with income. To discern whether patriarchy (in its many different cultural for ...
U.S. TRADE DEFICIT REVIiW COMMISSION HEARINGS Mr. Raymond Waldmann Vice-President, International Affairs
... interdependent. As a result, U.S. economic performance on the domestic front will be even more dependent in the years ahead on the world’s economic performance. The ...
... interdependent. As a result, U.S. economic performance on the domestic front will be even more dependent in the years ahead on the world’s economic performance. The ...
International Competitiveness and Comparative Advantage: A
... by help of the Balassa (1965) index of ‘revealed comparative advantage’ (RCA). This measure reflects the success in exporting of countries relative to a world-wide norm. Exports can result from subsidies or other incentives provided, for instance by exchange rate misalignment. Such incentives can ex ...
... by help of the Balassa (1965) index of ‘revealed comparative advantage’ (RCA). This measure reflects the success in exporting of countries relative to a world-wide norm. Exports can result from subsidies or other incentives provided, for instance by exchange rate misalignment. Such incentives can ex ...
Supply
... – Suppliers set prices at levels that are equal to marginal cost (cost to make). – If inputs increase the marginal cost increases. – Marginal costs could increase higher than the price, so the business is not as profitable. – If business has no control over price, then production is cut and marginal ...
... – Suppliers set prices at levels that are equal to marginal cost (cost to make). – If inputs increase the marginal cost increases. – Marginal costs could increase higher than the price, so the business is not as profitable. – If business has no control over price, then production is cut and marginal ...
ECO 2252
... regardless of course format (online, lecture, or hybrid) will be registered in a separate course in Blackboard where this exam is accessed. Instructors will not have access to this course, nor will they be allowed to preview the questions. See the last two pages for a detailed list of subtopics incl ...
... regardless of course format (online, lecture, or hybrid) will be registered in a separate course in Blackboard where this exam is accessed. Instructors will not have access to this course, nor will they be allowed to preview the questions. See the last two pages for a detailed list of subtopics incl ...
TRADE POLICIES: TARIFFS AND QUOTAS CLASSIFICATION OF
... PX = (1+t) P*X , PY = P*Y ; Relative price PX / PY = (1+t) P*X / P*Y If if levies ad valorem export tax at rate t PX = P*X , P*Y = (1+t) PY ; Relative price PX / PY = (1+t) P*X / P*Y So the two policies are equivalent in all their resource allocation and income distribution effects! Intuition: taxin ...
... PX = (1+t) P*X , PY = P*Y ; Relative price PX / PY = (1+t) P*X / P*Y If if levies ad valorem export tax at rate t PX = P*X , P*Y = (1+t) PY ; Relative price PX / PY = (1+t) P*X / P*Y So the two policies are equivalent in all their resource allocation and income distribution effects! Intuition: taxin ...
Chapter 3: National Income Accounting
... When an increase in the quantity of the inputs results in an equal increase in the quantity of the output ...
... When an increase in the quantity of the inputs results in an equal increase in the quantity of the output ...
Lecture notes
... Salvatore: International Economics, 10th Edition © 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
... Salvatore: International Economics, 10th Edition © 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.