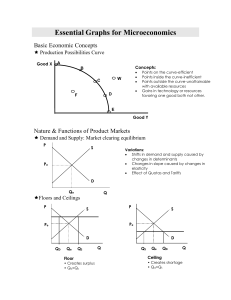
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...
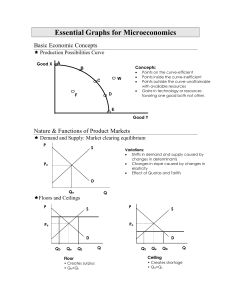
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics - pm
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...
Appendix to Chapter 22 Connecting Product Markets and Labor
... labor market. The connection is that the seller of the product is also the demander of labor. Any decision to increase production should also lead to a decision to increase hiring of workers. But we can formalize this here. We know that the demand for labor by an employer is the marginal revenue pro ...
... labor market. The connection is that the seller of the product is also the demander of labor. Any decision to increase production should also lead to a decision to increase hiring of workers. But we can formalize this here. We know that the demand for labor by an employer is the marginal revenue pro ...
Part and/or Chapter Number and Title
... Monopsonist will use MRP=MRC rule to determine how much labor to hire and pay wage corresponding to this quantity supplied. Monopsony is a market structure in which there is only a single buyer of a good, service, or resource. LO: 10-4 ...
... Monopsonist will use MRP=MRC rule to determine how much labor to hire and pay wage corresponding to this quantity supplied. Monopsony is a market structure in which there is only a single buyer of a good, service, or resource. LO: 10-4 ...
1.0 Introduction to Economics
... Model Building in Economics A popular tool in the Economist’s kit is the economic model. Just like scientists in other fields, economists use models to represent something from the real world. A model of the solar system: Allows astronomers to illustrate in a simplified model the relationships betwe ...
... Model Building in Economics A popular tool in the Economist’s kit is the economic model. Just like scientists in other fields, economists use models to represent something from the real world. A model of the solar system: Allows astronomers to illustrate in a simplified model the relationships betwe ...
ECO201 - Tutorial Week 3 - Chapter 5
... a. Greater than that of a perfectly competitive seller b. More elastic than that of a perfectly competitive seller c. Less elastic than that of a perfectly competitive seller d. The same as than that of a perfectly competitive seller 6. Which of the following best describes the output effect of a wa ...
... a. Greater than that of a perfectly competitive seller b. More elastic than that of a perfectly competitive seller c. Less elastic than that of a perfectly competitive seller d. The same as than that of a perfectly competitive seller 6. Which of the following best describes the output effect of a wa ...
Lecture 4: Markets In Action
... Two questions at $1 each and one $2 question. If you answer the question correctly, you keep $. If you answer incorrectly, you give up $. Answers must be written and complete in time. Decisions of the judges are final (honor system). ...
... Two questions at $1 each and one $2 question. If you answer the question correctly, you keep $. If you answer incorrectly, you give up $. Answers must be written and complete in time. Decisions of the judges are final (honor system). ...
Lecture 4: The Demand for Labor
... a. Sometimes collectively bargained or legislated restrictions make the demand for labor less elastic by reducing substitutability (not technically). b. Substitution possibility that are not feasible in the short run may well become feasible over longer periods of time, when employers are free to va ...
... a. Sometimes collectively bargained or legislated restrictions make the demand for labor less elastic by reducing substitutability (not technically). b. Substitution possibility that are not feasible in the short run may well become feasible over longer periods of time, when employers are free to va ...
FBLA-PBL
... Explain the effects of unions and specific union tactics on wages and employment in both competitive and monopolistic markets. ...
... Explain the effects of unions and specific union tactics on wages and employment in both competitive and monopolistic markets. ...
Introduction
... 4. (a) Explain briefly the difference between partial equilibrium (PE) and general equilibrium (GE) analyses, and suggest economic issues for which each type of analysis would be appropriate and inappropriate. (In your answer make use of both a simple supply-demand framework and an Edgeworth-Bowley ...
... 4. (a) Explain briefly the difference between partial equilibrium (PE) and general equilibrium (GE) analyses, and suggest economic issues for which each type of analysis would be appropriate and inappropriate. (In your answer make use of both a simple supply-demand framework and an Edgeworth-Bowley ...
UNIT 1 WHAT ECONOMICS IS ALL ABOUT
... Because the acronym means “There aint such a thing as free lunch” someone always has to pay. • Economics may be called the ‘dismal science” because it deals with scarcity. • Scarcity and poverty are different. • Scarcity affects everyone even the rich. The richest person on this world also has unlim ...
... Because the acronym means “There aint such a thing as free lunch” someone always has to pay. • Economics may be called the ‘dismal science” because it deals with scarcity. • Scarcity and poverty are different. • Scarcity affects everyone even the rich. The richest person on this world also has unlim ...
Krugman`s Chapter 20 PPT
... 1. There are markets for factors of production, including labor, land, and both physical capital and human capital. These markets determine the factor distribution of income. 2. Profit-maximizing price-taking producers will employ a factor up to the point at which its price is equal to its value of ...
... 1. There are markets for factors of production, including labor, land, and both physical capital and human capital. These markets determine the factor distribution of income. 2. Profit-maximizing price-taking producers will employ a factor up to the point at which its price is equal to its value of ...
No Slide Title
... The opportunity cost of any activity is what we give up when we make a choice.In other words,it is the loss of the opportunity to pursue the most attractive alternative given the same time and resources. A production possibility curve shows the maximum output of two goods or services that can be pro ...
... The opportunity cost of any activity is what we give up when we make a choice.In other words,it is the loss of the opportunity to pursue the most attractive alternative given the same time and resources. A production possibility curve shows the maximum output of two goods or services that can be pro ...
www.econclassroom.com
... Model Building in Economics A popular tool in the Economist’s kit is the economic model. Just like scientists in other fields, economists use models to represent something from the real world. A model of the solar system: Allows astronomers to illustrate in a simplified model the relationships betwe ...
... Model Building in Economics A popular tool in the Economist’s kit is the economic model. Just like scientists in other fields, economists use models to represent something from the real world. A model of the solar system: Allows astronomers to illustrate in a simplified model the relationships betwe ...
A Simple Model of Labor Demand
... Note: a. Sometimes collectively bargained or legislated restrictions make the demand for labor less elastic by reducing substitutability (not technically). b. Substitution possibility that are not feasible in the short run may well become feasible over longer periods of time, when employers are free ...
... Note: a. Sometimes collectively bargained or legislated restrictions make the demand for labor less elastic by reducing substitutability (not technically). b. Substitution possibility that are not feasible in the short run may well become feasible over longer periods of time, when employers are free ...
1.2 Economic Theory
... markets for computers or for unskilled labor. National economics – study of economic behavior of the economy as a whole, especially the national economy. ...
... markets for computers or for unskilled labor. National economics – study of economic behavior of the economy as a whole, especially the national economy. ...
CHAPTER 3
... If the minimum wage applies only to jobs in the covered sector, the displaced workers might move to the uncovered sector, shifting the supply curve to the right and reducing the uncovered sector’s wage. If it is easy to get a minimum wage job, workers in the uncovered sector might quit their jobs an ...
... If the minimum wage applies only to jobs in the covered sector, the displaced workers might move to the uncovered sector, shifting the supply curve to the right and reducing the uncovered sector’s wage. If it is easy to get a minimum wage job, workers in the uncovered sector might quit their jobs an ...
Slide 1
... This figure shows how the value of the marginal product (the marginal product times the price of the output) depends on the number of workers. The curve slopes downward because of diminishing marginal product. For a competitive, profit-maximizing firm, this value-of-marginal10 product curve is also ...
... This figure shows how the value of the marginal product (the marginal product times the price of the output) depends on the number of workers. The curve slopes downward because of diminishing marginal product. For a competitive, profit-maximizing firm, this value-of-marginal10 product curve is also ...
PDF
... making a choice from a limited number of alternatives. The conditional probability of a particular choice being made is related to various explanatory factors that include the characteristics of the decision makers as well as attributes of the alternatives (Amemiya; Judge et al., pp. 583-64). The ob ...
... making a choice from a limited number of alternatives. The conditional probability of a particular choice being made is related to various explanatory factors that include the characteristics of the decision makers as well as attributes of the alternatives (Amemiya; Judge et al., pp. 583-64). The ob ...
Lecture 11 - Econometrics Laboratory, UC Berkeley
... discrimination – “Price discrimination in Broadway Theatre,” Rand Journal of Economics ...
... discrimination – “Price discrimination in Broadway Theatre,” Rand Journal of Economics ...
print version
... minerals, rocks, soil, water, etc.) and those above ground (such as air, clouds, air space and also climate). Issues that impact on this factor of production can include land size, distribution, influence of culture on land uses, etc. Competition between farming activities and urbanization is anothe ...
... minerals, rocks, soil, water, etc.) and those above ground (such as air, clouds, air space and also climate). Issues that impact on this factor of production can include land size, distribution, influence of culture on land uses, etc. Competition between farming activities and urbanization is anothe ...
capacity-utilization-and-unemployment
... Households have a fixed amount of time to allocate to labor and leisure. – More labor supplied means less leisure time. ...
... Households have a fixed amount of time to allocate to labor and leisure. – More labor supplied means less leisure time. ...
Economics 11 Fall 2008 Prof Woolf
... B) it tells us that growth is based on the original level of income or money plus interest or growth on top of the previous year's growth. Correct C) it tells us that putting animals in compounds is better for the health, hence the nation's agricultural economy will grow faster. D) it is part of the ...
... B) it tells us that growth is based on the original level of income or money plus interest or growth on top of the previous year's growth. Correct C) it tells us that putting animals in compounds is better for the health, hence the nation's agricultural economy will grow faster. D) it is part of the ...
ECON 501
... The Efficiency of Perfect Competition Adam Smith put forth the idea that a competitive market would ensure that resources would find their way to where they were most valued (the invisible hand). He provided the framework that has given rise to modern welfare economics. The fundamental Theorem of We ...
... The Efficiency of Perfect Competition Adam Smith put forth the idea that a competitive market would ensure that resources would find their way to where they were most valued (the invisible hand). He provided the framework that has given rise to modern welfare economics. The fundamental Theorem of We ...